|
Neutron Absorption
Neutron capture is a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus and one or more neutrons collide and merge to form a heavier nucleus. Since neutrons have no electric charge, they can enter a nucleus more easily than positively charged protons, which are repelled electrostatically. Neutron capture plays a significant role in the cosmic nucleosynthesis of heavy elements. In stars it can proceed in two ways: as a rapid process (r-process) or a slow process (s-process). Nuclei of masses greater than 56 cannot be formed by thermonuclear reactions (i.e., by nuclear fusion) but can be formed by neutron capture. Neutron capture on protons yields a line at 2.223 MeV predicted and commonly observed in solar flares. Neutron capture at small neutron flux At small neutron flux, as in a nuclear reactor, a single neutron is captured by a nucleus. For example, when natural gold (197Au) is irradiated by neutrons (n), the isotope 198Au is formed in a highly excited state, and quickly deca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chart Of Nuclides - Thermal Neutron Capture Cross Sections
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of quality structure and provides different info. The term "chart" as a graphical representation of data has multiple meanings: * A data chart is a type of diagram or graph, that organizes and represents a set of numerical or qualitative data. * Maps that are adorned with extra information (map surround) for a specific purpose are often known as charts, such as a nautical chart or aeronautical chart, typically spread over several map sheets. * Other domain-specific constructs are sometimes called charts, such as the chord chart in music notation or a record chart for album popularity. Charts are often used to ease understanding of large quantities of data and the relationships between parts of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is then adapted to the Maxwell distribution known for thermal motion. Qualitatively, the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the free neutrons. The momentum and wavelength of the neutron are related through the de Broglie relation. The large wavelength of slow neutrons allows for the large cross section. Neutron energy distribution ranges But different ranges with different names are observed in other sources. The following is a detailed classification: Thermal A thermal neutron is a free neutron with a kinetic energy of about 0.025 eV (about 4.0×10−21 J or 2.4 MJ/kg, hence a speed of 2.19 km/s), which is the energy corresponding to the most prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Energy
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is then adapted to the Maxwell distribution known for thermal motion. Qualitatively, the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the free neutrons. The momentum and wavelength of the neutron are related through the de Broglie relation. The large wavelength of slow neutrons allows for the large cross section. Neutron energy distribution ranges But different ranges with different names are observed in other sources. The following is a detailed classification: Thermal A thermal neutron is a free neutron with a kinetic energy of about 0.025 eV (about 4.0×10−21 J or 2.4 MJ/kg, hence a speed of 2.19 km/s), which is the energy corresponding to the most pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barn (unit)
A barn (symbol: b) is a metric unit of area equal to (100 fm2). Originally used in nuclear physics for expressing the cross sectional area of nuclei and nuclear reactions, today it is also used in all fields of high-energy physics to express the cross sections of any scattering process, and is best understood as a measure of the probability of interaction between small particles. A barn is approximately the cross-sectional area of a uranium nucleus. The barn is also the unit of area used in nuclear quadrupole resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance to quantify the interaction of a nucleus with an electric field gradient. While the barn never was an SI unit, the SI standards body acknowledged it in the 8th SI Brochure (superseded in 2019) due to its use in particle physics. Etymology During Manhattan Project research on the atomic bomb during World War II, American physicists at Purdue University needed a secretive name for a unit with which to quantify the cross-secti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring elements occur in the Earth as compounds or mixtures. Air is primarily a mixture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
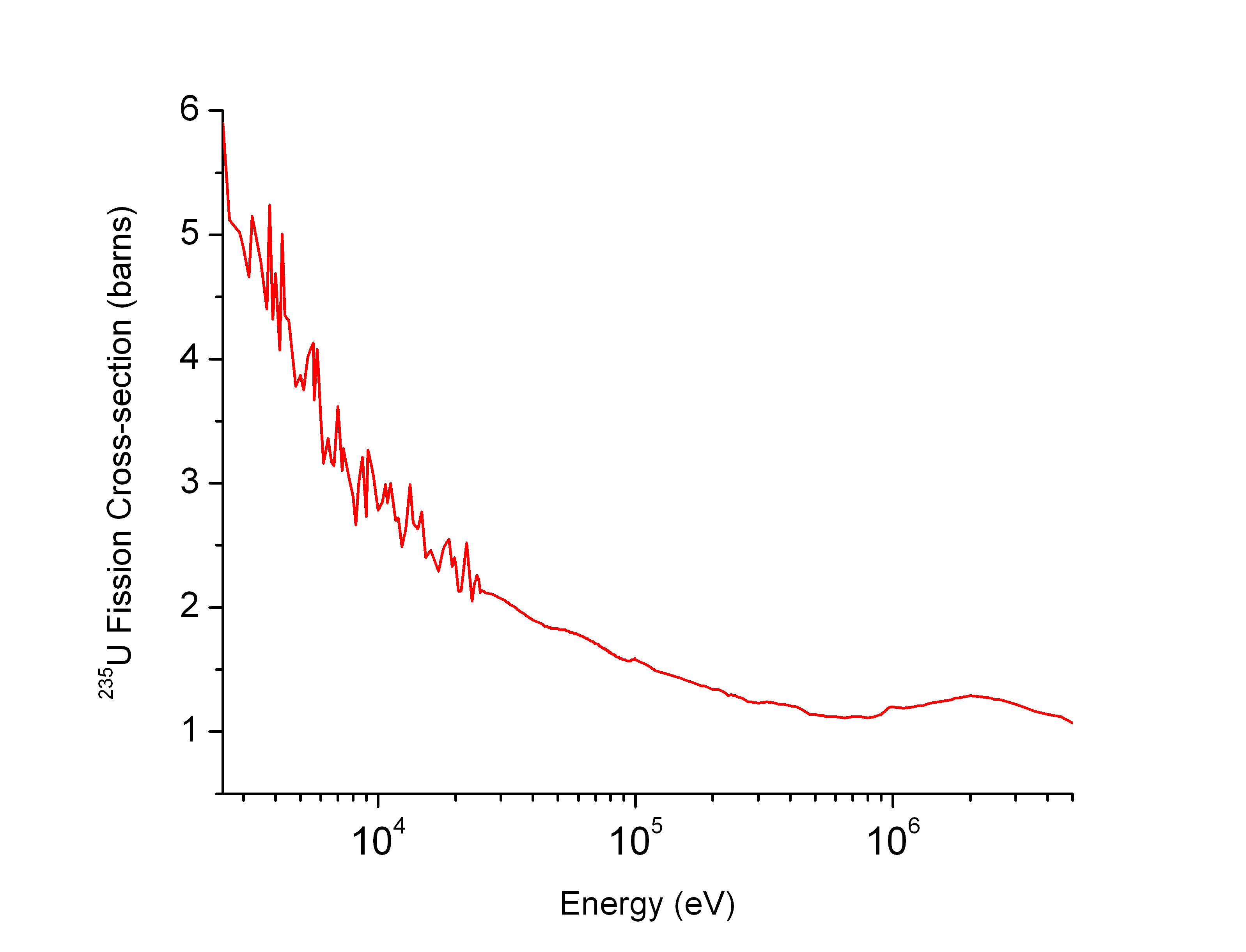
Neutron Cross Section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-stable
Beta-decay stable isobars are the set of nuclides which cannot undergo beta decay, that is, the transformation of a neutron to a proton or a proton to a neutron within the nucleus. A subset of these nuclides are also stable with regards to double beta decay or theoretically higher simultaneous beta decay, as they have the lowest energy of all nuclides with the same mass number. This set of nuclides is also known as the line of beta stability, a term already in common use in 1965. This line lies along the bottom of the nuclear valley of stability. Introduction The line of beta stability can be defined mathematically by finding the nuclide with the greatest binding energy for a given mass number, by a model such as the classical semi-empirical mass formula developed by C. F. Weizsäcker. These nuclides are local maxima in terms of binding energy for a given mass number. All odd mass numbers have only one beta decay stable nuclide. Among even mass number, six (124, 130, 136, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in unified atomic mass units (making a quantity called the "relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% of the whole number ''A''. Atoms with the same atomic number but dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called ''positron emission''. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Neutrons
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is then adapted to the Maxwell distribution known for thermal motion. Qualitatively, the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the free neutrons. The momentum and wavelength of the neutron are related through the de Broglie relation. The large wavelength of slow neutrons allows for the large cross section. Neutron energy distribution ranges But different ranges with different names are observed in other sources. The following is a detailed classification: Thermal A thermal neutron is a free neutron with a kinetic energy of about 0.025 eV (about 4.0×10−21 J or 2.4 MJ/kg, hence a speed of 2.19 km/s), which is the energy corresponding to the most pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word ''Atomgewicht'' tomic weight, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approximately equal to the ''atomic'' (also known as ''isotopic'') mass of the atom expressed in atomic mass units. Since protons and neutrons are both baryons, the mass number ''A'' is identical with the baryon number ''B'' of the nucleus (and also of the whole atom or ion). The mass number is different for each isotope of a given chemical element, and the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ''Z'' gives the number of neutrons (''N'') in the nucleus: . The mass number is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, the most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12, or , which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The full isotope symbol would also have the atomic number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_black_and_white.png)