|
Pore Space
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Void (composites)
A void or a pore is three-dimensional region that remains unfilled with polymer and fibers in a composite material. Voids are typically the result of poor manufacturing of the material and are generally deemed undesirable. Voids can affect the mechanical properties and lifespan of the composite. They degrade mainly the matrix-dominated properties such as interlaminar shear strength, longitudinal compressive strength, and transverse tensile strength. Voids can act as crack initiation sites as well as allow moisture to penetrate the composite and contribute to the anisotropy of the composite. For aerospace applications, a void content of approximately 1% is still acceptable, while for less sensitive applications, the allowance limit is 3-5%. Although a small increase in void content may not seem to cause significant issues, a 1-3% increase in void content of carbon fiber reinforced composite can reduce the mechanical properties by up to 20% Quantification Void content in comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Mathematical Symbols
A mathematical symbol is a figure or a combination of figures that is used to represent a mathematical object, an action on mathematical objects, a relation between mathematical objects, or for structuring the other symbols that occur in a formula or a mathematical expression. More formally, a ''mathematical symbol'' is any grapheme used in mathematical formulas and expressions. As formulas and expressions are entirely constituted with symbols of various types, many symbols are needed for expressing all mathematics. The most basic symbols are the decimal digits (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9), and the letters of the Latin alphabet. The decimal digits are used for representing numbers through the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. Historically, upper-case letters were used for representing points in geometry, and lower-case letters were used for variables and constants. Letters are used for representing many other types of mathematical object. As the number of these types has increased, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ratio 4:3). Similarly, the ratio of lemons to oranges is 6:8 (or 3:4) and the ratio of oranges to the total amount of fruit is 8:14 (or 4:7). The numbers in a ratio may be quantities of any kind, such as counts of people or objects, or such as measurements of lengths, weights, time, etc. In most contexts, both numbers are restricted to be Positive integer, positive. A ratio may be specified either by giving both constituting numbers, written as "''a'' to ''b''" or "''a'':''b''", or by giving just the value of their quotient Equal quotients correspond to equal ratios. A statement expressing the equality of two ratios is called a ''proportion''. Consequently, a ratio may be considered as an ordered pair of numbers, a Fraction (mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
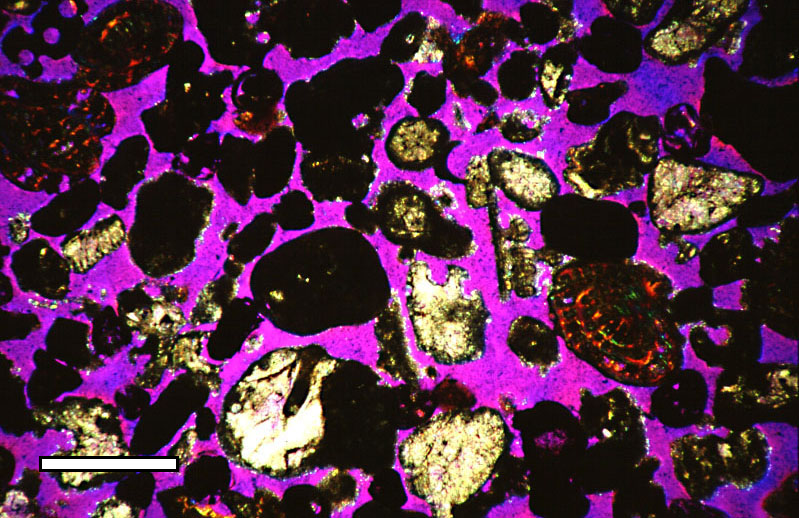
Sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension (chemistry), suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial, fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and stream channel, river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition (geology), deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
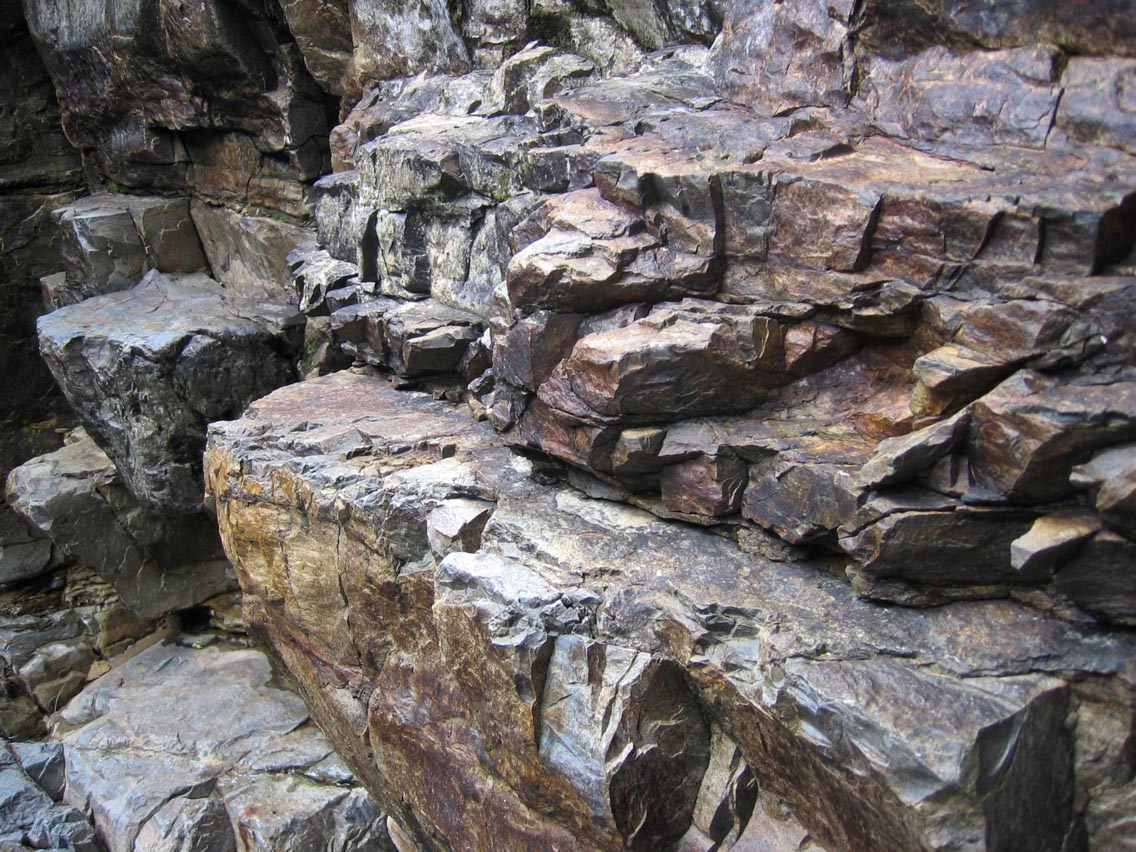
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous Medium
In materials science, a porous medium or a porous material is a material containing pores (voids). The skeletal portion of the material is often called the "matrix" or "frame". The pores are typically filled with a fluid (liquid or gas). The skeletal material is usually a solid, but structures like foams are often also usefully analyzed using concept of porous media. A porous medium is most often characterised by its porosity. Other properties of the medium (e.g. permeability, tensile strength, electrical conductivity, tortuosity) can sometimes be derived from the respective properties of its constituents (solid matrix and fluid) and the media porosity and pores structure, but such a derivation is usually complex. Even the concept of porosity is only straightforward for a poroelastic medium. Often both the solid matrix and the pore network (also known as the pore space) are continuous, so as to form two interpenetrating continua such as in a sponge. However, there is also a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Science
Building science is the science and technology-driven collection of knowledge to provide better indoor environmental quality (IEQ), energy-efficient built environments, and occupant comfort and satisfaction. ''Building physics, architectural science'', and ''applied physics'' are terms used for the knowledge domain that overlaps with building science. In building science, the methods used in natural and hard sciences are widely applied, which may include controlled and quasi-experiments, randomized control, physical measurements, remote sensing, and simulations. On the other hand, methods from social and soft sciences, such as case study, interviews & focus group, observational method, surveys, and experience sampling, are also widely used in building science to understand occupant satisfaction, comfort, and experiences by acquiring qualitative data. One of the recent trends in building science is a combination of the two different methods. For instance, it is widely know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the Earth including soil formation, soil classification, classification and Soil survey, mapping; Soil physics, physical, Soil chemistry, chemical, Soil biology, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and Soil management, management of soils.Jackson, J. A. (1997). Glossary of Geology (4. ed.). Alexandria, Virginia: American Geological Institute. p 604. The main branches of soil science are ''pedology'' ― the study of formation, chemistry, morphology, and classification of soil ― and ''edaphology'' ― the study of how soils interact with living things, especially plants. Sometimes terms which refer to those branches are used as if synonymous with soil science. The diversity of names associated with this discipline is related to the various associations concerned. Indeed, engineers, agronomy, agronomists, chemists, geologists, physical geography, phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rock (geology), rocks of the Earth's crust (geology), crust (commonly in aquifers). The terms groundwater hydrology, geohydrology, and hydrogeology are often used interchangeably, though hydrogeology is the most commonly used. Hydrogeology is the study of the laws governing the movement of subterranean water, the mechanical, chemical, and thermal interaction of this water with the porous solid, and the transport of energy, chemical constituents, and particulate matter by flow (Domenico and Schwartz, 1998). Groundwater engineering, another name for hydrogeology, is a branch of engineering which is concerned with groundwater movement and design of Well, wells, Pump, pumps, and drains. The main concerns in groundwater engineering include groundwater contamination, conservation of suppli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip Ratio (gas-liquid Flow)
Slip or The Slip may refer to: * Slip (clothing), an underdress or underskirt Music * The Slip (band), a rock band * ''Slip'' (album), a 1993 album by the band Quicksand * ''The Slip'' (album) (2008), a.k.a. Halo 27, the seventh studio album by Nine Inch Nails * "Slip" (song), a 2013 song by Stooshe * "Slip", a song by Linkin Park from '' LP Underground 11'' * "Slip", a song by Shawn Austin from the 2022 EP ''Planes Don't Wait'' * "Slip", an instrumental by Deadmau5 from the 2008 album '' Random Album Title'' * "The Slip", a 2024 song by the Smile Nickname * Slip Carr (1899–1971), Australian rugby union player and Olympic sprinter * Slip Madigan (1896–1966), American college football player and multi-sport college coach Science and technology Biology * Slip (fish), also known as Black Sole * Slip (horticulture), a small cutting of a plant as a specimen or for grafting * Muscle slip, a branching of a muscle, in anatomy Computing and telecommunication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |