|
Persulfate
A persulfate (sometimes known as peroxysulfate or peroxodisulfate) is a compound containing the anions or . The anion contains one peroxide group per sulfur center, whereas in , the peroxide group bridges the sulfur atoms. In both cases, sulfur adopts the normal tetrahedral geometry typical for the S(VI) oxidation state. These salts are strong oxidizers. Ions * Peroxomonosulfate ion, * Peroxydisulfate Acids * Peroxymonosulfuric acid (Caro's acid), H2SO5 * Peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8 Example salts * Sodium peroxomonosulfate, Na2SO5 * Potassium peroxymonosulfate Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent, for example, in pools and spas (usually referred to as monopersulfate or "MPS"). It is the potassium salt (chemistry), salt of peroxymonosulfuric acid. Potassium peroxymonosulfate ..., KHSO5 * Sodium persulfate (sodium peroxydisulfate), Na2S2O8 * Ammonium persulfate (ammonium peroxydisulfate), (NH4)2S2O8 * Potassium persulfate (potassium pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Persulfate
Ammonium persulfate (APS) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2S2O8. It is a colourless (white) salt that is highly soluble in water, much more so than the related potassium salt. It is a strong oxidizing agent that is used as a catalyst in polymer chemistry, as an etchant, and as a cleaning and bleaching agent. Preparation and structure Ammonium persulfate is prepared by electrolysis of a cold concentrated solution of either ammonium sulfate or ammonium bisulfate in sulfuric acid at a high current density.F. Feher, "Potassium Peroxydisulfate" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 390. The method was first described by Hugh Marshall. The ammonium, sodium, and potassium salts adopt very similar structures in the solid state, according to X-ray crystallography. In the ammonium salt, the O-O distance is 1.497Å. The sulfate groups are tetrahedral, with three short S-O distances near 1.44� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Persulfate
Sodium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2 S2 O8. It is the sodium salt of peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8, an oxidizing agent. It is a white solid that dissolves in water. It is almost non-hygroscopic and has good shelf-life. Production The salt is prepared by the electrolytic oxidation of sodium bisulfate: : Oxidation is conducted at a platinum anode. In this way about 165,000 tons were produced in 2005. The standard redox potential of sodium persulfate into hydrogen sulfate is 2.1 V, which is higher than that of hydrogen peroxide (1.8 V) but lower than ozone (2.2 V). The sulfate radical formed in situ has a standard electrode potential of 2.7 V. However, there are a few drawbacks in utilizing platinum anodes to produce the salts; the manufacturing process is inefficient due to oxygen evolution and the product could contain contaminants coming from platinum corrosion (mainly due to extremely oxidizing nature of the sulfate radical). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Persulfate
Potassium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 S2O8. Also known as potassium peroxydisulfate, it is a white solid that is sparingly soluble in cold water, but dissolves better in warm water. This salt is a powerful oxidant, commonly used to initiate polymerizations. Structure The sodium and potassium salts are very similar. In the potassium salt, the O-O distance is 1.495Å. The individual sulfate groups are tetrahedral, with three short S-O distances near 1.43 and one long S-O bond at 1.65Å. Preparation Potassium persulfate can be prepared by electrolysis of a cold solution potassium bisulfate in sulfuric acid at a high current density. : 2 KHSO4 → K2S2O8 + H2 It can also be prepared by adding potassium bisulfate (KHSO4) to a solution of the more soluble salt ammonium peroxydisulfate (NH4)2S2O8. In principle it can be prepared by chemical oxidation of potassium sulfate using fluorine. Several million kilograms of the ammonium, sodium, and potassium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxydisulfate
The peroxydisulfate ion, , is an oxyanion, the anion of peroxydisulfuric acid. It is commonly referred to as persulfate, but this term also refers to the peroxomonosulfate ion, . It is also called ''peroxodisulfate''. Approximately 500,000 tons of salts containing this anion are produced annually. Important salts include sodium persulfate (Na2S2O8), potassium persulfate (K2S2O8), and ammonium persulfate ((NH4)2S2O8). These salts are colourless, water-soluble solids that are strong oxidants. Applications Salts of peroxydisulfate are mainly used to initiate the polymerization of various alkenes, including styrene, acrylonitrile, and fluoroalkenes. Polymerization is initiated by the homolysis of the peroxydisulfate: : 3SO–OSO3sup>2− 2 O4sup>•− Moreover, sodium peroxydisulfate can be used for soil and groundwater remediation Groundwater remediation is the process that is used to treat polluted groundwater by removing the pollutants or converting them into harmless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persulfates
A persulfate (sometimes known as peroxysulfate or peroxodisulfate) is a compound containing the anions or . The anion contains one peroxide group per sulfur center, whereas in , the peroxide group bridges the sulfur atoms. In both cases, sulfur adopts the normal tetrahedral geometry typical for the S(VI) oxidation state. These salts are strong oxidizers. Ions * Peroxomonosulfate ion, * Peroxydisulfate Acids * Peroxymonosulfuric acid (Caro's acid), H2SO5 * Peroxydisulfuric acid, H2S2O8 Example salts * Sodium peroxomonosulfate, Na2SO5 * Potassium peroxymonosulfate, KHSO5 * Sodium persulfate (sodium peroxydisulfate), Na2S2O8 * Ammonium persulfate (ammonium peroxydisulfate), (NH4)2S2O8 * Potassium persulfate Potassium persulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2 S2O8. Also known as potassium peroxydisulfate, it is a white solid that is sparingly soluble in cold water, but dissolves better in warm water. This salt is a powerful oxidant, co ... (potassium peroxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
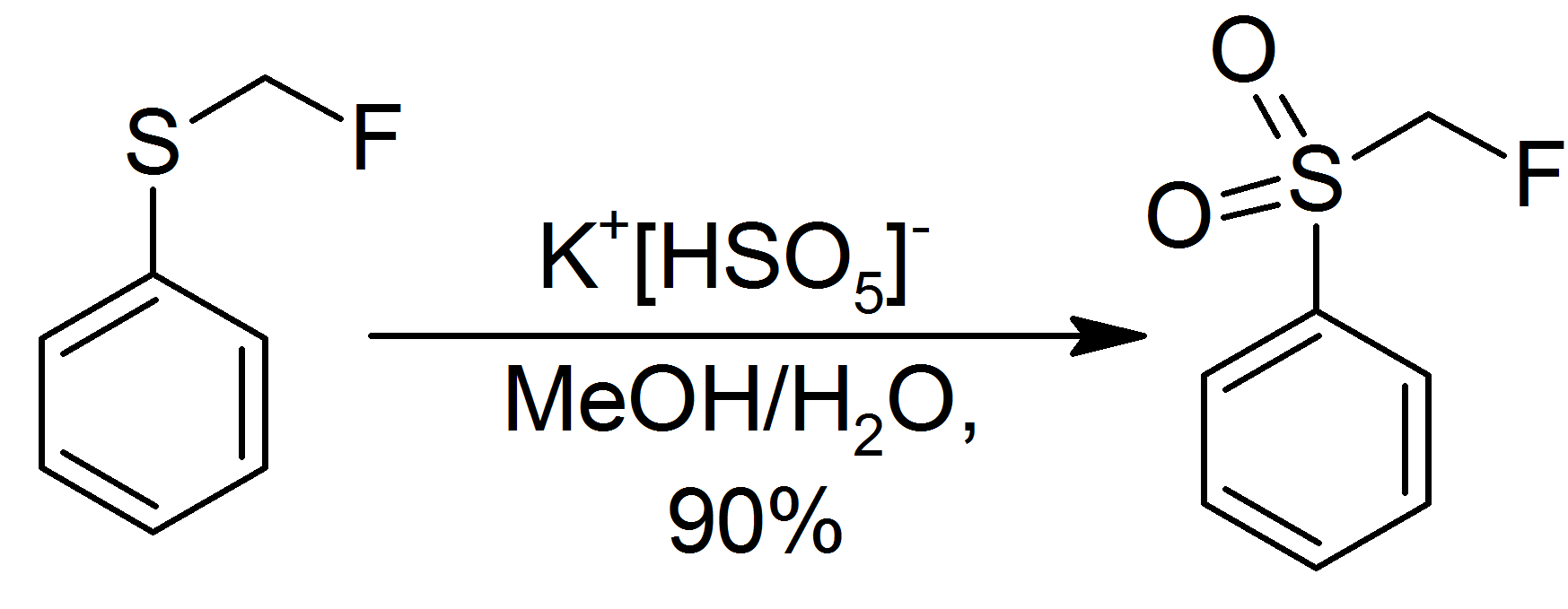
Potassium Peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent, for example, in pools and spas (usually referred to as monopersulfate or "MPS"). It is the potassium salt (chemistry), salt of peroxymonosulfuric acid. Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is rarely encountered. It is often confused with the triple salt , known as Oxone. The standard electrode potential for potassium peroxymonosulfate is +1.81 V with a half reaction generating the hydrogen sulfate (): : Oxone Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is a relatively obscure salt, but its derivative called Oxone is of commercial value. Oxone refers to the triple salt . As such about one third by weight is potassium peroxymonosulfate. Oxone has a longer shelf life than does potassium peroxymonosulfate. A white, water-soluble solid, Oxone loses <1% of its oxidizing power per month. Oxone, which is commercially available, is produced from peroxysulfuric acid, which is generated in situ by combining oleum and hydrogen perox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxydisulfuric Acid
Peroxydisulfuric acid is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula . It is also called Marshall's acid after Professor Hugh Marshall, who discovered it in 1891. Structure and bonding This oxoacid features sulfur in its +6 oxidation state and a peroxide group. Sulfur adopts the usual tetrahedral geometry. Synthesis The acid is prepared by the reaction of chlorosulfuric acid with hydrogen peroxide: : Another method is the electrolysis of moderately concentrated sulfuric acid (60-70%) with platinum electrodes at high current density and voltage: :H2SO4 + H2O → H3O+ + HSO4− (dissociation of sulfuric acid) :2 HSO4− → H2S2O8 + 2 e− (E0 = +2.4V) (bisulfate oxidation) :2 H2SO4 → H2S2O8 + H2 (overall reaction) :3 H2O → O3 + 6 H+ (ozone produced as a side product) Uses Peroxydisulfuric acid is a precursor to several salts including sodium peroxydisulfate, potassium peroxydisulfate, and ammonium peroxydisulfate. These salts are used to initiate the polymerization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxomonosulfate
The peroxomonosulfate ion, , is a sulfur oxoanion. It is sometimes referred to as the persulfate ion, but this term also refers to the peroxydisulfate The peroxydisulfate ion, , is an oxyanion, the anion of peroxydisulfuric acid. It is commonly referred to as persulfate, but this term also refers to the peroxomonosulfate ion, . It is also called ''peroxodisulfate''. Approximately 500,000 ton ... ion, . Its other IUPAC names are sulfuroperoxoate and trioxidoperoxidosulfate(2−). Compounds containing peroxomonosulfate * Na2SO5 * KHSO5 See also * Peroxymonosulfuric acid References * Sulfur oxyanions {{Inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxymonosulfuric Acid
Peroxymonosulfuric acid, also known as persulfuric acid, peroxysulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid. It is a component of Caro's acid, which is a solution of peroxymonosulfuric acid in sulfuric acid containing small amounts of water. Peroxymonosulfuric acid is a very strong oxidant ( ''E''0 = +2.51 V). Structure In peroxymonosulfuric acid, the S(VI) center adopts its characteristic tetrahedral geometry; the connectivity is indicated by the formula HO–O–S(O)2–OH. The S-O-''H'' proton is more acidic. History The German chemist Heinrich Caro first reported investigations of mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid. Synthesis and production One laboratory scale preparation of Caro's acid involves the combination of chlorosulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide: : Patents include more than one reaction for preparation of Caro's acid, usually as an intermediate for the production of potassium monopersulfate (PMPS), a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons (e.g. K+ ( potassium ion)) while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons (e.g. Cl− ( chloride ion) and OH− ( hydroxide ion)). Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed ''monatomic ions'', ''atomic ions'' or ''simple ions'', while ions consisting of two or more atoms are termed polyatomic ions or ''molecular ions''. If only a + or − is present, it indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined to each other and to adjacent elements through Single bond, single covalent bonds, denoted by dashes or lines. The group in a peroxide is often called the peroxide group, though some nomenclature discrepancies exist. This linkage is recognized as a common polyatomic ion, and exists in many molecules. General structure The characteristic structure of any regular peroxide is the oxygen–oxygen covalent single bond, which connects the two main atoms together. In the event that the molecule has no chemical Substituent, substituents, the peroxide group will have a [−2] Formal charge, net charge. Each oxygen atom has a charge of negative one, as 5 of its Valence electron, valence electrons remain in the outermost Atomic orbital, orbital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Oxyanions
Sulfur (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundance of the chemical elements, abundant, Polyvalency (chemistry), multivalent and Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetallic. Under standard conditions for temperature and pressure, normal conditions, sulfur atoms form octasulfur, cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula octasulfur, S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native element minerals, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide minerals, sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in Outline of ancient India, ancient India, ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |