|
Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)''P''3), abbreviated PIP3, is the product of the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases' (PI 3-kinases) phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2). It is a phospholipid that resides on the plasma membrane. Discovery In 1988, Lewis C. Cantley published a paper describing the discovery of a novel type of phosphoinositide kinase with the unprecedented ability to phosphorylate the 3' position of the inositol ring resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P). Working independently, Alexis Traynor-Kaplan and coworkers published a paper demonstrating that a novel lipid, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate (PIP3) occurs naturally in human neutrophils with levels that increased rapidly following physiologic stimulation with chemotactic peptide. Subsequent studies demonstrated that ''in vivo'' the enzyme originally identified by Cantley's group prefers PtdIns(4,5)P2 as a substrate, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer. PI3Ks are a family of related intracellular signal transducer enzymes capable of phosphorylating the 3 position hydroxyl group of the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns). The pathway, with oncogene PIK3CA and Tumor suppressor, tumor suppressor gene PTEN (gene), PTEN, is implicated in the sensitivity of cancer tumors to insulin and IGF1, and in calorie restriction. Discovery The discovery of PI3Ks by Lewis C. Cantley, Lewis Cantley and colleagues began with their identification of a previously unknown phosphoinositide kinase associated with the polyoma middle T protein. They observed unique substrate specificity and chromatographic properties of the products of the lipid kinase, leading to the disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4)''P''2) is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)''P''2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways. Of all the phospholipids found within the membrane, inositol phospholipids make up less than 10%. Phosphoinositides (PIs), also known as phosphatidylinositol phosphates, are synthesized in the cell's endoplasmic reticulum by the protein phosphatidylinositol synthase (PIS). PIs are highly compartmentalized; their main components include a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains enriched with stearic acid and arachidonic acid, and an inositol ring whose phosphate groups' regulation differs between organelles depending on the specific PI and PIP kinases and PIP phosphatases present in the organelle. These kinases and phosphatases conduct phosphorylation and dephosphorylation at the inositol sugar head groups 3’, 4’, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
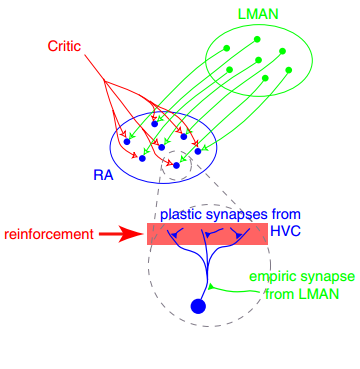
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to Chemical synapse#Synaptic strength, strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memory, memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both Excitatory synapse, excitatory and Inhibitory synapse, inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Depression , the pairing of two homologous chromosomes
{{disambig ...
Synaptic may refer to: * Synapse, part of the nervous system * Synaptic (software), a Linux graphical package management program * Synaptics, a semiconductor manufacturer * ''Synaptics'' (Mouse on Mars EP), 2017 See also * Synapse (other) * Synapsis Synapsis or Syzygy is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength. It is one of several phenomena underlying synaptic plasticity, the ability of chemical synapses to change their strength. As memories are thought to be encoded by modification of synaptic strength, LTP is widely considered one of the major cellular mechanisms that underlies learning and memory. LTP was discovered in the rabbit hippocampus by Terje Lømo in 1966 and has remained a popular subject of research since. Many modern LTP studies seek to better understand its basic biology, while others aim to draw a causal link between LTP and behavioral learning. Still, others try to develop methods, pharmacologic or otherwise, of enhanci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMPA Expression
α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, better known as AMPA, is a Chemical compound, compound that is a specific agonist for the AMPA receptor, where it mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter Glutamate (neurotransmitter), glutamate. There are several types of glutamatergic ion channels in the central nervous system including AMPA, kainic acid and N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid, ''N''-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) channels. In the Chemical synapse, synapse, these receptors serve very different purposes. AMPA can be used experimentally to distinguish the activity of one receptor from the other in order to understand their differing functions. AMPA generates fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP). AMPA activates AMPA receptors that are non-selective cationic channels allowing the passage of Na+ and K+ and therefore have an equilibrium potential near 0 mV. AMPA was first synthesized, along with several other ibotenic acid derivatives, by Povl Krogsgaard-Lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYTH2
Cytohesin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYTH2'' gene. Function Cytohesin-2 (CYTH2), formerly known as Pleckstrin homology, Sec7 and coiled/coil domains 2 (PSCD2), is a member of the cytohesin family. Members of this family have identical structural organization that consists of an N-terminal coiled-coil motif, a central Sec7 domain, and a C-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. The coiled-coil motif is involved in homodimerization, the Sec7 domain contains guanine-nucleotide exchange protein (GEP) activity, and the PH domain interacts with phospholipids and is responsible for association of CYTHs with membranes. Members of this family appear to mediate the regulation of protein sorting and membrane trafficking. CYTH2 exhibits GEP activity in vitro with ARF1, ARF3, and ARF6. CYTH2 protein is 83% homologous to CYTH1. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Interactions CYTH2 has been shown to interact with Arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (abbreviated Btk or BTK), also known as tyrosine-protein kinase BTK, is a tyrosine kinase that is encoded by the ''BTK'' gene in humans. BTK plays a crucial role in B cell development. Structure BTK contains five different protein interaction domains. These domains include an amino terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a proline-rich TEC homology (TH) domain, SRC homology (SH) domains SH2 and SH3, as well as a protein kinase domain with tyrosine phosphorylation activity. Part of the TH domain is folded against the PH domain while the rest is intrinsically disordered. Function BTK plays a crucial role in B cell development as it is required for transmitting signals from the pre-B cell receptor that forms after successful immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement. It also has a role in mast cell activation through the high-affinity IgE receptor. BTK contains a PH domain that binds phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3). PIP3 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-1
In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the ''PDPK1'' gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas. Function PDPK1 is a master kinase, which is crucial for the activation of AKT/PKB and many other AGC kinases including PKC, S6K, SGK. An important role for PDPK1 is in the signaling pathways activated by several growth factors and hormones including insulin signaling. Mice lacking PDPK1 die during early embryonic development, indicating that this enzyme is critical for transmitting the growth-promoting signals necessary for normal mammalian development. Mice that are deficient in PDPK1 have a ≈40% decrease in body mass, mild glucose intolerance, and are resistant to cancer brought about by hyperactivation of the PI3K pathway (PTEN+/-). Plant PDK1 plays an important role in regulating PIN-mediated auxin transport, and is thus involved in va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PH Domain
Pleckstrin homology domain (PH domain) or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton. This domain can bind phosphatidylinositol lipids within biological membranes (such as phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate), and proteins such as the βγ-subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins, and protein kinase C. Through these interactions, PH domains play a role in recruiting proteins to different membranes, thus targeting them to appropriate cellular compartments or enabling them to interact with other components of the signal transduction pathways. Lipid binding specificity Individual PH domains possess specificities for phosphoinositides phosphorylated at different sites within the inositol ring, e.g., some bind phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate but not phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol
In biochemistry, medicine, and related sciences, inositol generally refers to ''myo''-inositol (formerly ''meso''-inositol), the most important stereoisomer of the chemical compound cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol. Its elemental formula, formula is ; the molecule has a ring of six carbon atoms, each with a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group (–OH). In ''myo''-inositol, two of the hydroxyls, neither adjacent nor opposite, lie above the respective hydrogens relative to the mean plane of the ring. The compound is a carbohydrate, specifically a sugar alcohol (as distinct from aldoses like glucose) with half the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar). It is one of the most ancient components of living beings with multiple functions in eukaryotes, including structural lipids and secondary messengers. A human kidney makes about two grams per day from glucose, but other tissues synthesize it too. The highest concentration is in the brain, where it plays an important role in making other neurot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins. PIP2 is formed primarily by the type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases from PI(4)P. In metazoans, PIP2 can also be formed by type II phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinases from PI(5)P. The fatty acids of PIP2 are variable in different species and tissues, but the most common fatty acids are stearic in position 1 and arachidonic in 2. Signaling pathways PIP2 is a part of many cellular signaling pathways, including PIP2 cycle, PI3K signalling, and PI5P metabolism. Recently, it has been found in the nucleus with unknown function. Functions Cytoskeleton dynamics near membranes PIP2 regulates the organization, polymerization, and bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |