|
Polybrominated Diphenylethers
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers or PBDEs, are a class of organobromine compounds that are used as flame retardants. Like other brominated flame retardants, PBDEs have been used in a wide array of products, including building materials, electronics, furnishings, motor vehicles, airplanes, plastics, polyurethane foams, and textiles. They are structurally akin to polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other polyhalogenated compounds, consisting of two halogenated aromatic rings. PBDEs are classified according to the average number of bromine atoms in the molecule. The life-saving benefits of fire retardants led to their popularization. Standards for mass transit vehicles continues to increase as of 2021. Because of their toxicity and persistence, all commercially relevant PBDEs have been marked for elimination under the Stockholm Convention, a treaty to control and phase out major persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Classes of PBDEs The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decabromodiphenyl Ether
Decabromodiphenyl ether (also referred to as decaBDE, DBDE, BDE-209) is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). It was commercialised in the 1970s and was initially thought to be safe, but is now recognised as a hazardous and persistent pollutant. It was added to Annex A of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2017, which means that treaty members must take measures to eliminate its production and use. The plastics industry started switching to decabromodiphenyl ethane as an alternative in the 1990s, but this is now also coming under regulatory pressure due to concerns over human health. Composition, uses, and production Commercial decaBDE is a technical mixture of various PBDE congeners (related compounds). Congener number 209 (decabromodiphenyl ether) and nonabromodiphenyl ether are the main components.Joint Research Centre European inventory of Existing Commercial chemical Substances The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
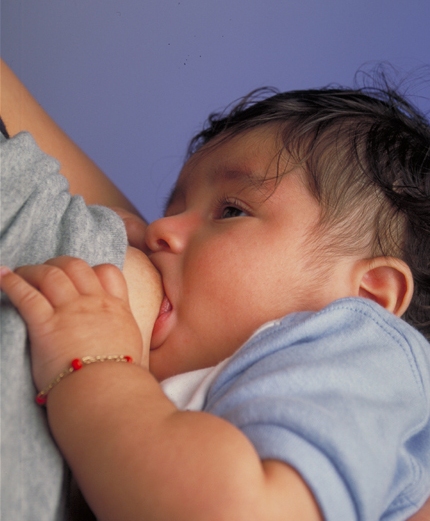
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes is composed of about 20–50% dead skin Cell (biology), cells. The rest, and in offices and other built environments, is composed of small amounts of plant pollen, human hairs, animal fur, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, burnt meteorite particles, and many other materials which may be found in the local environment. Atmospheric Atmospheric or wind-borne fugitive dust, also known as ''aeolian dust'', comes from dry regions where high-speed winds can remove mostly silt-sized material, abrading susceptible surfaces. This includes areas where grazing, ploughing, vehicle use, and other human behaviors have further destabilized the land, though not all so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
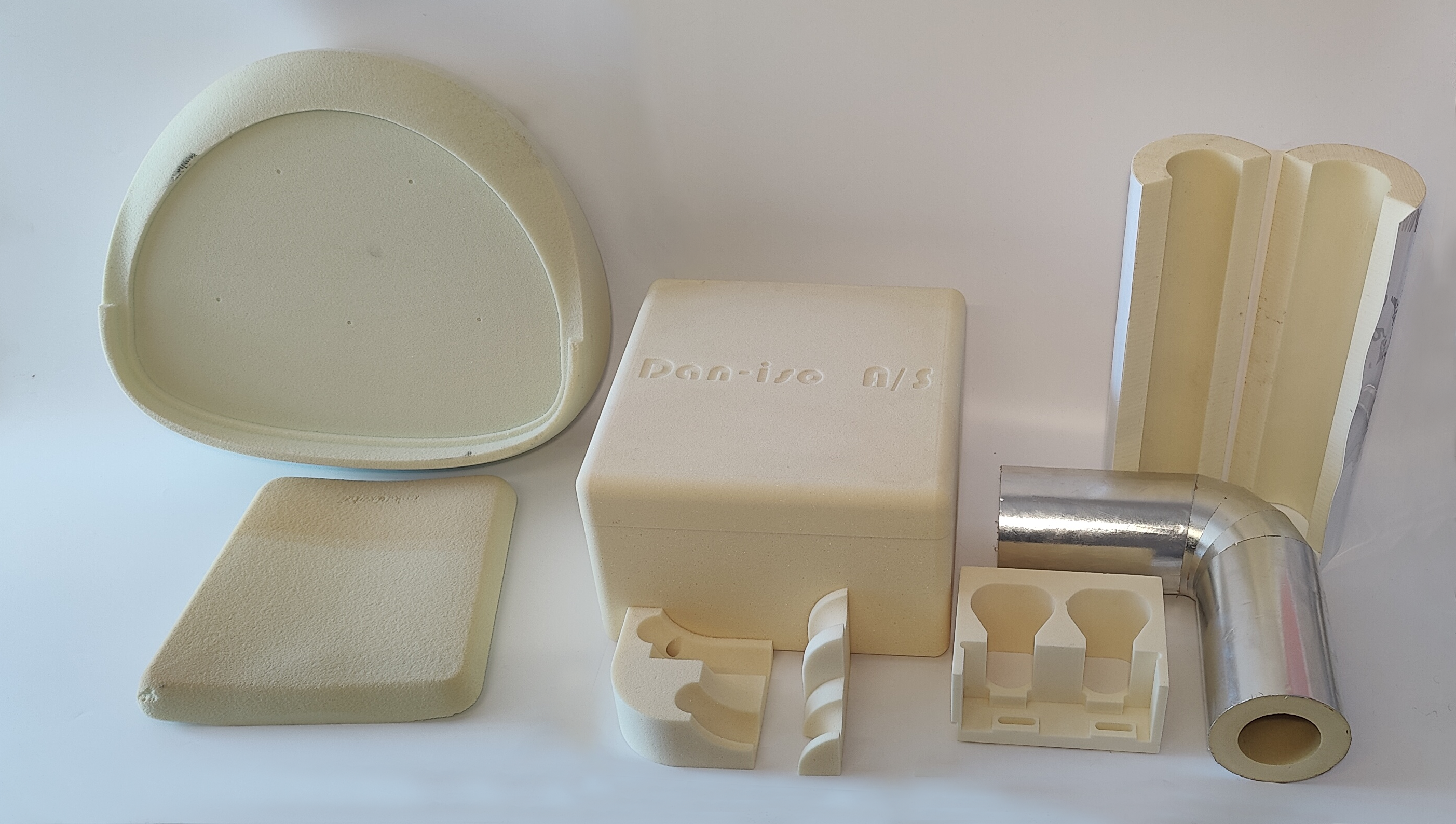
Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a solid polymeric foam based on polyurethane chemistry. As a specialist synthetic fibre, synthetic material with highly diverse applications, polyurethane foams are primarily used for thermal insulation and as a cushioning material in mattresses, upholstered furniture or as seating in vehicles. Its low density and thermal conductivity combined with its mechanical properties make them excellent thermal and sound insulators, as well as structural and comfort materials. Polyurethane foams are Thermosetting polymer, thermosetting polymers. They cannot be melted and reshaped after initially formed, because the chemical bonds between the molecules in the material are very strong and are not broken down by heating. Once cured and cooled, the material maintains its shape and properties.EURO-MOULDERS (2023) 'What is polyurethane foam' https://euromoulders.org/polyurethane-in-automobiles/what-is-polyurethane-foam/ Classification of polyurethane foams Polyurethane foa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
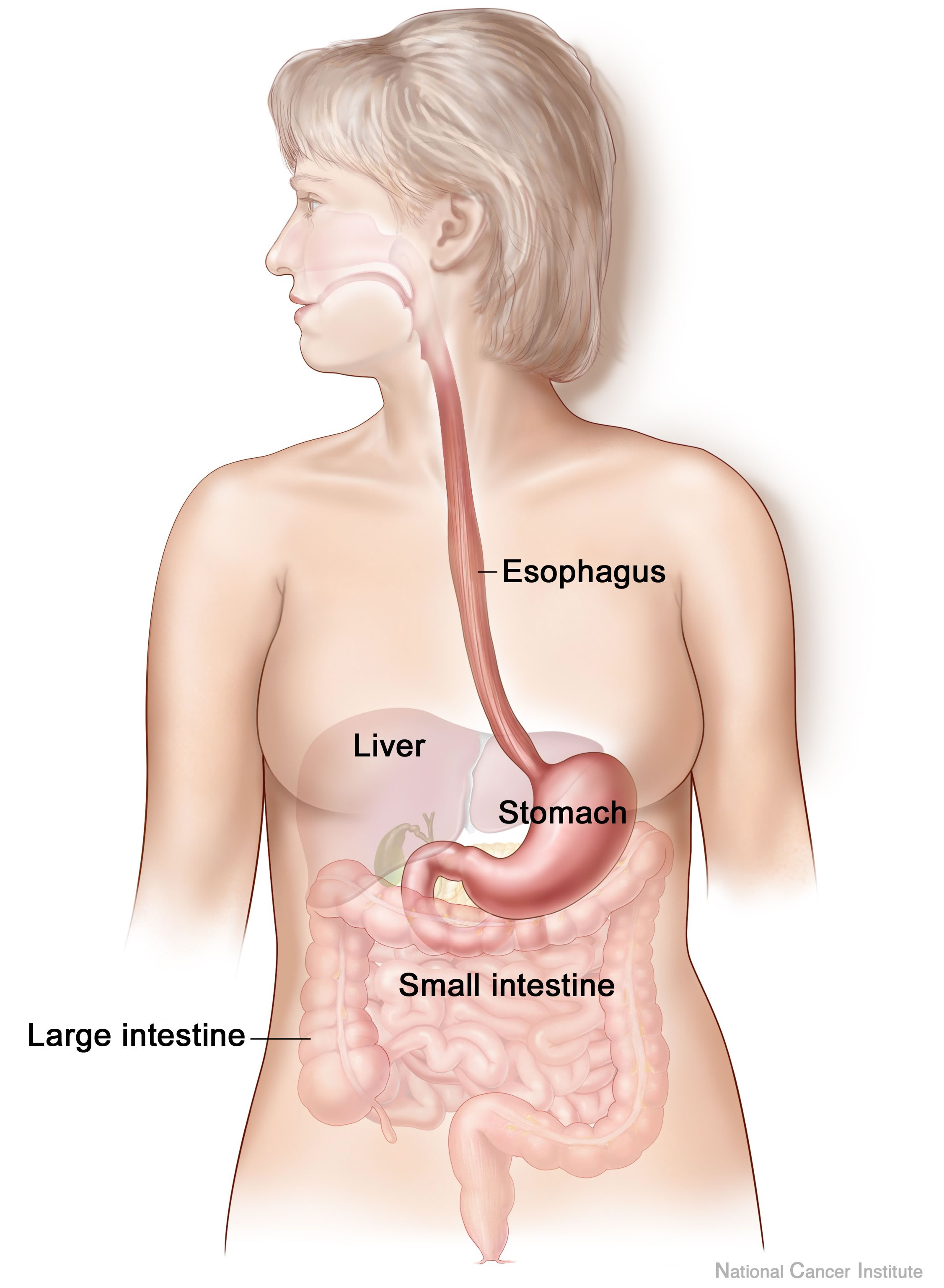
Human Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food, and continues in the mouth with the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes in the saliva. Saliva contains amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary glands, and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing mixes the food with saliva to produce a bolus to be swallowed down the esophagus to enter the stomach. The second stage, the gastric phase, takes place in the stomach, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octabromodiphenyl Ether
Octabromodiphenyl ether (octaBDE, octa-BDE, OBDE, octa, octabromodiphenyl oxide, OBDPO) is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Composition, uses, and production Commercial octaBDE (also known as "Octabrom") is a Chemical purity#Technical grade, technical mixture of different PBDE Congener (chemistry), congeners having an average of 7.2 to 7.7 bromine atoms per molecule of diphenyl ether.United States Patent and Trademark OfficeMelting point enhancement of partially brominated diphenyl oxide mixtures.US Patent 5,000,879 issued on March 19, 1991. The predominant congeners in commercial octaBDE are those of heptabromodiphenyl ether and octaBDE.Ad hoc working group on C-Octabromodiphenyl ether under the Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee of the Stockholm ConventionDraft risk profile: commercial octabromodiphenyl ether.United Nations Environment Programme, August 2007. The term octaBDE alone refers to isomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentabromodiphenyl Ether
Pentabromodiphenyl ether (also known as pentabromodiphenyl oxide) is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Because of their toxicity and persistence, their industrial production is to be eliminated under the Stockholm Convention, a treaty to control and phase out major persistent organic pollutants (POP). Composition, uses, and production Commercial pentaBDE is a technical mixture of different PBDE congeners, with BDE-47 (2,2',4,4'- tetrabromodiphenyl ether) and BDE-99 (2,2',4,4',5-pentabromodiphenyl ether) as the most abundant.Persistent Organic Pollutants Review Committee of the Stockholm ConventionCommercial Pentabromodiphenyl Ether: Risk Management Evaluation.United Nations Environment Programme, August 2007. The term pentaBDE alone refers to isomers of pentabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE congener numbers 82-127).Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease RegistryToxicological Profile for Polybrominated Biphenyls and Polyb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Health Perspectives
''Environmental Health Perspectives'' (''EHP'') is a peer-reviewed Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work ( peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ... open access journal published monthly with support from the U.S. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). The primary purposes of ''EHP'' are to communicate recent scientific findings and trends in the environmental health sciences; to improve the environmental health knowledge base among researchers, administrators, and policy makers; and to inform the public about important topics in environmental health. References Environmental social science journals Academic journals established in 1972 Monthly journals English-language journals Open access journals Environmental health journals Academic journals published by the United States gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenyl Ether
Diphenyl ether is the organic compound with the formula ( C6 H5)2 O. It is a colorless, low-melting solid. This compound, the simplest diaryl ether, has a variety of niche applications. Synthesis and reactions Diphenyl ether was discovered by Heinrich Limpricht and Karl List in 1855, when they reproduced Carl Ettling's destructive distillation of copper benzoate and separated it from the low-melting oily distillate components ignored by previous researchers. They named the compound phenyl oxide () and studied some of its derivatives. Now it is synthesized by a modification of the Williamson ether synthesis, here the reaction of phenol and bromobenzene in the presence of base and a catalytic amount of copper: :PhOH + PhBr → PhOPh + HBr Involving similar reactions, diphenyl ether is a significant side product in the high-pressure hydrolysis of chlorobenzene in the production of phenol. Related compounds are prepared by Ullmann reactions. The compound undergoes react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromination
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (). Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride. Organic chemistry Several pathways exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, including free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate determines the pathway. The facility of halogenation is influenced by the halogen. Fluorine and chlorine are more electrophilic and are more aggressive halogena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehalogenation
In organic chemistry, dehalogenation is a set of chemical reactions that involve the Bond cleavage, cleavage of carbon-halogen bonds; as such, it is the inverse reaction of halogenation. Dehalogenations come in many varieties, including defluorination (removal of fluorine), dechlorination (removal of chlorine), debromination (removal of bromine), and deiodination (removal of iodine). Incentives to investigate dehalogenations include both constructive and destructive goals. Complicated organic compounds such as pharmaceutical drugs are occasionally generated by dehalogenation. Many organohalides are hazardous, so their dehalogenation is one route for their detoxification. Mechanistic and thermodynamic concepts Removal of a halogen atom from an organohalide generates a radical. Such reactions are difficult to achieve and, when they can be achieved, these processes often lead to complicated mixtures. When a pair of halides are mutually adjacent (Vicinal (chemistry), vicinal), their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |