|
Orogen
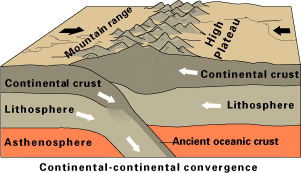
An orogenic belt, orogen, or mobile belt, is a zone of Earth's crust affected by orogeny. An orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological processes collectively called ''orogenesis''. Overview Orogeny typically produces ''orogenic belts'', which are elongated regions of deformation bordering continental cratons. Young orogenic belts, in which subduction is still taking place, are characterized by frequent volcanic activity and earthquakes. Older orogenic belts are typically deeply eroded to expose displaced and deformed strata. These are often highly metamorphosed and include vast bodies of intrusive igneous rock called batholiths. File:Active Margin.svg, Subduction of an oceanic plate beneath a continental plate to form an accretionary orogen. (example: the Andes) File:Continental-continental convergence Fig21contcont.gif, Continental collision of two continental pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny () is a mountain-mountain formation, building process that takes place at a convergent boundary, convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is tectonic uplift, uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation (physics), deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere (crust (geology), crust and uppermost mantle (geology), mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist Grove Karl Gilbert, G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Uplift
Tectonic uplift is the orogeny, geologic uplift of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While Isostasy, isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of Thrust tectonics, crustal thickening (such as Mountain formation, mountain building events), changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying Mantle (geology), mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere. Tectonic uplift results in denudation (processes that wear away the earth's surface) by raising buried rocks closer to the surface. This process can redistribute large loads from an elevated region to a topographically lower area as well – thus promoting an isostatic response in the region of denudation (which can cause local bedrock uplift). The timing, magnitude, and rate of denudation can be estimated by geologists using pressure-temperature studies. Crustal thickening C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Collision
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at Convergent boundary, convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is only known to occur on Earth. Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the Geologic fault, faulting and Fold (geology), folding caused by collisions stops. Geology of the Himalaya, The collision between Indian plate, India and Eurasian plate, Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogeny, East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). The collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, transports it to another location where it is deposit (geology), deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by Solvation, dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and Wind wave, waves; glacier, glacial Plucking (glaciation), plucking, Abrasion (geology), abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; Aeolian processes, wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and Mass wastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpide Belt
The Alpide belt or Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt,K.M. Storetvedt, K. M., ''The Tethys Sea and the Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt; mega-elements in a new global tectonic system,'' Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, Volume 62, Issues 1–2, 1990, Pages 141–18Abstract/ref> or more recently and rarely the Tethyan orogenic belt, is a seismic and orogenic belt that includes an array of mountain ranges extending for more than along the southern margin of Eurasia, stretching from Java and Sumatra, through the Indochinese Peninsula, the Himalayas and Transhimalayas, the mountains of Iran, Caucasus, Anatolia, the Mediterranean, and out into the Atlantic. It includes, from west to east, the major ranges of the Atlas Mountains, the Alps, the Caucasus Mountains, Alborz, Hindu Kush, Karakoram, and the Himalayas. It is the second most seismically active region in the world, after the circum-Pacific belt (the Ring of Fire), with 17% of the world's largest earthquakes. The bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long archipelago, chains of active volcanoes with intense earthquake, seismic activity found along convergent boundary, convergent plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the Earth's mantle, mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a oceanic trench, deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of highest mountains on Earth, 100 peaks exceeding elevations of above sea level lie in the Himalayas. The Himalayas abut on or cross territories of Himalayan states, six countries: Nepal, China, Pakistan, Bhutan, India and Afghanistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus River, Indus, the Ganges river, Ganges, and the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Tsangpo–Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |