|
Optical Microcavity
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name ''micro''cavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers, this forms an optical cavity or ''optical resonator'', allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring. Applications and effects The fundamental difference between a conventional optical cavity and microcavities is the effects that arise from the small dimensions of the system, but their operational principle can often be understood in the same way as for larger optical resonators. Quantum effects of the light's electromagnetic field can be observed. For example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-wave Mixing
Four-wave mixing (FWM) is an intermodulation phenomenon in nonlinear optics, whereby interactions between two or three wavelengths produce two or one new wavelengths. It is similar to the third-order intercept point in electrical systems. Four-wave mixing can be compared to the intermodulation distortion in standard electrical systems. It is a parametric nonlinear process, in that the energy of the incoming photons is conserved. FWM is a phase-sensitive process, in that the efficiency of the process is strongly affected by phase matching conditions. Mechanism When three frequencies (f1, f2, and f3) interact in a nonlinear medium, they give rise to a fourth frequency (f4) which is formed by the scattering of the incident photons, producing the fourth photon. Given inputs ''f1, f2,'' and ''f3'', the nonlinear system will produce : \pm f_ \pm f_ \pm f_ From calculations with the three input signals, it is found that 12 interfering frequencies are produced, three of which lie on o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whispering-gallery Wave
Whispering-gallery waves, or whispering-gallery modes, are a type of wave that can travel around a concave surface. Originally discovered for sound waves in the whispering gallery of St Paul's Cathedral, they can exist for light and for other waves, with important applications in nondestructive testing, lasing, cooling and sensing, as well as in astronomy. Introduction Whispering-gallery waves were first explained for the case of St Paul's Cathedral circa 1878 by Lord Rayleigh, who revised a previous misconception that whispers could be heard across the dome but not at any intermediate position. He explained the phenomenon of travelling whispers with a series of specularly reflected sound rays making up chords of the circular gallery. Clinging to the walls the sound should decay in intensity only as the inverse of the distance — rather than the inverse square as in the case of a point source of sound radiating in all directions. This accounts for the whispers being audib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Bragg Reflector
A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as optical fibers. It is a structure formed from multiple layers of alternating materials with varying refractive index, or by periodic variation of some characteristic (such as height) of a dielectric waveguide, resulting in periodic variation in the effective refractive index in the guide. Each layer boundary causes a partial reflection of an optical wave. For waves whose vacuum wavelength is close to four times the optical thickness of the layers, the many reflections combine with constructive interference, and the layers act as a high-quality reflector. The range of wavelengths that are reflected is called the photonic stopband. Within this range of wavelengths, light is "forbidden" to propagate in the structure. Reflectivity The DBR's reflectivity, R, for intensity is approximately given by :R = \left frac\right2, where n_o,\ n_1,\ n_2 and n_s\, are the respective refractive indices of the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum. Spectrum has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad range of cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter '' lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computer
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers may be too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, larger realizations are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science. There are several models of quantum computation with the most widely used being quantum circuits. Other models include the quantum Turing machine, quantum annealing, and adiabatic quantum computation. Most models are based on the quantum bit, or " qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution which offers an information-theoretically secure solution to the key exchange problem. The advantage of quantum cryptography lies in the fact that it allows the completion of various cryptographic tasks that are proven or conjectured to be impossible using only classical (i.e. non-quantum) communication. For example, it is impossible to copy data encoded in a quantum state. If one attempts to read the encoded data, the quantum state will be changed due to wave function collapse ( no-cloning theorem). This could be used to detect eavesdropping in quantum key distribution (QKD). History In the early 1970s, Stephen Wiesner, then at Columbia University in New York, introduced the concept of quantum conjugate coding. His seminal paper titled "Conjugate Coding" was rejected by the IEEE Informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Dot
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size, having optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles as a result of quantum mechanics. They are a central topic in nanotechnology. When the quantum dots are illuminated by UV light, an electron in the quantum dot can be excited to a state of higher energy. In the case of a semiconducting quantum dot, this process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conductance band. The excited electron can drop back into the valence band releasing its energy as light. This light emission (photoluminescence) is illustrated in the figure on the right. The color of that light depends on the energy difference between the conductance band and the valence band, or the transition between discrete energy states when band structure is no longer a good definition in QDs. In the language of materials science, nanoscale semiconductor materials tightly confine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




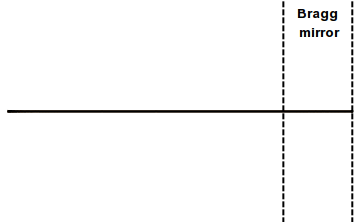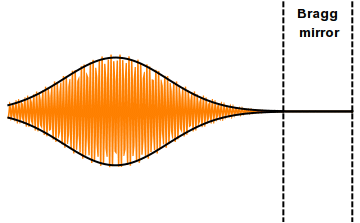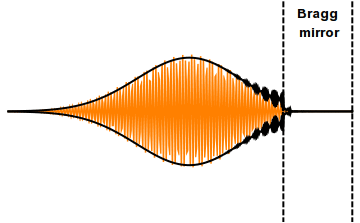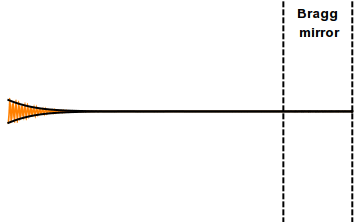

.jpg)
