|
Polytely
__NOTOC__ Polytely (from Greek roots ''poly-'' and ''-tel-'' meaning "many goals") comprises complex problem-solving situations characterized by the presence of multiple simultaneous goals.Funke 2001, p.72. These goals may be contradictory or otherwise conflict with one another, requiring prioritisation of desired outcomes.Funke 2001, p.72. Polytely is a feature of complex problem-solving that adds difficulty to finding an optimum solution. Funke describes polytely as a feature "not... inherent in a system, but eferringto certain decisions of the experimenter", especially decisions relating to what goals are to be followed in solving the problem.Funke 2001, p.73. In the complex problem of nuclear waste disposal, Flüeler cites both trust between states (as a factor in nuclear proliferation: "Some states disarm whilst others re-arm – both do it for the sake of our planet's peace"), and safe and sustainable disposal of nuclear waste as situations where considering in terms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
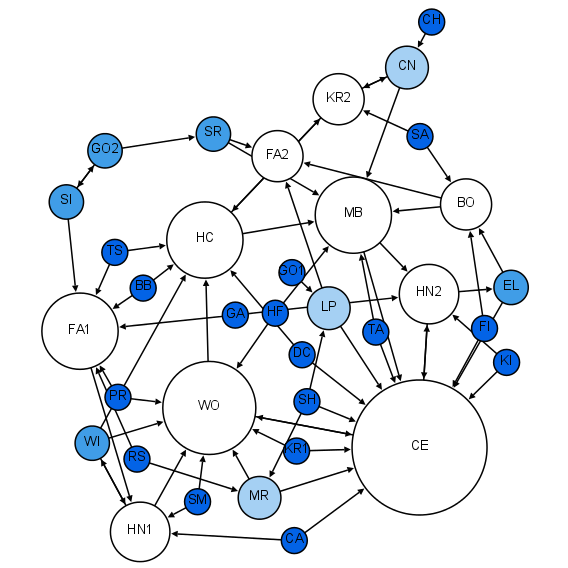
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, Cognitive network, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential statistics, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telos
Telos (; ) is a term used by philosopher Aristotle to refer to the final cause of a natural organ or entity, or of human art. ''Telos'' is the root of the modern term teleology, the study of purposiveness or of objects with a view to their aims, purposes, or intentions. Teleology is central in Aristotle's work on plant and animal biology, and human ethics, through his theory of the four causes. Aristotle's notion that everything has a ''telos'' also gave rise to epistemology. In Aristotle ''Telos'' has been consistently used in the writings of Aristotle, in which the term, on several occasions, denotes 'goal'. It is considered synonymous to ''teleute'' ('end'), particularly in Aristotle's discourse about the plot-structure in '' Poetics''. The philosopher went as far as to say that ''telos'' can encompass all forms of human activity. One can say, for instance, that the ''telos'' of warfare is victory, or the ''telos'' of business is the creation of wealth. Within this conceptua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-agent System
A multi-agent system (MAS or "self-organized system") is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. Multi-agent systems can solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve.Hu, J.; Turgut, A.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Robust Formation Coordination of Robot Swarms with Nonlinear Dynamics and Unknown Disturbances: Design and Experiments IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2021. Intelligence may include methodic, functional, procedural approaches, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning. With advancements in large language models (LLMs), LLM-based multi-agent systems have emerged as a new area of research, enabling more sophisticated interactions and coordination amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Theory
Systems theory is the Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, defined by its structure, function and role, and expressed through its relations with other systems. A system is "more than the sum of its parts" when it expresses synergy or emergent behavior. Changing one component of a system may affect other components or the whole system. It may be possible to predict these changes in patterns of behavior. For systems that learn and adapt, the growth and the degree of adaptation depend upon how well the system is engaged with its environment and other contexts influencing its organization. Some systems support other systems, maintaining the other system to prevent failure. The goals of systems theory are to model a system's dynamics, Theory of constraints, constraints, conditions, and relations; and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycentric Law
Polycentric law is a theoretical legal structure in which "providers" of legal systems compete or overlap in a given jurisdiction, as opposed to monopolistic statutory law according to which there is a sole provider of law for each jurisdiction. Devolution of this monopoly occurs by the principle of jurisprudence in which they rule according to higher law. Overview Tom W. Bell, former director of telecommunications and technology studies at Cato Institute, now a professor of law at Chapman University School of Law in California, wrote "Polycentric Law", published by the Institute for Humane Studies, when he was a law student at the University of Chicago. In it he notes that others use phrases such as "non-monopolistic law" to describe these polycentric alternatives.Tom W. BellPolycentric Law Institute for Humane Studies Review, Volume 7, Number 1 Winter 1991/92. He outlines traditional customary law (also known as consuetudinary law) before the creation of states, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcome (game Theory)
In game theory, the outcome of a game is the ultimate result of a strategic interaction with one or more people, dependant on the choices made by all participants in a certain exchange. It represents the final payoff resulting from a set of actions that individuals can take within the context of the game. Outcomes are pivotal in determining the payoffs and expected utility for parties involved. Game theorists commonly study how the outcome of a game is determined and what factors affect it. A strategy is a set of actions that a player can take in response to the actions of others. Each player’s strategy is based on their expectation of what the other players are likely to do, often explained in terms of probability. Outcomes are dependent on the combination of strategies chosen by involved players and can be represented in a number of ways; one common way is a payoff matrix showing the individual payoffs for each players with a combination of strategies, as seen in the payoff mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Studies
Organization studies (also called organization science or organizational studies) is the academic field interested in a ''collective activity, and how it relates to organization, organizing, and management''. It is "the examination of how individuals construct organizational structures, processes, and practices and how these, in turn, shape social relations and create institutions that ultimately influence people". Organizational studies comprise different areas that deal with the different aspects of the organizations, many of the approaches are functionalist but critical research also provide an alternative frame for understanding in the field. Fundamental to the study of management is organizational change. Historically, facilitating organizational change has proven to be a difficult subject, which is why different theoretical frameworks have evolved in an attempt to strategically streamline this process, such as utilizing external actors, or interim organizations, where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiobjective Optimization
Multi-objective optimization or Pareto optimization (also known as multi-objective programming, vector optimization, multicriteria optimization, or multiattribute optimization) is an area of MCDM, multiple-criteria decision making that is concerned with Mathematical optimization, mathematical optimization problems involving more than one Loss function, objective function to be optimized simultaneously. Multi-objective is a type of vector optimization that has been applied in many fields of science, including engineering, economics and logistics where optimal decisions need to be taken in the presence of trade-offs between two or more conflicting objectives. Minimizing cost while maximizing comfort while buying a car, and maximizing performance whilst minimizing fuel consumption and emission of pollutants of a vehicle are examples of multi-objective optimization problems involving two and three objectives, respectively. In practical problems, there can be more than three objectives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-criteria Decision Analysis
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings such as business, government and medicine). It is also known as known as multi-attribute decision making (MADM), multiple attribute utility theory, multiple attribute value theory, multiple attribute preference theory, and multi-objective decision analysis. Conflicting criteria are typical in evaluating options: cost or price is usually one of the main criteria, and some measure of quality is typically another criterion, easily in conflict with the cost. In purchasing a car, cost, comfort, safety, and fuel economy may be some of the main criteria we consider – it is unusual that the cheapest car is the most comfortable and the safest one. In portfolio management, managers are interested in getting high returns while simultaneously reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Problem Solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification of problem-solving tasks is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring G factor (psychometrics), psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as Emotional intelligence, tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices. Solutions require suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |