|
Phosphorus Oxide
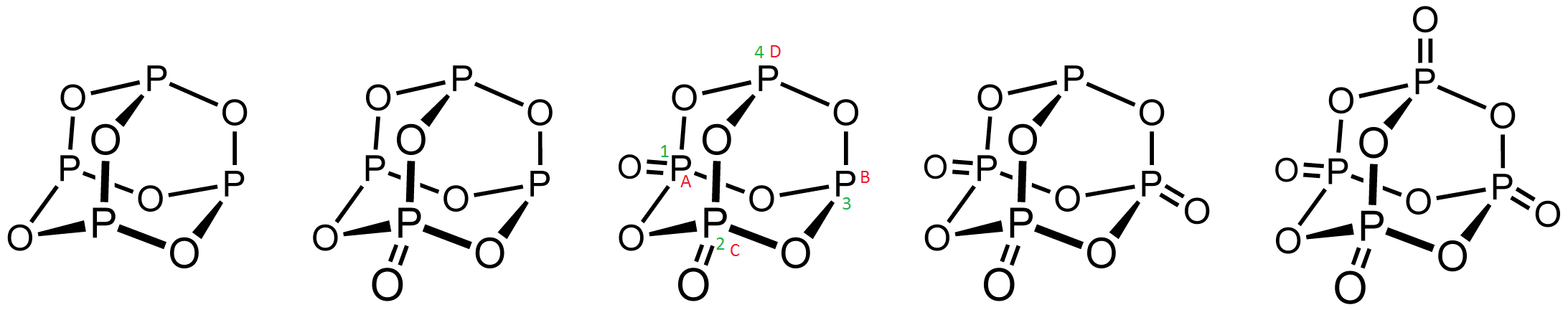
Phosphorus oxide can refer to: * Phosphorus pentoxide (phosphorus(V) oxide, phosphoric anhydride), P2O5 * Phosphorus trioxide (phosphorus(III) oxide, phosphorous anhydride), P2O3 * Phosphorus tetroxide, Between the commercially important phosphorus trioxide, P4O6 and P4O10, several other, less common oxides of phosphorus are known. Specifically, P4O7, P4O9, and P2O6 all bear structures intermediate between the endmembers:Luer, B.; Jansen, M. "Crystal Structure Refinement of Tetraphosphorus Nonaoxide, P4O9" Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 1991, volume 197, pages 247-8. On observation it will be seen that double bonded oxygen in P4O8 at 1,2 position or 1,3 position are identical and both positions have same steric hindrance. Cycle 12341 and ABCDA are identical. Gases: * Phosphorus monoxide, PO * Phosphorus dioxide, References {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula Phosphorus, P4Oxygen, O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydration reaction, dehydrating agent. Structure Phosphorus pentoxide crystallizes in at least four forms or polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs. The most familiar one, a metastable form (shown in the figure), comprises molecules of P4O10. Weak van der Waals forces hold these molecules together in a hexagonal lattice (However, in spite of the high symmetry of the molecules, the crystal packing is not a close packing). The structure of the P4O10 cage is reminiscent of adamantane with ''T''d symmetry point group. It is closely related to the corresponding anhydride of phosphorous acid, phosphorus trioxide, P4O6. The latter lacks terminal oxo groups. Its density is 2.30 g/cm3. It boils at 423 °C under atmospheric pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Trioxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, and its usage continues today. This colorless solid is structurally related to adamantane. It is formally the anhydride of phosphorous acid, H3PO3, but cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the acid. A white solid that melts at room temperature, it is waxy, crystalline and highly toxic, with garlic odor. Preparation It is obtained by the combustion of phosphorus in a limited supply of air at low temperatures. :P4 + 3 O2 → P4O6 By-products include red phosphorus suboxide. Chemical properties Phosphorus trioxide reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, reflecting the fact that it is the anhydride of that acid. : P4O6 + 6 H2O → 4 H3PO3 It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form H3PO3 and phosphorus trichloride. : P4O6 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Tetroxide
Diphosphorus tetroxide, or phosphorus tetroxide is an inorganic compound of phosphorus and oxygen. It has the empirical chemical formula . Solid phosphorus tetroxide (also referred to as phosphorus(III,V)-oxide) consists of variable mixtures of the mixed-valence oxides P4O7, P4O8 and P4O9. Preparation Phosphorus tetroxide can be produced by thermal decomposition of phosphorus trioxide, which disproportionates above 210 °C to form phosphorus tetroxide, with elemental phosphorus as a byproduct: : In addition, phosphorus trioxide can be converted into phosphorus tetroxide by controlled oxidation with oxygen in carbon tetrachloride solution. Careful reduction of phosphorus pentoxide with red phosphorus Red phosphorus is an Allotropes of phosphorus, allotrope of phosphorus. It is an amorphous polymeric red solid that is stable in air. It can be easily converted from white phosphorus under light or heating. It finds applications as matches and fir ... at 450-525 °C al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Trioxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, and its usage continues today. This colorless solid is structurally related to adamantane. It is formally the anhydride of phosphorous acid, H3PO3, but cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the acid. A white solid that melts at room temperature, it is waxy, crystalline and highly toxic, with garlic odor. Preparation It is obtained by the combustion of phosphorus in a limited supply of air at low temperatures. :P4 + 3 O2 → P4O6 By-products include red phosphorus suboxide. Chemical properties Phosphorus trioxide reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, reflecting the fact that it is the anhydride of that acid. : P4O6 + 6 H2O → 4 H3PO3 It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form H3PO3 and phosphorus trichloride. : P4O6 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further oxidation.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of an equation or reaction) and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared artificially, the two most common allotropes being white phosphorus and red phosphorus. With as its only stable isotope, phosphorus has an occurrence in Earth's crust of about 0.1%, generally as phosphate rock. A member of the pnictogen family, phosphorus readily forms a wide variety of organic compound, organic and inorganic compound, inorganic compounds, with as its main oxidation states +5, +3 and −3. The isolation of white phosphorus in 1669 by Hennig Brand marked the scientific community's first discovery since Antiquity of an element. The name phosphorus is a reference to the Phosphorus (morning star), god of the Morning star in Greek mythology, inspired by the faint glow of white phosphorus when exposed to oxygen. This property is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structures Of Phosphorus Oxides Edit
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Monoxide
Phosphorus monoxide is an unstable radical inorganic compound with molecular formula P O. Phosphorus monoxide is notable as one of the few molecular compounds containing phosphorus that has been detected outside of Earth. Other phosphorus containing molecules found in space include PN, PC, PC2, HCP and PH3. It was detected in the circumstellar shell of VY Canis Majoris and in the star forming region catalogued as AFGL 5142. The compound has been found to have been initially produced in star-forming regions, and speculated to be carried by interstellar comets throughout outer space, including to the early Earth. Phosphorus monoxide plays a role in the phosphorescence of phosphorus. Discovery In 1894 W. N. Hartley was the first to report an observation of ultraviolet emission from a phosphorus compound, that was later expanded on by Geuter. The source of the spectral lines and bands were known to be related to phosphorus, but the exact nature was unknown. In 1927 H. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |