|
Percentage In Point
In foreign exchange markets (forex), a percentage in point (pip) is a unit of change in an exchange rate of a currency pair. A pip is the smallest whole unit price move that an exchange rate can make, based on forex market convention. It's important because forex trading involves tiny fluctuations in exchange rates, and Pips provides a standardized way to express these changes. By using Pip, traders can easily understand and discuss price movements, and calculate profits and losses, and manage risks more effectively. The major currencies (except the Japanese yen) are traditionally priced to four decimal places, and a pip is one unit of the fourth decimal place: for dollar currencies this is to of a cent. For the yen, a pip is one unit of the second decimal place, because the yen is much closer in value to one-hundredth of other major currencies. In the forward foreign exchange market, the time value adjustment made to the spot rate is quoted in pips, or FX points or forward p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market. The main participants are the larger international banks. Financial centres function as anchors of trading between a range of multiple types of buyers and sellers around the clock, with the exception of weekends. As currencies are always traded in pairs, the market does not set a currency's absolute value, but rather determines its relative value by setting the market price of one currency if paid for with another. Example: 1 USD is worth 1.1 Euros or 1.2 Swiss Francs etc. The market works through financial institutions and operates on several levels. Behind the scenes, banks turn to a smaller number of financial firms known as "dealers", who are involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchange Rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of the euro. The exchange rate is also regarded as the value of one country's currency in relation to another currency. For example, an Interbank lending market, interbank exchange rate of 141 Japanese yen to the United States dollar means that ¥141 will be exchanged for or that will be exchanged for ¥141. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in relation to yen is ¥141, or equivalently that the price of a yen in relation to dollars is $1/141. Each country determines the exchange rate regime that will apply to its currency. For example, a currency may be floating exchange rate, floating, fixed exchange rate, pegged (fixed), or a hybrid. Governments can impose certain limits and controls on exchange rates. Countries can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Pair
A currency pair is the quotation of the relative value of a currency unit against the unit of another currency in the foreign exchange market. The currency that is used as the reference is called the counter currency, quote currency, or currency and the currency that is quoted in relation is called the base currency or transaction currency. Currency pairs are generally written by concatenating the ISO currency codes (ISO 4217) of the base currency and the counter currency, and then separating the two codes with a slash. Alternatively the slash may be omitted, or replaced by either a dot or a dash. A widely traded currency pair is the relation of the euro against the US dollar, designated as EUR/USD. The quotation ''EUR/USD 1.2500'' means that one euro is exchanged for 1.2500 US dollars. Here, EUR is the base currency and USD is the quote currency (counter currency). This means that 1 Euro can be exchangeable to 1.25 US Dollars. The most traded currency pairs in the world ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro. The New Currency Act of 1871 introduced Japan's modern currency system, with the yen defined as of gold, or of silver, and divided decimally into 100 ''sen'' or 1,000 ''rin''. The yen replaced the previous Tokugawa coinage as well as the various ''hansatsu'' paper currencies issued by feudal ''han'' (fiefs). The Bank of Japan was founded in 1882 and given a monopoly on controlling the money supply. Following World War II, the yen lost much of its pre-war value as Japan faced a debt crisis and hyperinflation. Under the Bretton Woods system, the yen was pegged to the US dollar alongside other major currencies. After this system was abandoned in 1971 with the Nixon shock, Nixon Shock, the short-lived Smithsonian Agreement temporarily reinstat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
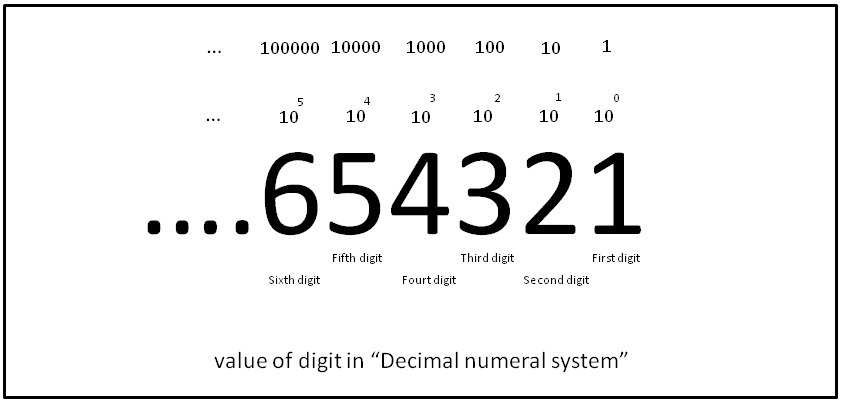
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cent (currency)
The cent is a monetary unit of many national currencies that equals a hundredth () of the basic monetary unit. The word derives from the Latin , 'hundred'. The cent sign is commonly a simple minuscule (lower case) letter . In North America, the c is crossed by a diagonal or vertical stroke (depending on typeface), yielding the character . The United States one cent coin is generally known by the nickname "penny", alluding to the British coin and unit of that name. Australia ended production of their 1c coin in 1990, New Zealand last produced their 1c coin in 1988, as did Canada in 2012. Some Eurozone countries ended production of the 1 euro cent coin, most recently Slovakia in 2022. Symbol The cent may be represented by the cent sign, written in various ways according to the national convention and font choice. Most commonly seen forms are a minuscule letter ''c'' crossed by a diagonal stroke, a vertical line, a simple ''c'', depending on the currency (''see below' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick Size
In financial markets, the tick size is the smallest price increment in which the prices are quoted. The meaning of the term varies depending on whether stocks, bonds, or futures are being quoted. Bonds U.S. mortgage bonds and certain corporate bonds are quoted in increments of one thirty-second () of one percent. That means that prices will be quoted as, for instance, "99-30" (read as "99 and 30 ticks"), meaning 99 and percent of the face value. Prices can also be quoted with a "plus", adding one sixty-fourth () of one percent or half a tick. That means that a price is quoted as, for instance, "99-30+", meaning 99 and percent (or percent) of the face value. As an example, "par the buck plus" means 100% plus of 1% or 100.015625% of face value. Most European and Asian bond and futures prices are quoted in decimals so the "tick" size is of 1%. Stocks and futures Tick size is the smallest increment (tick) by which the price of stocks, futures contracts or other exchange-traded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the euro area or, more commonly, the eurozone. The euro is divided into 100 1 euro cent coin, euro cents. The currency is also used officially by the institutions of the European Union, by International status and usage of the euro, four European microstates that are not EU members, the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, as well as unilaterally by Montenegro and Kosovo. Outside Europe, a number of special territories of EU members also use the euro as their currency. The euro is used by 350 million people in Europe and additionally, over 200 million people worldwide use currencies pegged to the euro. It is the second-largest reserve currency as well as the second-most traded currency in the world after the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margin Account
In finance, margin is the collateral that a holder of a financial instrument has to deposit with a counterparty (most often their broker or an exchange) to cover some or all of the credit risk the holder poses for the counterparty. This risk can arise if the holder has done any of the following: * Borrowed cash from the counterparty to buy financial instruments, * Borrowed financial instruments to sell them short, * Entered into a derivative contract. The collateral for a margin account can be the cash deposited in the account or securities provided, and represents the funds available to the account holder for further share trading. On United States futures exchanges, margins were formerly called performance bonds. Most of the exchanges today use SPAN ("Standard Portfolio Analysis of Risk") methodology, which was developed by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange in 1988, for calculating margins for options and futures. Margin account A margin account is a loan account with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity (finance)
In finance, equity is an ownership interest in property that may be subject to debts or other liabilities. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business. A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity in order to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. When liabilities attached to an asset exceed its value, the difference is called a deficit and the asset is informally said to be "underwater" or "upside-down". In government finance or other non-profit settings, equity is known as "net position" or "net assets". Origins The term "equity" describes this type of ownership in English because it was regulated through the system of equity law that devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Trading Platform
In finance, an electronic trading platform, also known as an online trading platform, is a computer software program that can be used to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. Various financial products can be traded by the trading platform, over a communication network with a financial intermediary or directly between the participants or members of the trading platform. This includes products such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives and others, with a financial intermediary such as brokers, market makers, investment banks or stock exchanges. Such platforms allow electronic trading to be carried out by users from any location and are in contrast to traditional floor trading using open outcry and telephone-based trading. Sometimes the term trading platform is also used in reference to the trading software alone. Electronic trading platforms typically stream live market prices on which users can trade and may provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |