|
Polysiloxane
In organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, grease, rubber, resin, and caulk. Silicone is often confused with one of its constituent elements, silicon, but they are distinct substances. Silicon is a chemical element, a hard dark-grey semiconducting metalloid, which in its crystalline form is used to make integrated circuits ("electronic chips") and solar cells. Silicones are compounds that contain silicon, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and perhaps other kinds of atoms as well, and have many very different physical and chemical properties. History F. S. Kipping coined the word ''silicone'' in 1901 to describe the formula of polydiphenylsiloxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is an elastomer composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are often one- or two-part polymers, and may contain fillers to improve properties or reduce cost. Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants. The term "silicone" is actually a misnomer. The suffix ''-one'' is used by chemists to den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
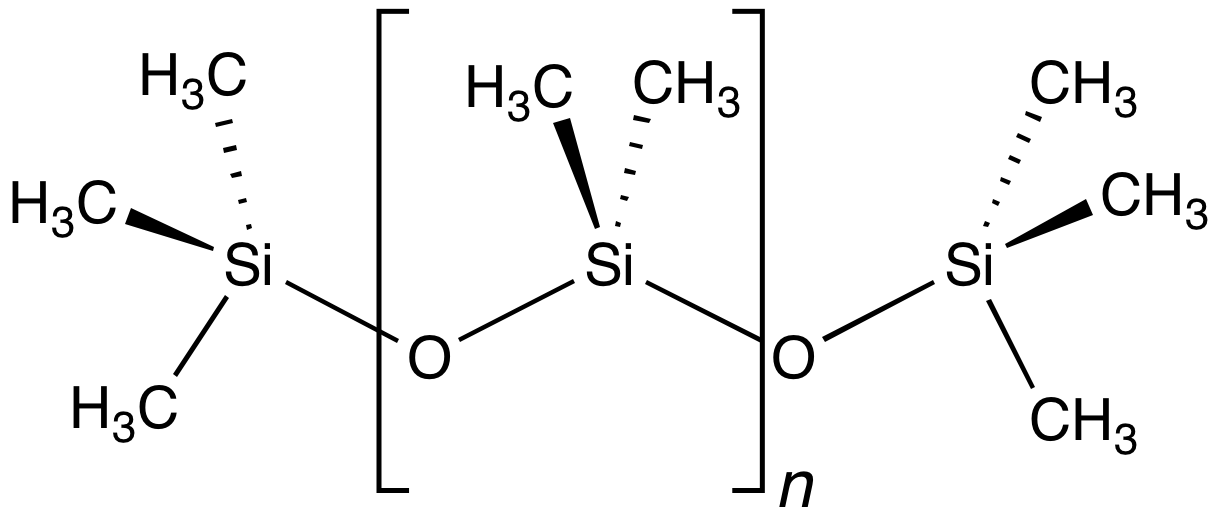
Siloxane
In organosilicon chemistry, a siloxane is an organic compound containing a functional group of two silicon atoms bound to an oxygen atom: . The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae and . Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones , the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility. Structure Siloxanes generally adopt structures expected for linked tetrahedral ("''sp''3-like") centers. The Si−O bond length is 1.64 Å (vs Si–C distance of 1.92 Å) and the Si-O-Si angle is rather open at 142.5°. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silicone Resin
Silicone resins are a type of silicone material which is formed by branched, cage-like oligosiloxanes with the general formula of where R is a non-reactive substituent, usually methyl (Me = ) or phenyl (Ph = ), and X is a functional group: hydrogen (), hydroxyl (), chlorine () or alkoxy (). These groups are further condensed in many applications, to give highly crosslinked, insoluble polysiloxane networks.S.J. Clarson, J.A. Semlyen, ''Siloxane Polymers'', Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1993). When R is methyl, the four possible functional siloxane monomeric units are described as follows: * "M" stands for trimethylsilanol, ; * "D" for ; * "T" for ; * "Q" for . Note that a network of only Q groups becomes fused quartz. The most abundant silicone resins are built of D and T units (DT resins) or from M and Q units (MQ resins); however, many other combinations (MDT, MTQ, QDT) are also used in industry. Silicone resins represent a broad range of products. Materials of molecular wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Silicon is a significant element that is essential for several physiological and metabolic processes in plants. Silicon is widely regarded as the predominant semiconductor material due to its versatile applications in various electrical devices such as transistors, solar cells, integrated circuits, and others. These may be due to its significant band gap, expansive optical transmission range, extensive absorption spectrum, surface roughening, and effective anti-reflection coating. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journal Of The Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the Chemical Society'' was a scientific journal established by the Chemical Society in 1849 as the ''Quarterly Journal of the Chemical Society''. The first editor was Edmund Ronalds. The journal underwent several renamings, splits, and mergers throughout its history. In 1980, the Chemical Society merged with several other organizations into the Royal Society of Chemistry. The journal's continuity is found in '' Chemical Communications'', '' Dalton Transactions'', '' Faraday Transactions'', and '' Perkin Transactions'', all of which are published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. History ;'' Proceedings of the Chemical Society'' * ''Memoirs of the Chemical Society of London'' (1841) * ''Proceedings of the Chemical Society of London'' (1842–1843) * ''Memoirs and Proceedings of the Chemical Society'' (1843–1848) * ''Proceedings of the Chemical Society, London'' (1885–1914) * Published as a supplement to ''Journal of the Chemical Society'' from 1914 to 1956 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula , and is often represented by the symbol Ph (archaically φ) or Ø. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen atom, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with and is represented by the symbol Ph (archaically, Φ), or Ø. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. Benzophenone has been found in some fungi, fruits and plants, including grapes. It is a white solid with a low melting point and rose-like odor that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is the simplest diaromatic ketone. It is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. History Carl Graebe of the University of Königsberg, in an early literature report from 1874, described working with benzophenone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in ultraviolet (UV)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents UV light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fused Quartz
Fused quartz, fused silica or quartz glass is a glass consisting of almost pure silica (silicon dioxide, SiO2) in amorphous (non-crystalline) form. This differs from all other commercial glasses, such as soda-lime glass, lead glass, or borosilicate glass, in which other ingredients are added which change the glasses' optical and physical properties, such as lowering the melt temperature, the spectral transmission range, or the mechanical strength. Fused quartz, therefore, has high working and melting temperatures, making it difficult to form and less desirable for most common applications, but is much stronger, more chemically resistant, and exhibits lower thermal expansion, making it more suitable for many specialized uses such as lighting and scientific applications. The terms ''fused quartz'' and ''fused silica'' are used interchangeably but can refer to different manufacturing techniques, resulting in different trace impurities. However fused quartz, being in the glassy s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
James Franklin Hyde
James Franklin Hyde (born 11 March 1903) was an American chemist and inventor. He has been called the “Father of Silicones” and is credited with the launch of the silicone industry in the 1930s. His most notable contributions include his creation of silicone from silicon compounds and his method of making fused silica, a high-quality glass later used in aeronautics, advanced telecommunications, and computer chips. His work led to the formation of Dow Corning, an alliance between the Dow Chemical Company and Corning Incorporated, Corning Glass Works that was specifically created to produce silicone products. Life Early years and education James Franklin Hyde was born in Solvay, New York on March 11, 1903. He attended Solvay High School and graduated on June 25, 1919, at the age of 16. He was partly encouraged by one of his science teachers to enter into the field of science. After high school, Hyde attended Syracuse University, where he earned both his Bachelor of Arts and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solar Cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.Solar Cells chemistryexplained.com It is a type of photoelectric cell, a device whose electrical characteristics (such as Electric current, current, voltage, or Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance) vary when it is exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of solar panel, photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as "solar panels". Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells account for the remainder. The common single-junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dow Corning
Dow Corning Corporation, was an American multinational corporation headquartered in Midland, Michigan, United States, and was originally established as a joint venture between The Dow Chemical Company and Corning Inc., Corning Incorporated. In 2016, Dow bought out Corning, Inc. making Dow Corning a 100% Dow subsidiary. After a brief existence as a DowDuPont-owned company, Dow spun out from DowDuPont on April 1, 2019. The new company, Dow Silicones Corporation, which is wholly owned by Dow, specializes in silicone and silicon-based technology, and is the largest silicone product producer in the world. DOWSIL™ is the trade name for Dow Corning's 7,000+ products and services. History Dow Corning was formally established in 1943 as a joint venture between the American conglomerates Dow Chemical and Corning Glass to explore the potential of silicone and was a manufacturer of products for use by the U.S. military in World War II. The company began operating its first plant, in Midlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |