|
Optical Resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged. An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. Each of these contributes (given suitable design, and adequate alignment) to the optical resolution of the system; the environment in which the imaging is done often is a further important factor. Lateral resolution Resolution depends on the distance between two distinguishable radiating points. The sections below describe the theoretical estimates of resolution, but the real values may differ. The results below are based on mathematical models of Airy discs, which assumes an adequate level of contrast. In low-contrast systems, the resolution may be much lower than predicted by the theory outlined below. Real optical systems are complex, and practical difficulties often increase the distance between distinguishable point sources. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image). Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images. Imaging science is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the generation, collection, duplication, analysis, modification, and visualization of images,Joseph P. Hornak, ''Encyclopedia of Imaging Science and Technology'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2002) including imaging things that the human eye cannot detect. As an evolving field it includes research and researchers from physics, mathematics, electrical engineering, computer vision, computer science, and perceptual psychology. ''Imager, Imagers'' are imaging sensors. Imaging chain The foundation of imaging science as a discipline is the "imaging chain" – a conceptual model describing all of the factors which must be considered when developing a system for creating visual renderings (image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
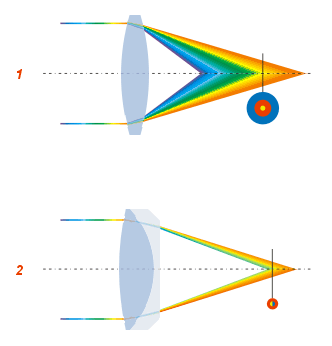
Aberration In Optical Systems
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as Lens (optics), lenses and mirrors, that causes the ''image'' created by the optical system to not be a faithful reproduction of the ''object'' being observed. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred, distorted in shape or have color fringing or other effects not seen in the object, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Form
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficients ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbolometer
A microbolometer is a specific type of bolometer used as a detector in a thermal camera. Infrared radiation with wavelengths between 7.5–14 μm strikes the detector material, heating it, and thus changing its electrical resistance. This resistance change is measured and processed into temperatures which can be used to create an image. Unlike other types of infrared detecting equipment, microbolometers do not require cooling. Theory of construction A microbolometer is an uncooled thermal sensor. High resolution thermal sensors require exotic and expensive cooling methods including stirling cycle coolers and liquid nitrogen coolers. These methods of cooling high resolution thermal imagers are expensive to operate and unwieldy to move. Also, high resolution thermal imagers require a cool down time in excess of 10 minutes before being usable. A microbolometer consists of an array of pixels, each pixel being made up of several layers. The cross-sectional diagram shown in Figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroelectricity
Pyroelectricity (from Greek: ''pyr'' (πυρ), "fire" and electricity) is a property of certain crystals which are naturally electrically polarized and as a result contain large electric fields. Pyroelectricity can be described as the ability of certain materials to generate a temporary voltage when they are heated or cooled. The change in temperature modifies the positions of the atoms slightly within the crystal structure, so that the polarization of the material changes. This polarization change gives rise to a voltage across the crystal. If the temperature stays constant at its new value, the pyroelectric voltage gradually disappears due to leakage current. The leakage can be due to electrons moving through the crystal, ions moving through the air, or current leaking through a voltmeter attached across the crystal. Explanation Pyroelectric charge in minerals develops on the opposite faces of asymmetric crystals. The direction in which the propagation of the charge tends is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumbicon
Video camera tubes are devices based on the cathode-ray tube that were used in television cameras to capture television images, prior to the introduction of charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors in the 1980s. Several different types of tubes were in use from the early 1930s, and as late as the 1990s. In these tubes, an cathode ray, electron beam is scanned across an image of the scene to be broadcast focused on a target. This generated a current that is dependent on the brightness of the image on the target at the scan point. The size of the striking ray is tiny compared to the size of the target, allowing 480–486 horizontal scan lines per image in the NTSC format, 576 lines in PAL, and as many as 1035 lines in Multiple sub-Nyquist sampling encoding, Hi-Vision. Cathode-ray tube Any vacuum tube which operates using a focused beam of electrons, originally called cathode rays, is known as a cathode-ray tube (CRT). These are usually seen as display devices as used in older (i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InSb
Indium antimonide (InSb) is a crystalline compound made from the elements indium (In) and antimony (Sb). It is a narrow- gap semiconductor material from the III- V group used in infrared detectors, including thermal imaging cameras, FLIR systems, infrared homing missile guidance Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its P ... systems, and in infrared astronomy. Indium antimonide detectors are sensitive to infrared wavelengths between 1 and 5 μm. Indium antimonide was a very common detector in the old, single-detector mechanically scanned thermal imaging systems. Another application is as a terahertz radiation source as it is a strong photo–Dember effect, photo-Dember emitter. History The intermetallic compound was first reported by Liu and Peretti in 1951, who gav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum Silicide
Platinum silicide, also known as platinum monosilicide, is the inorganic compound with the formula PtSi. It is a semiconductor that turns into a superconductor when cooled to 0.8 K. Structure and bonding The crystal structure of PtSi is orthorhombic, with each silicon atom having six neighboring platinum atoms. The distances between the silicon and the platinum neighbors are as follows: one at a distance of 2.41 angstroms, two at a distance of 2.43 angstroms, one at a distance of 2.52 angstroms, and the final two at a distance of 2.64 angstroms. Each platinum atom has six silicon neighbors at the same distances, as well as two platinum neighbors, at a distance of 2.87 and 2.90 angstroms. All of the distances over 2.50 angstroms are considered too far to really be involved in bonding interactions of the compound. As a result, it has been shown that two sets of covalent bonds compose the bonds forming the compound. One set is the three center Pt–Si–Pt bond, and the other set th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS Sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and lensless imaging for, e.g., blood cells. CMOS sensors emerged as an alternative to charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors and eventually outsold them by the mid-2000s. The term ''active pixel sensor'' is also used to refer to the individual pixel sensor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by Doping (semiconductor), p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |