|
Orthoester
In organic chemistry, an ortho ester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula . Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxylic acids and it is from these that the name 'ortho ester' is derived. An example is ethyl orthoacetate, , more correctly known as 1,1,1-triethoxyethane. Synthesis Ortho esters can be prepared by the Pinner reaction, in which nitriles react with alcohols in the presence of one equivalent of hydrogen chloride. The reaction proceeds by formation of imido ester hydrochloride: :RCN + OH + HCl → C(O)=NH2sup>+Cl− Upon standing in the presence of excess alcohol, this intermediate converts to the ortho ester: : C(O)=NH2sup>+Cl− + 2OH → RC(O)3 + NH4Cl The reaction requires anhydrous conditions, and ideally a nonpolar solvent. Acid chlorides can also drive the reaction from the corresponding amide, e.g.: :HCONH2 + BzCl → H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claisen Rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon chemical bond, bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl Vinyl group, vinyl ether will initiate a Sigmatropic reaction, [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation with Δ(Δf''H'') ca. . Mechanism The Claisen rearrangement is an exothermic, concerted (bond cleavage and recombination) pericyclic reaction. Woodward–Hoffmann rules show a suprafacial, stereospecific reaction pathway. The kinetics are of the first order and the whole transformation proceeds through a highly ordered cyclic transition state and is intramolecular. Crossover experiment (chemistry), Crossover experiments eliminate the possibility of the rearrangement occurring via an intermolecular reaction mechanism and are consistent with an intramolecular process. There are substantial solvent effects observed in the Claisen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinner Reaction
The Pinner reaction refers to the acid catalysed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to form an imino ester salt (alkyl imidate salt); this is sometimes referred to as a Pinner salt. The reaction is named after Adolf Pinner, who first described it in 1877. Pinner salts are themselves reactive and undergo additional nucleophilic additions to give various useful products: * With an excess of alcohol to form an orthoester * With ammonia or an amine to form an amidine (di-nitriles may form imidines, for instance succinimidine from succinonitrile) * With water to form an ester * With hydrogen sulfide to form a thionoester Commonly, the Pinner salt itself is not isolated, with the reaction being continued to give the desired functional group (orthoester etc.) in one go. The imidium chloride salt is thermodynamically unstable, and low temperatures help prevent elimination to an amide and alkyl chloride. It should be appreciated that the Pinner reaction refers specifically to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Orthoacetate
Triethyl orthoacetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(OC2H5)3. It is the ethyl orthoester of acetic acid. It is a colorless oily liquid. Triethyl orthoacetate is used in organic synthesis for acetylation : In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react .... It is also used in the Johnson-Claisen rearrangement. References {{reflist Orthoesters Reagents for organic chemistry Ethyl esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethyl Orthoacetate
Triethyl orthoacetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(OC2H5)3. It is the ethyl orthoester of acetic acid. It is a colorless oily liquid. Triethyl orthoacetate is used in organic synthesis for acetylation : In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react .... It is also used in the Johnson-Claisen rearrangement. References {{reflist Orthoesters Reagents for organic chemistry Ethyl esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethyl Orthoformate
Trimethyl orthoformate (TMOF) is the organic compound with the formula HC(OCH3)3. A colorless liquid, it is the simplest orthoester. It is a reagent used in organic synthesis for the formation of methyl ethers. The product of reaction of an aldehyde with trimethyl orthoformate is an acetal. In general cases, these acetals can be deprotected back to the aldehyde by using hydrochloric acid. Synthesis Trimethyl orthoformate is prepared on an industrial scale by the methanolysis of hydrogen cyanide:Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, Third edition, 2011, , page 10744 :HCN + 3 HOCH3 → HC(OCH3)3 + NH3 Trimethyl orthoformate can also be prepared from the reaction between chloroform and sodium methoxide, an example of the Williamson ether synthesis. Use Trimethyl orthoformate is a useful building block for creating methoxymethylene groups and heterocyclic ring systems. It introduces a formyl group to a nucleophilic substrate, e.g. RNH2 to form R-NH-CHO, which can und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
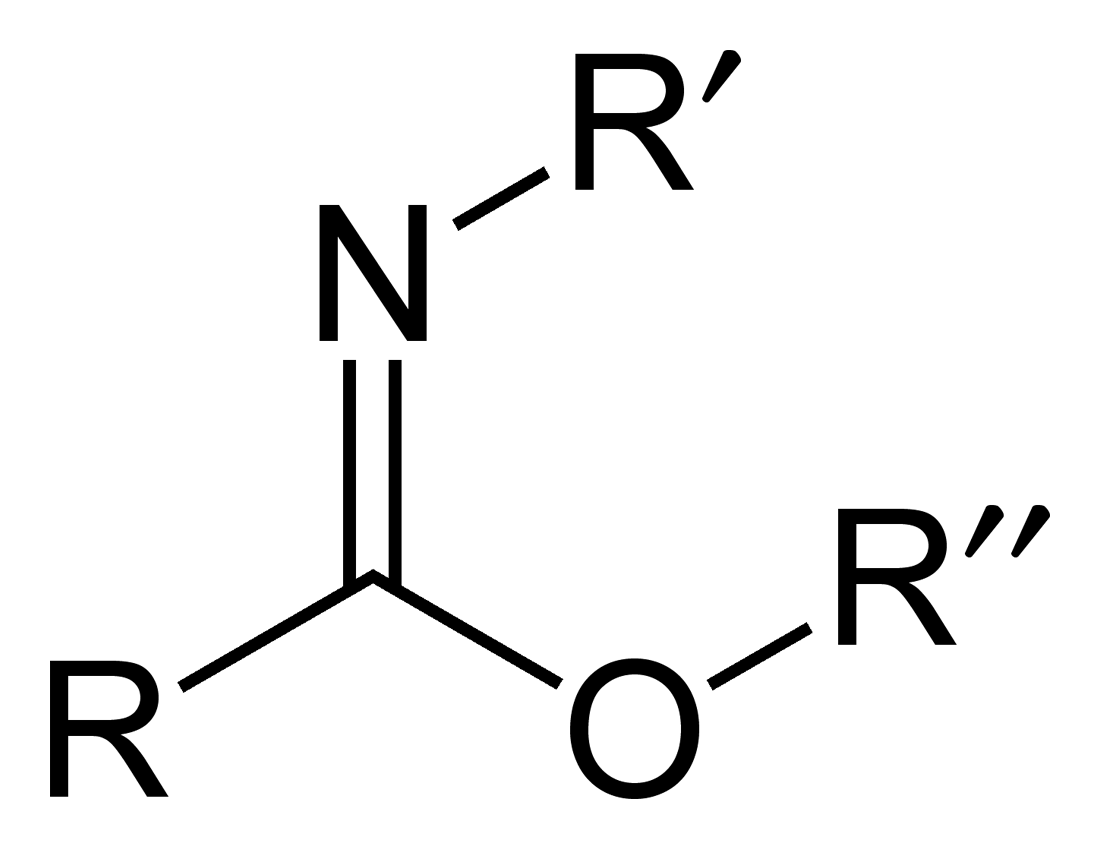
Carboximidate
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between an imidic acid () and an alcohol, with the general formula . They are also known as imino ethers, since they resemble imines () with an oxygen atom connected to the carbon atom of the C=N double bond. Synthesis Imidates may be generated by a number of synthetic routes, but are in general formed by the Pinner reaction. This proceeds via the acid catalyzed attack of nitriles by alcohols. Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement. Imidate/amidate anions An amidate/imidate anion is formed upon deprotonation of an amide or imidic acid. Since amides and imidic acids are tautomers, they form the same anion upon deprotonation. The two names are thus synonyms describing the same anion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol), but is more acutely toxic than the latter. Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced through destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl ''tert''-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formic Acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts, and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol. Natural occurrence Formic acid, which has a pungent, penetrating odor, is found naturally in insects, weeds, fruits and vegetables, and forest emissions. It appears in most ants and in stingless bees of the genus '' Oxytrigona''. Wood ants from the genus ''Formica'' can spray formic acid on their prey or to defend the nest. The puss moth caterpillar (''Cerura vinula'') will spray it as well when threatened by predators. It is also found in the trichomes of stinging nettle (''Urtica dioica''). Apart from that, this acid is incorporated in many fruits such as pineapple (0.21 mg per 100 g), apple (2 mg per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Carbon
In the nomenclature of organic chemistry, a locant is a term to indicate the position of a functional group or substituent within a molecule. Numeric locants The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends the use of numeric prefixes to indicate the position of substituents, generally by identifying the parent hydrocarbon chain and assigning the carbon atoms based on their substituents in order of precedence. For example, there are at least two isomers of the linear form of pentanone, a ketone that contains a chain of exactly five carbon atoms. There is an oxygen atom bonded to one of the middle three carbons (if it were bonded to an end carbon, the molecule would be an aldehyde, not a ketone), but it is not clear where it is located. In this example, the carbon atoms are numbered from one to five, which starts at one end and proceeds sequentially along the chain. Now the position of the oxygen atom can be defined as on carbon atom number two, three o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |