|
Naringenin
Naringenin is a flavorless, colorless flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, and is found in a variety of fruits and herbs. Structure Naringenin has the skeleton structure of a flavanone with three hydroxy groups at the 4', 5, and 7 carbons. It may be found both in the aglycol form, naringenin, or in its glycosidic form, naringin, which has the addition of the disaccharide neohesperidose attached via a glycosidic linkage at carbon 7. Like the majority of flavanones, naringenin has a single chiral center at carbon 2, although the optical purity is variable. Racemization of S(-)-naringenin has been shown to occur fairly quickly. Sources and bioavailability Naringenin and its glycoside has been found in a variety of herbs and fruits, including grapefruit, bergamot, sour orange, tart cherries, tomatoes, cocoa, Greek oregano, water mint, as well as in beans. Ratios of naringenin to naringin vary among sources, as do enantiomeric rati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringin
Naringin is a flavanone-7-''O''-glycoside between the flavanone naringenin and the disaccharide neohesperidose. The flavonoid naringin occurs naturally in citrus fruits, especially in grapefruit, where naringin is responsible for the fruit's bitter taste. In commercial grapefruit juice production, the enzyme naringinase can be used to remove the bitterness created by naringin. In humans naringin is metabolized to the aglycone naringenin (not bitter) by naringinase present in the gut. Structure Naringin belongs to the flavonoid family. Flavonoids consist of 15 carbon atoms in 3 rings, 2 of which must be benzene rings connected by a 3 carbon chain. Naringin contains the basic flavonoid structure along with one rhamnose and one glucose unit attached to its aglycone portion, called naringenin, at the 7-carbon position. The steric hindrance provided by the two sugar units makes naringin less potent than its aglycone counterpart, naringenin. Metabolism In humans, naringinase is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
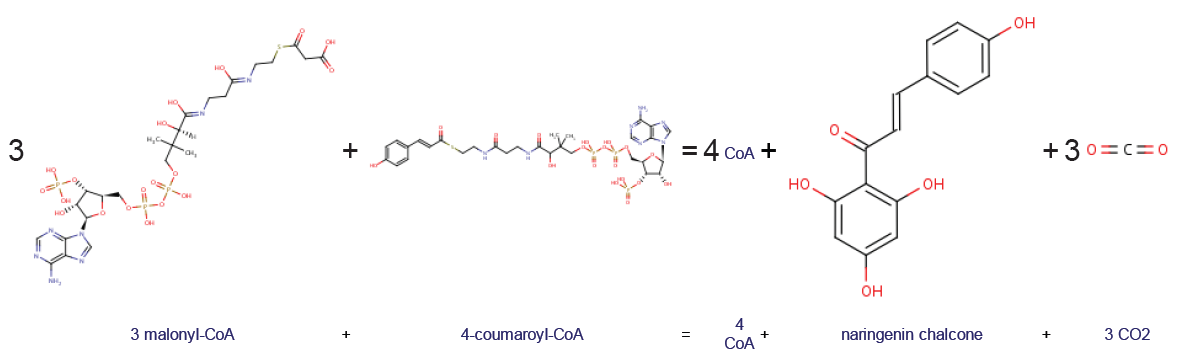
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavanone
The flavanones, a type of flavonoids, are various aromatic, colorless ketones derived from flavone that often occur in plants as glycosides. List of flavanones * Blumeatin * Butin * Eriodictyol * Hesperetin * Hesperidin * Homoeriodictyol * Isosakuranetin * Naringenin * Naringin * Pinocembrin * Poncirin * Sakuranetin * Sakuranin * Sterubin * Pinostrobin Metabolism The enzyme chalcone isomerase uses a chalcone-like compound to produce a flavanone. Flavanone 4-reductase is an enzyme that uses (2''S'')-flavan-4-ol The flavan-4-ols (3-deoxyflavonoids) are flavone-derived alcohols and a family of flavonoids. Flavan-4-ols are colorless precursor compounds that polymerize to form red phlobaphene pigments. They can be found in the sorghum. Glycosides (abacopteri ... and NADP+ to produce (2''S'')-flavanone, NADPH, and H+. Synthesis Numerous methods exist for the enantioselective chemical and biochemical synthesis of flavanones and related compounds. References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaempferol
Kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a natural flavonol, a type of flavonoid, found in a variety of plants and plant-derived foods including kale, beans, tea, spinach, and broccoli. Kaempferol is a yellow crystalline solid with a melting point of . It is slightly soluble in water and highly soluble in hot ethanol, ethers, and DMSO. Kaempferol is named for 17th-century German naturalist Engelbert Kaempfer.Kaempferol at Merriam-Webster.com; retrieved October 20, 2017 Natural occurrence Kaempferol is a secondary metabolite found in many plants, plant-derived foods, and traditional medicines. Its flavor is considered bitter.In plants and food Kaempferol is common in |
Coumaroyl-CoA
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids. Biosynthesis and significance It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase: :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A * Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase * Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase * Chalcone synthase * 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase * 6'-Deoxychalcone synthase * Agmatine N4-coum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase
In enzymology, a naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :dimethylallyl diphosphate + (-)-(2S)-naringenin \rightleftharpoons diphosphate + sophoraflavanone B Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are dimethylallyl diphosphate and (-)-(2S)-naringenin, whereas its two products are diphosphate and sophoraflavanone B. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring aryl or alkyl groups other than methyl groups. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is dimethylallyl-diphosphate:naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme is also called N8DT. References * * EC 2.5.1 Enzymes of unknown structure {{2.5-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink. Grapefruit is a citrus hybrid originating in Barbados. It is an accidental cross between the sweet orange (''C. sinensis'') and the pomelo or shaddock (''C. maxima''), both of which were introduced from Asia in the 17th century. It has also been called the ''forbidden fruit''. In the past it was referred to as the ''pomelo'', but that term is now mostly used as the common name for ''Citrus maxima''. In 2019, world production of grapefruits (combined with pomelos) was 9.3 million tonnes, of which 53% was in China. Other significant producers include Vietnam, United States and Mexico. Description The evergreen grapefruit trees usually grow to around tall, although they may reach . The leaves are long (up to ), thin, glossy, and dark green. They produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenyl chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins ( flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin. It is encoded by the codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement for its analgesic and antidepressant effects. It is a direct precursor to the neuromodulator phenethylamine, a commonly used dietary supplement. As an essential amino acid, phenylalanine is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvia Fruticosa
''Salvia fruticosa'', or Greek sage, is a perennial herb or sub-shrub native to the eastern Mediterranean, including Southern Italy, the Canary Islands and North Africa. It is especially abundant in Israel and Lebanon. Description Greek sage grows high and wide, with the flower stalks rising or more above the foliage. The entire plant is covered with hairs, with numerous leaves of various sizes growing in clusters, giving it a silvery and bushy appearance. The flowers are pinkish-lavender, about long, growing in whorls along the inflorescence, and held in a small oxblood-red five-pointed hairy calyx. In its native environment it grows as part of the Maquis shrubland and several other open plant communities, but populations composed entirely of ''Salvia fruticosa'' are not uncommon. It is also grown as an ornamental flowering shrub, preferring full sun, well-draining soil, and good air circulation. Hardy to 20 degrees F., it is very drought resistant. The leaves have a hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonyl CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Functions It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commits them to fatty acid chain synthesis. Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate,Nelson D, Cox M (2008) ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry''. 5th Ed: p. 806 requiring energy rendered from ATP. Malonyl-CoA is utilised in fatty acid biosynthesis by the enzyme malonyl coenzyme A:acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT). MCAT serves to transfer malonate from malonyl-CoA to the terminal thiol of ''holo''-acyl carrier protein (ACP). Polyketide biosynthesis MCAT is also involved in bacterial polyketide biosynthesis. The enzyme MCAT together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP), and a polyketide synthase (PKS) and chain-length f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |