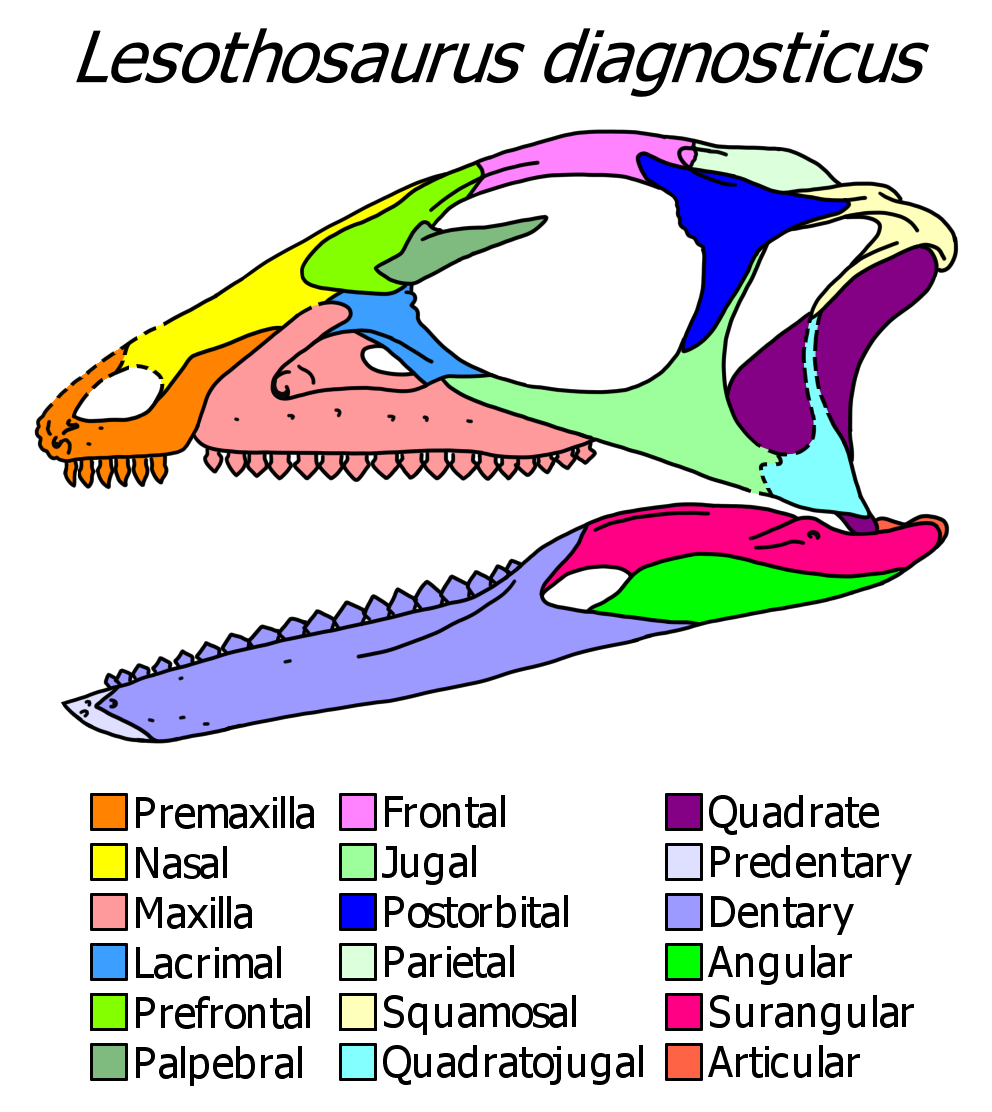
|
Pachycephalosaurs
Pachycephalosauria (; from Ancient Greek, Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, dating between about 85.8 and 66 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere, all of them being found in North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found. Candidates for the earliest-known pachycephalosaur include Ferganocephale, ''Ferganocephale adenticulatum'' from Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegoceras
''Stegoceras'' is a genus of Pachycephalosauria, pachycephalosaurid (dome-headed) dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 77.5 to 74 million years ago (mya). The first specimens from Alberta, Canada, were described in 1902, and the type species ''Stegoceras validum'' was based on these remains. The generic name means "horn roof", and the specific name means "strong". Several other species have been placed in the genus over the years, but these have since been moved to other genera or deemed junior synonyms. Currently only ''S. validum'' and ''S. novomexicanum'', named in 2011 from fossils found in New Mexico, remain. The validity of the latter species has also been debated, and it may not even belong to the genus ''Stegoceras.'' ''Stegoceras'' was a small, bipedal dinosaur about long, and weighed around . The skull was roughly triangular with a short snout, and had a thick, broad, and relatively smooth dome o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrotholus
''Acrotholus'' (Greek for "highest dome"- akros meaning highest and tholos meaning dome) is an extinct genus of pachycephalosaur dinosaur that lived during the Santonian of the late Cretaceous, in the Milk River Formation of Canada. The type species, ''A. audeti'', was named after Roy Audet allowing access to his ranch leading to the discovery of the species. The discovery of this specimen lead to several new revelations in the fossil records questioning the preservation of small-bodied organisms along with the evolution of early pachycephalosaurs. The iconic cranial dome found on ''Acrotholus'' makes it one of the earliest indisputable known members of the pachycephalosaur family. Like others of its clade, ''Acrotholus'' was a bipedal herbivore characterized by a dome-shaped head. The dome had often been associated with intra-species combat though exact method of contact have been debated. History of discovery The holotype was found in the Deadhorse Coulee Member of the Milk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycephalosaurus
''Pachycephalosaurus'' (; meaning "thick-headed lizard", from Greek ''pachys-/'' "thickness", ''kephalon/'' "head" and ''sauros/'' "lizard") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid ornithischian dinosaur. The type species, ''P. wyomingensis'', is the only known definitive species. The possibly synonymous taxon, ''Stygimoloch'', might represent a distinct genus or a second species, ''P. spinifer''. It lived during the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous period in what is now western North America. Remains have been excavated in Montana, South Dakota, Wyoming, and Alberta. Mainly known from a single skull and a few extremely thick skull roofs (at 22 cm or 9 in thick), ''Pachycephalosaurus'' is estimated to have reached long and weighed . More complete fossils would come to be found in the following years. ''Pachycephalosaurus'' was among the last species of non-avian dinosaurs on Earth before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The genus ''Tylosteus'' has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycephalosaurus Wyomingensis
''Pachycephalosaurus'' (; meaning "thick-headed lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek ''pachys-/'' "thickness", ''kephalon/'' "head" and ''sauros/'' "lizard") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid Ornithischia, ornithischian dinosaur. The type species, ''P. wyomingensis'', is the only known definitive species. The possibly synonymous taxon, ''Stygimoloch'', might represent a distinct genus or a second species, ''P. spinifer''. It lived during the Maastrichtian Geologic time scale, age of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period in what is now Laramidia, western North America. Remains have been excavated in Montana, South Dakota, Wyoming, and Alberta. Mainly known from a single skull and a few extremely thick skull roofs (at 22 cm or 9 in thick), ''Pachycephalosaurus'' is estimated to have reached long and weighed . More complete fossils would come to be found in the following years. ''Pachycephalosaurus'' was among the last species of non-avian dinosaurs on Earth before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphaerotholus
''Sphaerotholus'' is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of the western United States and Canada. To date, five species have been described: the type species, ''S. goodwini'', from the Den-na-zin Member of the Kirtland Formation and possibly the Fossil Forest Member of the Fruitland Formation (Late Campanian) of San Juan County, New Mexico, USA; ''S. buchholtzae'', from the Hell Creek Formation (Late Maastrichtian) of western Carter County, Montana, USA and the Frenchman Formation of Saskatchewan, Canada; ''S. edmontonensis'', from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada; ''S. lyonsi'', from the Dinosaur Park Formation (Campanian) of Alberta, Canada; and ''S. triregnum'' from the Hell Creek Formation of Garfield County, Montana, USA. History of discovery The etymology of ''Sphaerotholus'' is a combination of the Greek ''sphaira'', meaning "ball", and ''tholos'', meaning "dome", and is a reference to the characteristically dome-shaped pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinocephale
''Sinocephale'' (meaning "Chinese head") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur that lived in Inner Mongolia, China during the Cretaceous period. The only species, ''Sinocephale bexelli'', was originally named as a species of the genus ''Troodon'' in 1953, and later transferred to the genus ''Stegoceras''. After decades of being considered nomen dubium, dubious, it was re-evaluated in 2021 and recognized as a valid taxon, being given a unique generic name. The original holotype was lost, with modern research conducted using rediscovered plaster casts. Scant material makes for limited knowledge of its life appearance, but it is distinguished by an embayment on the back of the domed skull, which would give it a heart shape as seen from above. It is potentially the oldest known pachycephalosaurid and falls within the subset of the family called Pachycephalosaurinae, related to animals such as ''Pachycephalosaurus'' and ''Prenocephale''. The geologic context of the species has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texacephale
''Texacephale'' is a possibly dubious genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils come from the Aguja Formation of Big Bend National Park, in Texas, and were described in 2010 by Longrich, Sankey and Tanke. The generic name means Texas + "head" (''kephale'' in Greek) in reference to its place of discovery, and the specific name ''langstoni'' honors Wann Langston. It may be a synonym of ''Stegoceras.'' Discovery The holotype specimen of ''Texacephale'', LSUMNS 20010, is composed of fused frontals and parietals. A second specimen, LSUMNS 20012, is composed of an incomplete frontoparietal dome. It was found in the same WPA quarries that produced '' Agujaceratops'', and may have been excavated and tossed aside, being mistaken for a rock or concretion, before being picked up decades later. According to the team, the fossilized dome of the animal possessed five to six vertical flanges on each lateral side, connecting it with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goyocephale
''Goyocephale'' is an extinct genus of pachycephalosaurian ornithischian that lived in Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous about 76 million years ago. It was first described in 1982 by Altangerel Perle, Teresa Maryańska and Halszka Osmólska for a disarticulated skeleton with most of a skull, part of the forelimb and hindlimb, some of the pelvic girdle, and some vertebrae. Perle ''et al.'' named the remains ''Goyocephale lattimorei'', from the Mongolian language, Mongolian гоё (''goyo''), meaning "decorated", and the Ancient Greek κεφαλή (''kephale''), for head. The species name honours Owen Lattimore. Description ''Goyocephale'' is known from a partial skull, including both mandibles, the skull roof, part of the occiput, part of the braincase region, the anatomical terms of location#Anterior and posterior, posterior skull, the premaxilla, and the maxilla. The posterior edge of the skull roof, at the edge of the squamosal bones, has many small bony bumps, which would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithischian
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek stem ' (), meaning "bird", and ' (), meaning "hip". However, as theropod dinosaurs, birds are only distantly related to this group. Ornithischians with well known anatomical adaptations include the ceratopsians or "horn-faced" dinosaurs (e.g. ''Triceratops''), the pachycephalosaurs or "thick-headed" dinosaurs, the armored dinosaurs (Thyreophora) such as stegosaurs and ankylosaurs, and the ornithopods. There is strong evidence that certain groups of ornithischians lived in herds, often segregated by age group, with juveniles forming their own flocks separate from adults. Some were at least partially covered in filamentous (hair- or feather- like) pelts, and there is much debate over whether these filaments found in specimens of '' Tianyulong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |