|
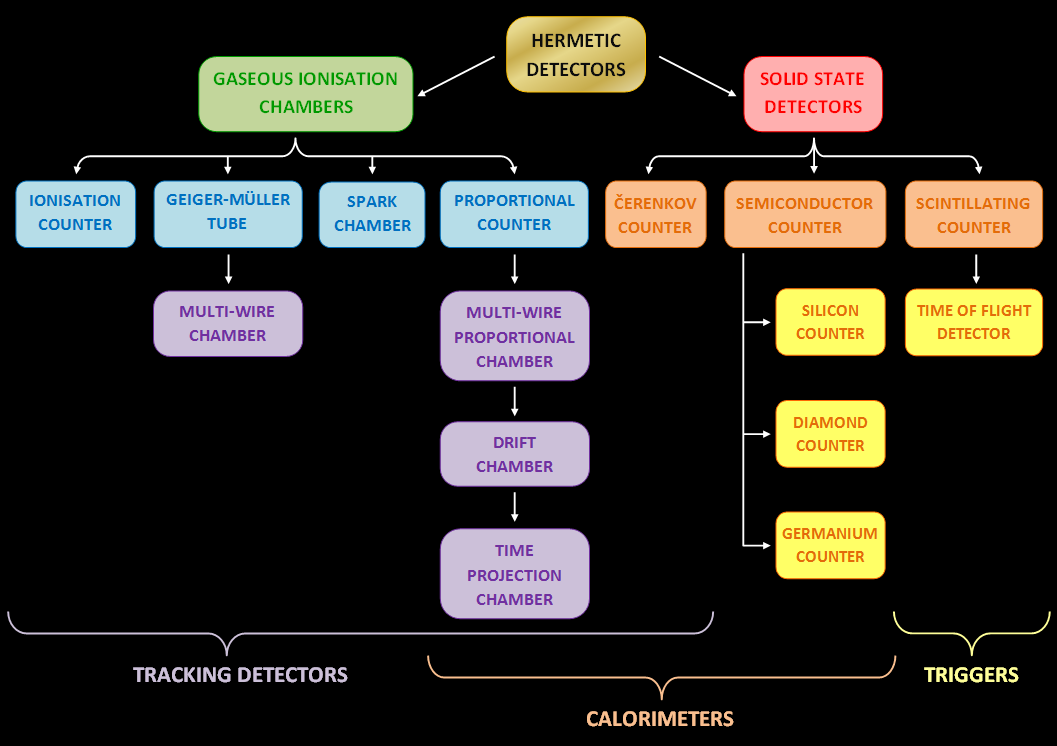
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
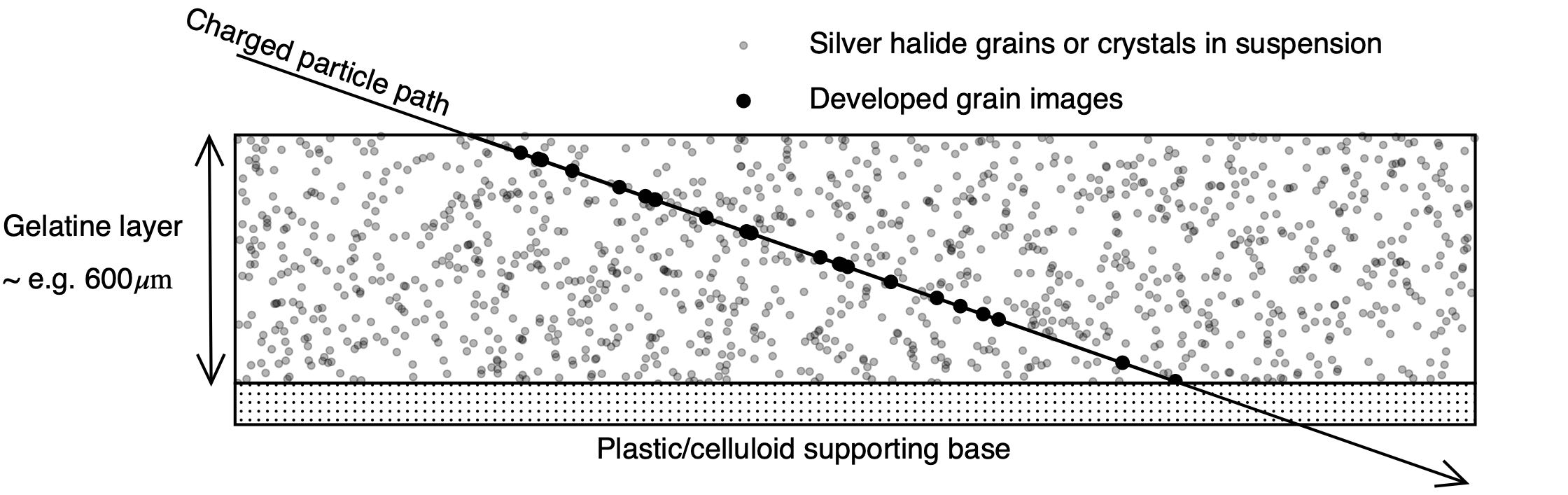
Nuclear Emulsion
A nuclear emulsion plate is a type of particle detector first used in nuclear and particle physics experiments in the early decades of the 20th century. https://cds.cern.ch/record/1728791/files/vol6-issue5-p083-e.pdf''The Study of Elementary Particles by the Photographic Method'', C.F.Powell, P.H.Fowler, D.H.Perkins: Pergamon Press, New York, 1959.Walter H. Barkas, ''Nuclear Research Emulsions I. Techniques and Theory'', in ''Pure and Applied Physics: A Series of Monographs and Textbooks, Vol. 15'', Academic Press, New York and London, 1963. http://becquerel.jinr.ru/text/books/Barkas_NUCL_RES_EMULSIONS.pdf It is a modified form of photographic plate that can be used to record and investigate fast charged particles like alpha-particles, nucleons, leptons or mesons. After exposing and developing the emulsion, single particle tracks can be observed and measured using a microscope. Description The nuclear emulsion plate is a modified form of photographic plate, coated with a thick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geiger–Müller Tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborated with Geiger in developing the technique further in 1928 to produce a practical tube that could detect a number of different radiation types. It is a gaseous ionization detector and uses the Townsend avalanche phenomenon to produce an easily detectable electronic pulse from as little as a single ionizing event due to a radiation particle. It is used for the detection of gamma radiation, X-rays, and alpha and beta particles. It can also be adapted to detect neutrons. The tube operates in the "Geiger" region of ion pair generation. This is shown on the accompanying plot for gaseous detectors showing ion current against applied voltage. While it is a robust and inexpensive detector, the G–M is unable to measure high radiation rates effi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropattern Gaseous Detector
Micropattern gaseous detectors (MPGDs) are a group of gaseous ionization detectors consisting of microelectronic structures with sub-millimeter distances between anode and cathode electrodes. When interacting with the gaseous medium of the detector, particles of ionizing radiation create electrons and ions that are subsequently drifted apart by means of an electric field. The accelerated electrons create further electron-ion pairs in an avalanche process in regions with a strong electrostatic field. The various types of MPGDs differ in the way this strong field region is created. Examples of MPGDs include the microstrip gas chamber, the gas electron multiplier and the Micromegas detector. The main advantages of MPGDs over previous types of gaseous detectors, such as the multiwire proportional chamber, are their count rate capability, time and position resolution, granularity, stability and radiation hardness. References {{reflist Particle detectors Ionising radiation dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Projection Chamber
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particle trajectory or interaction. The original design The original TPC was invented by David R. Nygren, an American physicist, at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory in the late 1970s. Its first major application was in the PEP-4 detector, which studied 29 GeV electron–positron collisions at the PEP storage ring at SLAC. A time projection chamber consists of a gas-filled detection volume in an electric field with a position-sensitive electron collection system. The original design (and the one most commonly used) is a cylindrical chamber with multi-wire proportional chambers (MWPC) as endplates. Along its length, the chamber is divided into halves by means of a central high-voltage electrode disc, which establishes an electric field between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via Dr. C.N. BootPHY304 Particle Physics Sheffield University The technique was an improvement over the bubble chamber particle detection method, which used photographic techniques, as it allowed high speed electronics to track the particle path. Description The multi-wire chamber uses an array of wires at a positive dc voltage (anode)s, which run through a chamber with conductive walls held at a lower potential (cathode). The chamber is filled with gas, such as an argon/methane mix, so that any ionizing particle that passes through the tube will ionize surrounding gaseous atoms and produce ion pairs, consisting of positive ions and electrons. These are accelerated by the electric field across the chamber, preventing recombination; the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Detector
In ionizing radiation detection physics, a semiconductor detector is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons. Semiconductor detectors find broad application for radiation protection, gamma spectroscopy, gamma and x-ray spectroscopy, X-ray spectrometry, and as particle detectors. Detection mechanism In semiconductor detectors, ionizing radiation is measured by the number of charge carriers set free in the detector material which is arranged between two electrodes, by the radiation. Ionizing radiation produces free electrons and electron holes. The number of electron-hole pairs is proportional to the energy of the radiation to the semiconductor. As a result, a number of electrons are transferred from the valence band to the conduction band, and an equal number of holes are created in the valence band. Under the influence of an electric field, electrons and holes travel to the electrodes, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillation Counter
A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the Electron excitation, excitation effect of incident radiation on a Scintillation (physics), scintillating material, and detecting the resultant light pulses. It consists of a scintillator which generates photons in response to incident radiation, a sensitive photodetector (usually a photomultiplier tube (PMT), a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera, or a photodiode), which converts the light to an electrical signal and electronics to process this signal. Scintillation counters are widely used in radiation protection, assay of radioactive materials and physics research because they can be made inexpensively yet with good quantum efficiency, and can measure both the intensity and the Electronvolt, energy of incident radiation. History The first electronic scintillation counter was invented in 1944 by Samuel Curran, Sir Samuel Curran whilst he was working on the Manhattan Project at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Counter
The proportional counter is a type of gaseous ionization detector device used to measure Charged particle, particles of ionizing radiation. The key feature is its ability to measure the Electronvolt, energy of incident radiation, by producing a detector output pulse that is ''proportional'' to the radiation energy absorbed by the detector due to an ionizing event; hence the detector's name. It is widely used where energy levels of incident radiation must be known, such as in the discrimination between alpha particle, alpha and beta particles, or accurate measurement of X-ray radiation absorbed dose, dose. A proportional counter uses a combination of the mechanisms of a Geiger–Müller tube and an ionization chamber, and operates in an intermediate voltage region between these. The accompanying plot shows the proportional counter operating voltage region for a co-axial cylinder arrangement. Operation In a proportional counter the fill gas of the chamber is an inert gas which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest type of gaseous ionisation detector, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of many types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, alpha particles and beta particles. Conventionally, the term "ionization chamber" refers exclusively to those detectors which collect all the charges created by ''direct ionization'' within the gas through the application of an electric field. It uses the discrete charges created by each interaction between the incident radiation and the gas to produce an output in the form of a small direct current. This means individual ionising events cannot be measured, so the energy of different types of radiation cannot be differentiated, but it gives a very good measurement of overall ionising effect. It has a good uniform response to radiation over a wide range of energies and is the preferred means of measuring high levels of gamma radiation, such as in a hot cell, radiation hot cell as they ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geiger Counter
A Geiger counter (, ; also known as a Geiger–Müller counter or G-M counter) is an electronic instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation with the use of a Geiger–Müller tube. It is widely used in applications such as radiation dosimetry, radiological protection, experimental physics and the nuclear industry. "Geiger counter" is often used generically to refer to any form of dosimeter (or, ''radiation-measuring device''), but scientifically, a Geiger counter is only one specific type of dosimeter. It detects ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays using the ionization effect produced in a Geiger–Müller tube, which gives its name to the instrument. In wide and prominent use as a hand-held radiation survey instrument, it is perhaps one of the world's best-known radiation detection instruments. The original detection principle was realized in 1908 at the University of Manchester, but it was not until the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |