|
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive non-surgical procedure used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. The procedure is used to place and deploy coronary stents, a permanent wire-meshed tube, to open narrowed coronary arteries. PCI is considered 'non-surgical' as it uses a small hole in a peripheral artery (leg/arm) to gain access to the arterial system; an equivalent surgical procedure would involve the opening of the chest wall to gain access to the heart area. The term 'coronary angioplasty with stent' is synonymous with PCI. The procedure visualises the blood vessels via fluoroscopic imaging and contrast dyes. PCI is performed by an interventional cardiologists in a catheterization laboratory setting. Patients who undergo PCI broadly fall into two patient groups. Those who are suffering from a heart attack and are in a critical care emergency room setting and patients who are clinically at a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
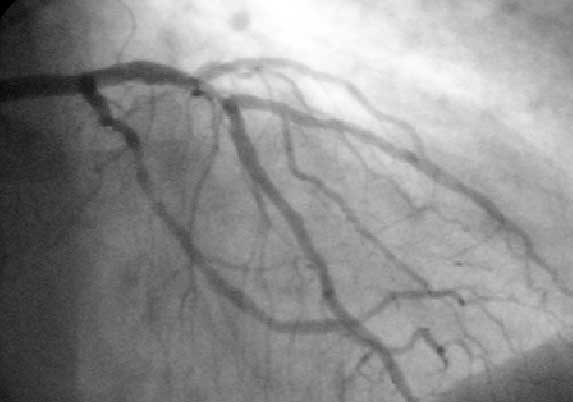
Coronary Angiogram
A coronary catheterization is a minimally invasive procedure to access the coronary circulation and blood filled chambers of the heart using a catheter. It is performed for both diagnostic and interventional (treatment) purposes. Coronary catheterization is one of the several cardiology diagnostic tests and procedures. Specifically, through the injection of a liquid radiocontrast agent and illumination with X-rays, angiocardiography allows the recognition of Vascular occlusion, occlusion, stenosis, restenosis, thrombosis or aneurysmal enlargement of the coronary artery lumen (anatomy), lumens; heart chamber size; heart muscle contraction performance; and some aspects of heart valve function. Important internal heart and lung blood pressures, not measurable from outside the body, can be accurately measured during the test. The relevant problems that the test deals with most commonly occur as a result of advanced atherosclerosis – atheroma activity within the wall of the coronary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergic Reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include allergic conjunctivitis, red eyes, an itchy rash, sneeze, sneezing, coughing, a rhinorrhea, runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to FcεRI, a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissection (medical)
An arterial dissection is a tear within the wall of an artery, which allows blood to separate the wall layers. There are several types. Tears almost always occur in arterial walls, but a vein wall tear has been documented. By separating a portion of the wall of the artery (a layer of the tunica media or in some cases tunica intima), a tear creates two lumens or passages within the vessel, the original or true lumen, and the false lumen created by the new space within the wall of the artery. It is not yet clear if the tear in the innermost layer, the tunica intima, is secondary to the tear in the tunica media. Dissections originating in the tunica media are caused by disruption of the vasa vasorum. It is thought that dysfunction in the vasa vasorum is an underlying cause of dissections. Description Arterial dissections become life-threatening when growth of the false lumen prevents perfusion of the true lumen and the related end organs. For example, in an aortic dissection, if th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm. They may occur among and or within many areas such as skin and other organs, connective tissues, bone, joints and muscle. A collection of blood (or even a hemorrhage) may be aggravated by anticoagulant medication (blood thinner). Blood seepage and collection of blood may occur if heparin is given via an intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneously. Signs and symptoms Some hematomas are visible under the surface of the skin (commonly called bruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone. Bruises are not to be confused with other similar-looking lesions. Such lesions include petechia (less than , resulting from numerous and diverse etiologies such as adverse reactions from medications such as warfarin, straining, asphyxiation, platelet disorders and diseases such as ''cytomegalovirus''); and purpura (), classified as palpable purpura or non-palpable purpura and indicating various pathologic conditions su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiplatelet Drug
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effective in the arterial circulation where classical Vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants have minimal effect. Antiplatelet drugs are widely used in primary and secondary prevention of thrombotic disease, especially myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. Antiplatelet therapy with one or more of these drugs decreases the ability of blood clots to form by interfering with the platelet activation process in primary hemostasis. Antiplatelet drugs can reversibly or irreversibly inhibit the process involved in platelet activation resulting in decreased tendency of platelets to adhere to one another and to damaged blood vessels' endothelium. Choice Antiplatelet medications are one of the primary recommendations for treatment of both stable a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a heart chamber, chamber or Blood vessel, vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes. A common example of cardiac catheterization is coronary catheterization that involves catheterization of the coronary arteries for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarctions ("heart attacks"). Catheterization is most often performed in special laboratories with fluoroscopy and highly maneuverable tables. These "cath labs" are often equipped with cabinets of catheters, stents, Balloon catheter, balloons, etc. of various sizes to increase efficiency. Monitors show the fluoroscopy imaging, electrocardiogram (ECG), pressure waves, and more. Uses Coronary angiography is a diagnostic procedure that allows visualization of the coronary vessels. Fluoroscopy is used to visualize the lumens of the arteries as a 2-D projection. Should these arteries show narrowing or blockage, then techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evidence-based Medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research." The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of the patient, and the best available scientific information to guide decision-making about clinical management. The term was originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients. The EBM Pyramid is a tool that helps in visualizing the hierarchy of evidence in medicine, from least authoritative, like expert opinions, to most authoritative, like systematic reviews. Adoption of evidence-based medicine is necessary in a human Rights-based approach to development, rights-based approach to public health and a precondition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern Ireland) which was created separately and is often referred to locally as "the NHS". The original three systems were established in 1948 (NHS Wales/GIG Cymru was founded in 1969) as part of major social reforms following the Second World War. The founding principles were that services should be comprehensive, universal and free at the point of delivery. Each service provides a comprehensive range of health services, provided without charge for residents of the United Kingdom apart from dental treatment and optical care. In England, NHS patients have to pay prescription charges; some, such as those aged over 60, or those on certain state benefits, are exempt. Taken together, the four services in 2015–16 employed around 1.6 million people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antianginal
An antianginal is a drug used in the treatment of ''angina pectoris'', a symptom of ischaemic heart disease. Myocardial ischemia arises from the dysfunction of coronary macrovascular or microvascular components, leading to a compromised supply of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium. The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms encompass a range of factors, including atherosclerosis in epicardial coronary arteries, vasospasm in large or small vessels, and microvascular dysfunction—whose clinical significance is increasingly acknowledged. The diverse clinical presentations of myocardial ischemia collectively fall under the term chronic coronary syndromes. Addressing these conditions involves a multifaceted approach, where the most common antianginal medications alleviate symptoms by inducing coronary vasodilation and modifying the determinants of myocardial oxygen consumption, such as heart rate, myocardial wall stress, and ventricular contractility. Additionally, these medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |