|
Part-of-speech Tagging
In corpus linguistics, part-of-speech tagging (POS tagging, PoS tagging, or POST), also called grammatical tagging, is the process of marking up a word in a text ( corpus) as corresponding to a particular part of speech, based on both its definition and its context. A simplified form of this is commonly taught to school-age children, in the identification of words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Once performed by hand, POS tagging is now done in the context of computational linguistics, using algorithms which associate discrete terms, as well as hidden parts of speech, by a set of descriptive tags. POS-tagging algorithms fall into two distinctive groups: rule-based and stochastic. E. Brill's tagger, one of the first and most widely used English POS taggers, employs rule-based algorithms. Principle Part-of-speech tagging is harder than just having a list of words and their parts of speech, because some words can represent more than one part of speech at different t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Linguistics
Corpus linguistics is an empirical method for the study of language by way of a text corpus (plural ''corpora''). Corpora are balanced, often stratified collections of authentic, "real world", text of speech or writing that aim to represent a given linguistic variety. Today, corpora are generally machine-readable data collections. Corpus linguistics proposes that a reliable analysis of a language is more feasible with corpora collected in the field—the natural context ("realia") of that language—with minimal experimental interference. Large collections of text, though corpora may also be small in terms of running words, allow linguists to run quantitative analyses on linguistic concepts that may be difficult to test in a qualitative manner. The text-corpus method uses the body of texts in any natural language to derive the set of abstract rules which govern that language. Those results can be used to explore the relationships between that subject language and other language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamanship
Seamanship is the skill, art, competence (human resources), competence, and knowledge of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary of English, Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea." It involves topics and development of specialised skills, including navigation and international Admiralty law, maritime law and regulatory knowledge; weather, meteorology and forecasting; watchkeeping; ship-handling and small boat handling; operation of deck equipment, anchors and cables; ropework and line handling; communications; sailing; engines; execution of evolutions such as towing; cargo handling equipment, dangerous cargoes and cargo storage; dealing with emergencies; survival at sea and search and rescue; and fire fighting. The degree of knowledge needed within these areas is dependent upon the nature of the work and the type of vessel employed by a sailor, seafarer. History Shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature (linguistics)
In linguistics, a feature is any characteristic used to classify a phoneme or word. These are often binary or unary conditions which act as constraints in various forms of linguistic analysis. In phonology In phonology, segments are categorized into natural classes on the basis of their distinctive features. Each feature is a quality or characteristic of the natural class, such as voice or manner. A unique combination of features defines a phoneme. Examples of phonemic or distinctive features are: /- voice Advanced tongue root">ATR (binary features) and [ coronal consonant">CORONAL (a unary feature; also a place of articulation">place feature). Surface representations can be expressed as the result of rules acting on the features of the underlying representation. These rules are formulated in terms of transformations on features. In morphology and syntax In morphology (linguistics), morphology and syntax, words are often organized into lexical categories or word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Corpus
The Brown University Standard Corpus of Present-Day American English, better known as simply the Brown Corpus, is an electronic collection of text samples of American English, the first major structured Text_corpus, corpus of varied genres. This corpus first set the bar for the scientific study of the frequency and distribution of word categories in everyday language use. Compiled by Henry Kučera and W. Nelson Francis at Brown University, in Rhode Island, it is a general language corpus containing 500 samples of English with 2000+ words each, compiled from works published in the United States in 1961, covering a wide range of styles and varieties of prose. It contained 1,014,312 words. Its construction cost the United States Office of Education, U.S. Office of Education ~$23,000 in 1963-64. History Its original name was "A Standard Sample of Present-day Edited American English for use with digital computers", as described in a manual in 1964.Francis, W. N., and H. Kučera. Manua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, tense, grammatical case, case, grammatical voice, voice, grammatical aspect, aspect, grammatical person, person, grammatical number, number, grammatical gender, gender, grammatical mood, mood, animacy, and definiteness. The inflection of verbs is called ''grammatical conjugation, conjugation'', while the inflection of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc. can be called ''declension''. An inflection expresses grammatical categories with affixation (such as prefix, suffix, infix, circumfix, and transfix), apophony (as Indo-European ablaut), or other modifications. For example, the Latin verb ', meaning "I will lead", includes the suffix ', expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense-mood (future indicative or present subjunctive). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Aspect
In linguistics, aspect is a grammatical category that expresses how a verbal action, event, or state, extends over time. For instance, perfective aspect is used in referring to an event conceived as bounded and unitary, without reference to any flow of time during the event ("I helped him"). Imperfective aspect is used for situations conceived as existing continuously or habitually as time flows ("I was helping him"; "I used to help people"). Further distinctions can be made, for example, to distinguish states and ongoing actions ( continuous and progressive aspects) from repetitive actions ( habitual aspect). Certain aspectual distinctions express a relation between the time of the event and the time of reference. This is the case with the perfect aspect, which indicates that an event occurred prior to but has continuing relevance at the time of reference: "I have eaten"; "I had eaten"; "I will have eaten". Different languages make different grammatical aspectual disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Tense
In grammar, tense is a grammatical category, category that expresses time reference. Tenses are usually manifested by the use of specific forms of verbs, particularly in their grammatical conjugation, conjugation patterns. The main tenses found in many languages include the past tense, past, present tense, present, and future tense, future. Some languages have only two distinct tenses, such as past and nonpast, or future and Nonfuture tense, nonfuture. There are also tenseless languages, like most of the Varieties of Chinese, Chinese languages, though they can possess a future and Nonfuture tense, nonfuture system typical of Sino-Tibetan languages. In recent work Maria Bittner and Judith Tonhauser have described the different ways in which tenseless languages nonetheless mark time. On the other hand, some languages make finer tense distinctions, such as remote vs recent past, or near vs remote future. Tenses generally express time relative to the TUTT (linguistics), moment of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''. The values present in a given language, of which there are usually two or three, are called the ''genders'' of that language. Some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", whereas others use different definitions for each. Many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to Sex–gender distinction, sex or gender. According to one estimate, gender is used in approximately half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behavior of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a Nominal group (functional grammar), nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the Dative case, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interjection
An interjection is a word or expression that occurs as an utterance on its own and expresses a spontaneous feeling, situation or reaction. It is a diverse category, with many different types, such as exclamations ''(ouch!'', ''wow!''), curses (''damn!''), greetings (''hey'', ''bye''), response particles (''okay'', ''oh!'', ''m-hm'', '' huh?''), hesitation markers (''uh'', ''er'', ''um''), and other words (''stop'', ''cool''). Due to its diverse nature, the category of interjections partly overlaps with a few other categories like profanities, discourse markers, and fillers. The use and linguistic discussion of interjections can be traced historically through the Greek and Latin Modistae over many centuries. Historical classification Greek and Latin intellectuals as well as the Modistae have contributed to the different perspectives of interjections in language throughout history. The Greeks held that interjections fell into the grammatical category of adverbs. They thought inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Conjunction
In grammar, a conjunction (List of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a part of speech that connects Word, words, phrases, or Clause, clauses'','' which are called its conjuncts. That description is vague enough to overlap with those of other parts of speech because what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each language. In English language, English, a given word may have several Word sense, senses and in some contexts be a Preposition and postposition, preposition but a conjunction in others, depending on the syntax. For example, ''after'' is a preposition in "he left after the fight" but a conjunction in "he left after they fought". In general, a conjunction is an invariant (non-Inflection, inflecting) grammatical particle that stands between conjuncts. A conjunction may be placed at the beginning of a sentence, but some superstition about the practice persists. The definition may be extended to idiomatic phrases that behave as a unit and perform the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
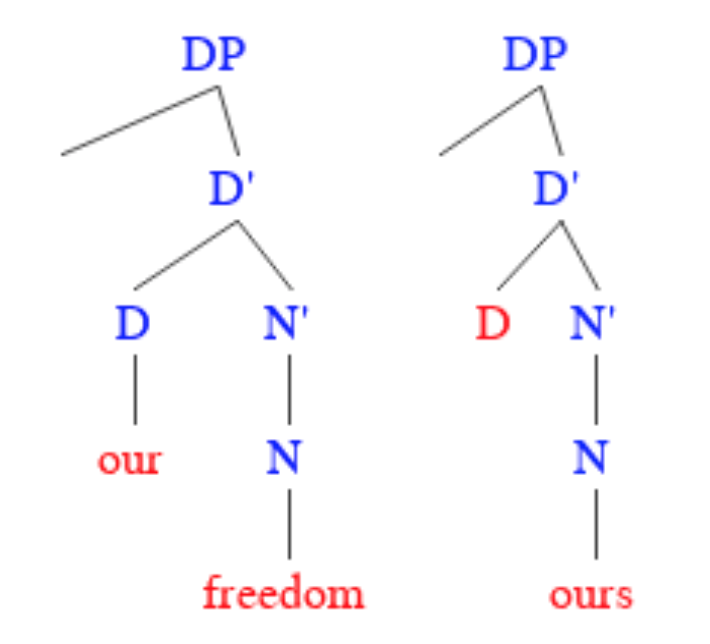
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |