|
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapist is the term used for such professionals in the United States, and physiotherapist is the term used in many other countries. The career has many specialties including musculoskeletal, orthopedics, cardiopulmonary, neurology, endocrinology, sports medicine, geriatrics, pediatrics, women's health, wound care and electromyography. PTs practice in many settings, both public and private. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapy practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports Medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the late 20th century that sports medicine emerged as a distinct field of health care. In many countries, now over 50, sports medicine (or sport and exercise medicine) is a recognized medical specialty (with similar training and standards to other medical specialties or sub-specialties). In the majority of countries where sports medicine is recognized and practiced, it is a physician (non-surgical) specialty, but in some (such as the USA), it can equally be a surgical or non-surgical medical specialty, and also a specialty field within primary care. In other contexts, the field of sports medicine encompasses the scope of both medical specialists as well as Allied health professions, allied health practitioners who work in the field of sport, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a treatment primarily used by physical therapists, occupational therapists, and massage therapists to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability. It mostly includes kneading and manipulation of muscles, joint mobilization and joint manipulation. It is also used by Rolfers, athletic trainers, osteopaths, and physicians. Definitions Irvin Korr, J. S. Denslow and colleagues did the original body of research on manual therapy. Korr described it as the "Application of an accurately determined and specifically directed manual force to the body, in order to improve mobility in areas that are restricted; in joints, in connective tissues or in skeletal muscles." According to the ''Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Description of Advanced Specialty Practice'' manual therapy is defined as a clinical approach utilizing specific hands-on techniques, including but not limited to manipulation/mobilization, used by the physical therapist to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
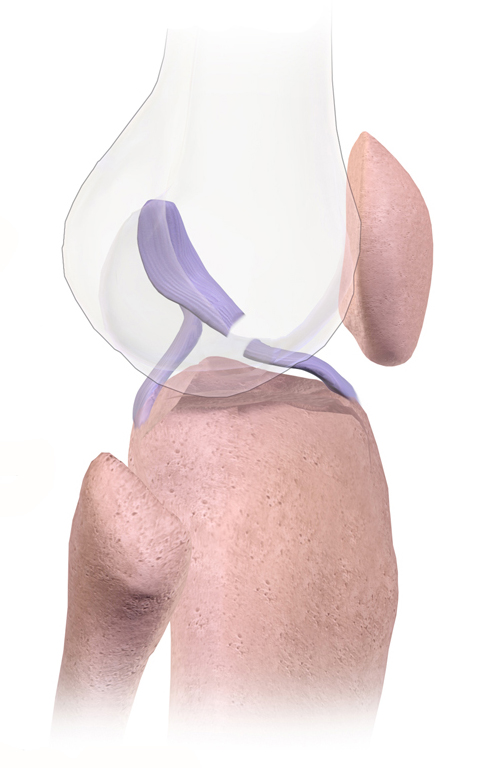
Orthopedic
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually became the cornerstone of orthopedic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Care
The history of wound care spans from prehistory to modern medicine. Wounds naturally Wound healing, heal by themselves, but hunter-gatherers would have noticed several factors and certain herbalism, herbal remedies would speed up or assist the process, especially if it was grievous. In ancient history, ancient history, this was followed by the realisation of the necessity of hygiene and the halting of bleeding, where wound dressing techniques and surgery developed. Eventually the germ theory of disease also assisted in improving wound care. Ancient medical practice Over time, different civilizations began to create their own herbal medicinal treatments for wounds depending on the trees, shrubs, or any other type of plants located in their environment. These herbal treatments became the oldest form of wound therapy. It is logically assumed that this may not have been a very safe way of treating humans with wounds due to overdosing or choosing the wrong plants to treat a person unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromyograms
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In computer science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical uses EMG testing has a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g., distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies greater than 20,000 Hz, which is the approximate upper threshold of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis. Diagnosis is often challenging because many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For example, redness of the skin ( erythema), by itself, is a sign of many disorders and thus does not tell the healthcare professional what is wrong. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. This involves the correlation of various pieces of information followed by the recognition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
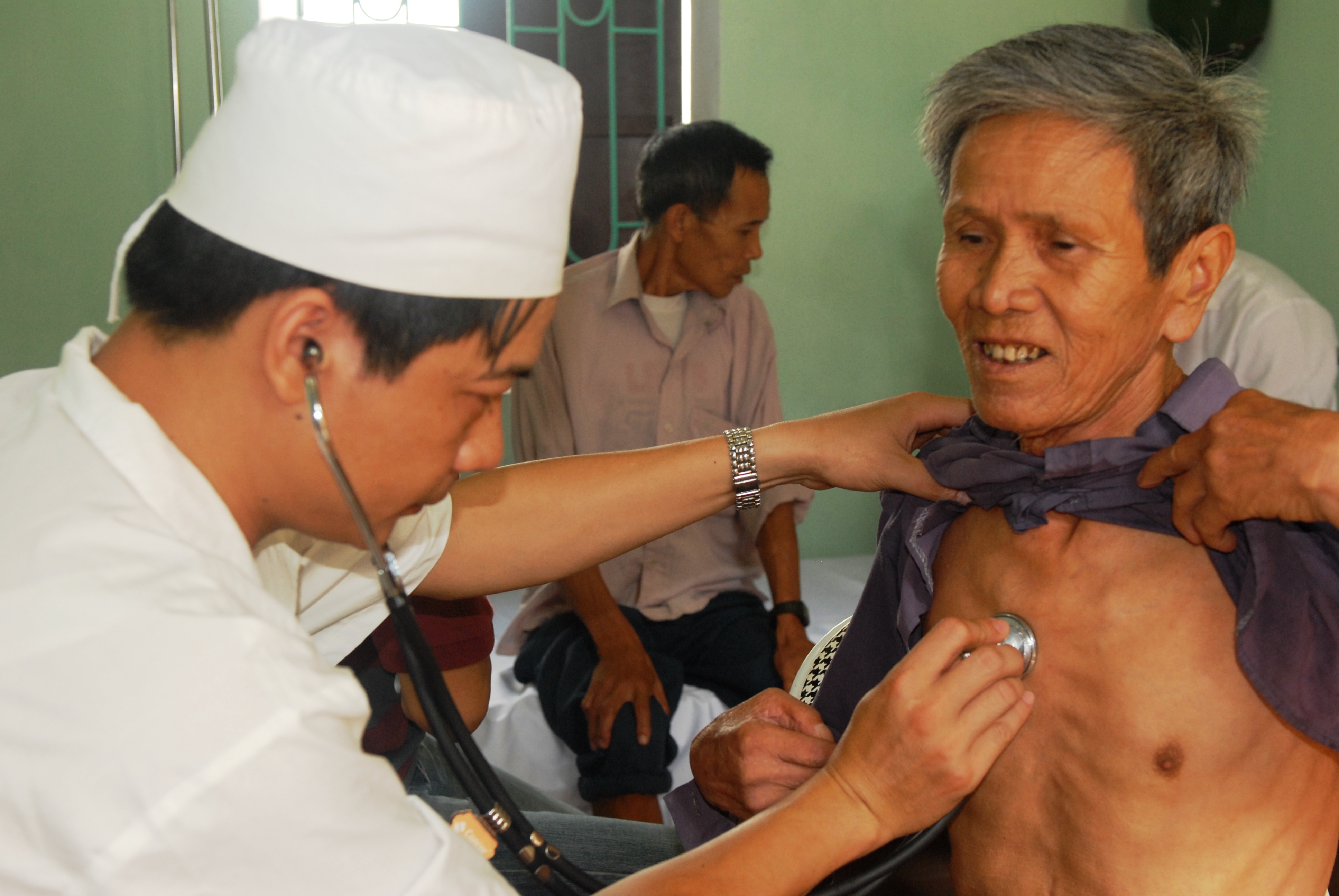
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical History
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and eventually people close to them, so to collect reliable/objective information for managing the medical diagnosis and proposing efficient medical treatments. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and in depth, as man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illnesses
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structure and funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapy
A therapy or medical treatment is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis. Both words, ''treatment'' and ''therapy'', are often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx. As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different types of therapy. Not all therapies are effective. Many therapies can produce unwanted adverse effects. ''Treatment'' and ''therapy'' are often synonymous, especially in the usage of health professionals. However, in the context of mental health, the term ''therapy'' may refer specifically to psychotherapy. Semantic field The words ''care'', ''therapy'', ''treatment'', and ''intervention'' overlap in a semantic field, and thus they can be synonymous depending on context. Moving rightward through that order, the connotative level of holism decreases and the level of specificity (to concrete instances) increases. Thus, in health-care contexts (where its senses are always nonc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |