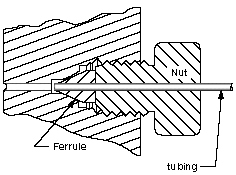
|
Pneumatic Cylinder
Pneumatic cylinders (sometimes known as air cylinders) are mechanical devices which use the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion. Like hydraulic cylinders, something forces a piston to move in the desired direction. The piston is a disc or cylinder, and the piston rod transfers the force it develops to the object to be moved. Engineers sometimes prefer to use pneumatics because they are quieter, cleaner, and do not require large amounts of space for fluid storage. Because the operating fluid is a gas, leakage from a pneumatic cylinder will not drip out and contaminate the surroundings, making pneumatics more desirable where cleanliness is a requirement. For example, in the mechanical puppets of the Disney Tiki Room, pneumatics are used to prevent fluid from dripping onto people below the puppets. Operation General Once actuated, compressed air enters into the tube at one end of the piston and imparts force on the piston. Consequently, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trunnion
A trunnion (from Old French "''trognon''", trunk) is a cylindrical protrusion used as a mounting or pivoting point. First associated with cannons, they are an important military development. Alternatively, a trunnion is a shaft that positions and supports a tilting plate. This is a misnomer, as in reality it is a cradle for the true trunnion. In mechanical engineering (see the trunnion bearing section below), it is one part of a rotating joint where a shaft (the trunnion) is inserted into (and turns inside) a full or partial cylinder. Medieval history In a cannon, the trunnions are two projections cast just forward of the center of mass of the cannon and fixed to a two-wheeled movable gun carriage. As they allowed the muzzle to be raised and lowered easily, the integral casting of trunnions is seen by military historians as one of the most important advances in early field artillery. With the creation of larger and more powerful siege guns in the early 15th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatics
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air. Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and electrically-powered compressor powers cylinders, air motors, pneumatic actuators, and other pneumatic devices. A pneumatic system controlled through manual or automatic solenoid valves is selected when it provides a lower cost, more flexible, or safer alternative to electric motors, and hydraulic actuators. Pneumatics also has applications in dentistry, construction, mining, and other areas. Gases used in pneumatic systems Pneumatic systems in fixed installations, such as factories, use compressed air because a sustainable supply can be made by compressing atmospheric air. The air usually has moisture removed, and a small quantity of oil is added at the compressor to prevent corrosion and lubricate mechanical components. Facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic Motor
A pneumatic motor (air motor), or compressed air engine, is a type of motor which does mechanical work by expanding compressed air. Pneumatic motors generally convert the compressed air energy to mechanical work through either linear or rotary motion. Linear motion can come from either a diaphragm or piston actuator, while rotary motion is supplied by either a vane type air motor, piston air motor, air turbine or gear type motor. Pneumatic motors have existed in many forms over the past two centuries, ranging in size from hand-held motors to engines of up to several hundred horsepower. Some types rely on pistons and cylinders; others on slotted rotors with vanes (vane motors) and others use turbines. Many compressed air engines improve their performance by heating the incoming air or the engine itself. Pneumatic motors have found widespread success in the hand-held tool industry, but are also used stationary in a wide range of industrial applications. Continual attempts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment ( engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. Operation Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is incompressible. Typically oil is used as hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth. The barrel is closed on one end by the cylinder bottom (also called the cap) and the other end by the cylinder head (also called the gland) where the piston rod comes out of the cylinder. The piston has sliding rings and seals. The piston divides the inside of the cylinder into two chambers, the bottom chamber (cap end) and the piston rod side chamber (rod end/head-end). Flanges, trunnions, clevises, and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Power
Fluid power is the use of fluids under pressure to generate, control, and transmit power. Fluid power is subdivided into hydraulics using a liquid such as mineral oil or water, and pneumatics using a gas such as air or other gases. Compressed-air and water-pressure systems were once used to transmit power from a central source to industrial users over extended geographic areas; fluid power systems today are usually within a single building or mobile machine. Fluid power systems perform work by a pressurized fluid bearing directly on a piston in a cylinder or in a fluid motor. A fluid cylinder produces a force resulting in linear motion, whereas a fluid motor produces torque resulting in rotary motion. Within a fluid power system, cylinders and motors (also called actuators) do the desired work. Control components such as valves regulate the system. Elements A fluid power system has a pump driven by a prime mover (such as an electric motor or internal combustion engine) tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including '' aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Sectional Area
In geometry and science, a cross section is the non-empty intersection of a solid body in three-dimensional space with a plane, or the analog in higher- dimensional spaces. Cutting an object into slices creates many parallel cross-sections. The boundary of a cross-section in three-dimensional space that is parallel to two of the axes, that is, parallel to the plane determined by these axes, is sometimes referred to as a contour line; for example, if a plane cuts through mountains of a raised-relief map parallel to the ground, the result is a contour line in two-dimensional space showing points on the surface of the mountains of equal elevation. In technical drawing a cross-section, being a projection of an object onto a plane that intersects it, is a common tool used to depict the internal arrangement of a 3-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is traditionally crosshatched with the style of crosshatching often indicating the types of materials being used. With compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Model
In mathematical logic, and particularly in its subfield model theory, a saturated model ''M'' is one that realizes as many complete types as may be "reasonably expected" given its size. For example, an ultrapower model of the hyperreals is \aleph_1-saturated, meaning that every descending nested sequence of internal sets has a nonempty intersection. Definition Let ''κ'' be a finite or infinite cardinal number and ''M'' a model in some first-order language. Then ''M'' is called ''κ''-saturated if for all subsets ''A'' ⊆ ''M'' of cardinality less than ''κ'', the model ''M'' realizes all complete types over ''A''. The model ''M'' is called saturated if it is , ''M'', -saturated where , ''M'', denotes the cardinality of ''M''. That is, it realizes all complete types over sets of parameters of size less than , ''M'', . According to some authors, a model ''M'' is called countably saturated if it is \aleph_1-saturated; that is, it realizes all complete types over coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Compressor
An air compressor is a pneumatic device that converts power (using an electric motor, diesel or gasoline engine, etc.) into potential energy stored in pressurized air (i.e., compressed air). By one of several methods, an air compressor forces more and more air into a storage tank, increasing the pressure. When the tank's pressure reaches its engineered upper limit, the air compressor shuts off. The compressed air, then, is held in the tank until called into use. The kinetic energy provided by the compressed air can be used for a variety of applications such as pneumatic tool as it is released air and the tank depressurizes. When tank pressure reaches its lower limit, the air compressor turns on again and re-pressurizes the tank. An air compressor must be differentiated from a pump because it works for any gas/air, while pumps work on a liquid. Classification Compressors may be classified according to the pressure delivered: # Low-pressure air compressors (LPACs), which have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directly Proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product, also called the coefficient of proportionality. This definition is commonly extended to related varying quantities, which are often called ''variables''. This meaning of ''variable'' is not the common meaning of the term in mathematics (see variable (mathematics)); these two different concepts share the same name for historical reasons. Two functions f(x) and g(x) are ''proportional'' if their ratio \frac is a constant function. If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio). Proportionality is closely re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |