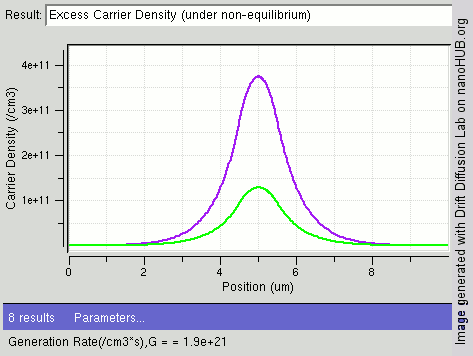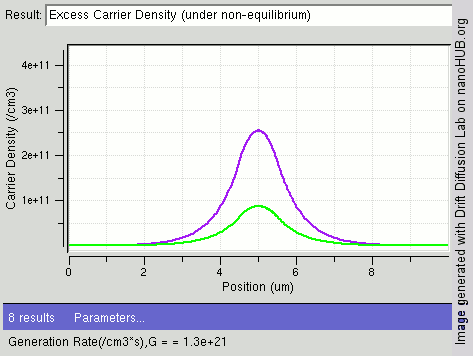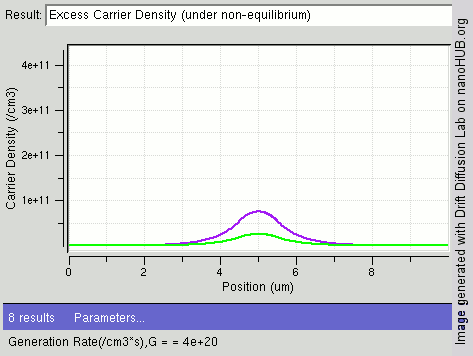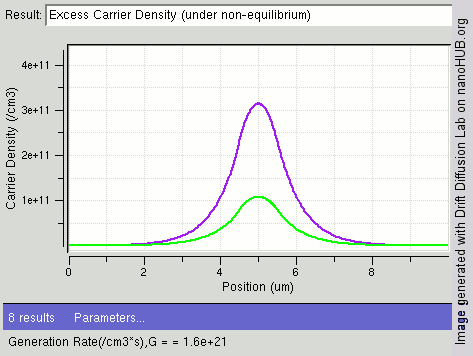
|
Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics (or optronics) is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that find, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, ''light'' often includes invisible forms of radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet and infrared, in addition to visible light. Optoelectronic devices are electrical-to-optical or optical-to-electrical transducers, or instruments that use such devices in their operation. '' Electro-optics'' is often erroneously used as a synonym, but is a wider branch of physics that concerns all interactions between light and electric fields, whether or not they form part of an electronic device. Optoelectronics is based on the quantum mechanical effects of light on electronic materials, especially semiconductors, sometimes in the presence of electric fields. * Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect, used in: ** photodiodes (including solar cells) ** phototransistors ** photomultipliers ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum, most photonic applications are in the range of visible and near-infrared light. The term photonics developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s. History The word 'Photonics' is derived from the Greek word "phos" meaning light (which has genitive case "photos" and in compound words the root "photo-" is used); it appeared in the late 1960s to describe a research field whose goal was to use light to perform functions that traditionally fell within the typical domain of electronics, such as telecommunications, information processing, etc. Photonics as a field began with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diode
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD, or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation, in the form of an emitted photon is generated. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from infra-red to the UV spectrum. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide range of uses that include fiber optic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optics
Electro–optics is a branch of electrical engineering, electronic engineering, materials science, and material physics involving components, electronic devices such as lasers, laser diodes, LEDs, waveguides, etc. which operate by the propagation and interaction of light with various tailored materials. It is closely related to the branch of optics, involving application of generation of photons, called photonics. It is not only concerned with the " electro–optic effect", since it deals with the interaction between the electromagnetic ( optical) and the electrical ( electronic) states of materials. Electro-optical devices The electro-optic effect is a change in the optical properties of an optically active material due to interaction with light. This interaction usually results in a change in the birefringence, and not simply the refractive index of the medium. In a Kerr cell, the change in birefringence is proportional to the square of the optical electric field, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optoisolator
An opto-isolator (also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or optical isolator) is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal.Lee et al., p. 2. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kVHasse, p. 145. and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/ μs.Joffe and Kai-Sang Lock, p. 279. A common type of opto-isolator consists of an LED and a phototransistor in the same opaque package. Other types of source-sensor combinations include LED- photodiode, LED- LASCR, and lamp-photoresistor pairs. Usually opto-isolators transfer digital (on-off) signals, but some techniques allow them to be used with analog signals. History The value of optically coupling a solid state light emitter to a semiconductor detector for the purpose of electrical isolation was recognized in 1963 by Akmenkalns, et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow. Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The central driving force behind the entire electronics industry is the semiconductor industry sector, which has annual sales of over $481 billion as of 2018. The largest industry sector is e-commerce, which generated over $29 trillion in 2017. History and development Electronics has hugely influenced the development of modern society. The identification of the electron in 1897, along with the subsequent invention of the vacuum tube which could amplify and rectify small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED or organic LED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current. This organic layer is situated between two electrodes; typically, at least one of these electrodes is transparent. OLEDs are used to create digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, and portable systems such as smartphones and handheld game consoles. A major area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications. There are two main families of OLED: those based on small molecules and those employing polymers. Adding mobile ions to an OLED creates a light-emitting electrochemical cell (LEC) which has a slightly different mode of operation. An OLED display can be driven with a passive-matrix (PMOLED) or active-matrix ( AM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Cascade Laser
Quantum-cascade lasers (QCLs) are semiconductor lasers that emit in the mid- to far-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and were first demonstrated by Jérôme Faist, Federico Capasso, Deborah Sivco, Carlo Sirtori, Albert Hutchinson, and Alfred Cho at Bell Laboratories in 1994. Unlike typical interband semiconductor lasers that emit electromagnetic radiation through the recombination of electron–hole pairs across the material band gap, QCLs are unipolar, and laser emission is achieved through the use of intersubband transitions in a repeated stack of semiconductor multiple quantum well heterostructures, an idea first proposed in the article "Possibility of amplification of electromagnetic waves in a semiconductor with a superlattice" by R. F. Kazarinov and R. A. Suris in 1971. Intersubband vs. interband transitions Within a bulk semiconductor crystal, electrons may occupy states in one of two continuous energy bands — the valence band, which is heavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulated Emission
Stimulated emission is the process by which an incoming photon of a specific frequency can interact with an excited atomic electron (or other excited molecular state), causing it to drop to a lower energy level. The liberated energy transfers to the electromagnetic field, creating a new photon with a frequency, polarization, and direction of travel that are all identical to the photons of the incident wave. This is in contrast to spontaneous emission, which occurs at a characteristic rate for each of the atoms/oscillators in the upper energy state regardless of the external electromagnetic field. According to the American Physical Society, the first person to correctly predict the phenomenon of stimulated emission was Albert Einstein in a series of papers starting in 1916, culminating in what is now called the Einstein B Coefficient. Einstein's work became the theoretical foundation of the MASER and LASER. The process is identical in form to atomic absorption in which the energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Imaging Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |