|
Nanocomposite Hydrogels
Nanocomposite hydrogels (NC gels) are nanomaterial-filled, hydrated, polymeric networks that exhibit higher elasticity and strength relative to traditionally made hydrogels. A range of natural and synthetic polymers are used to design nanocomposite network. By controlling the interactions between nanoparticles and polymer chains, a range of physical, chemical, and biological properties can be engineered. The combination of organic (polymer) and inorganic (clay) structure gives these hydrogels improved physical, chemical, electrical, biological, and swelling/de-swelling properties that cannot be achieved by either material alone. Inspired by flexible biological tissues, researchers incorporate carbon-based, polymeric, ceramic and/or metallic nanomaterials to give these hydrogels superior characteristics like optical properties and stimulus-sensitivity which can potentially be very helpful to medical (especially drug delivery and stem cell engineering) and mechanical fields. Nanocompos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanogel
A nanogel is a polymer-based, crosslinked hydrogel particle on the sub-micron scale. These complex networks of polymers present a unique opportunity in the field of drug delivery at the intersection of nanoparticles and hydrogel synthesis. Nanogels can be natural, synthetic, or a combination of the two and have a high degree of tunability in terms of their size, shape, surface functionalization, and degradation mechanisms. Given these inherent characteristics in addition to their biocompatibility and capacity to encapsulate small drugs and molecules, nanogels are a promising strategy to treat disease and dysfunction by serving as delivery vehicles capable of navigating across challenging physiological barriers within the body. Nanogels are not to be confused with ''Nanogel aerogel'', a lightweight thermal insulator, or with ''nanocomposite hydrogels (NC gels)'', which are nanomaterial-filled, hydrated, polymeric networks that exhibit higher elasticity and strength relative to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanocomposite
Nanocomposite is a multiphase solid material where one of the phases has one, two or three dimensions of less than 100 nanometers (nm) or structures having nano-scale repeat distances between the different phases that make up the material. The idea behind Nanocomposite is to use building blocks with dimensions in nanometre range to design and create new materials with unprecedented flexibility and improvement in their physical properties. In the broadest sense this definition can include porous media, colloids, gels and copolymers, but is more usually taken to mean the solid combination of a bulk matrix and nano-dimensional phase(s) differing in properties due to dissimilarities in structure and chemistry. The mechanical, electrical, thermal, optical, electrochemical, catalytic properties of the nanocomposite will differ markedly from that of the component materials. Size limits for these effects have been proposed: in Kelly, A, ''Concise encyclopedia of composites materials'', El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay Minerals
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces. Clay minerals form in the presence of water and have been important to life, and many theories of abiogenesis involve them. They are important constituents of soils, and have been useful to humans since ancient times in agriculture and manufacturing. Properties Clay is a very fine-grained geologic material that develops plasticity when wet, but becomes hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. It is a very common material, and is the oldest known ceramic. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. The chemistry of clay, including its capacity to retain nutrient cations such as potassium and ammonium, is important to soil fertility. Because the individual particles in clay are less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Testing
Tensile testing, also known as tension testing, is a fundamental materials science and engineering test in which a sample is subjected to a controlled tension until failure. Properties that are directly measured via a tensile test are ultimate tensile strength, breaking strength, maximum elongation and reduction in area. From these measurements the following properties can also be determined: Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, yield strength, and strain-hardening characteristics. ''Uniaxial tensile testing'' is the most commonly used for obtaining the mechanical characteristics of isotropic materials. Some materials use biaxial tensile testing. The main difference between these testing machines being how load is applied on the materials. Purposes of tensile testing Tensile testing might have a variety of purposes, such as: *Select a material or item for an application *Predict how a material will perform in use: normal and extreme forces. * Determine if, or verify that, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems it is often associated with irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect. Hysteresis can be found in physics, chemistry, engineering, biology, and economics. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
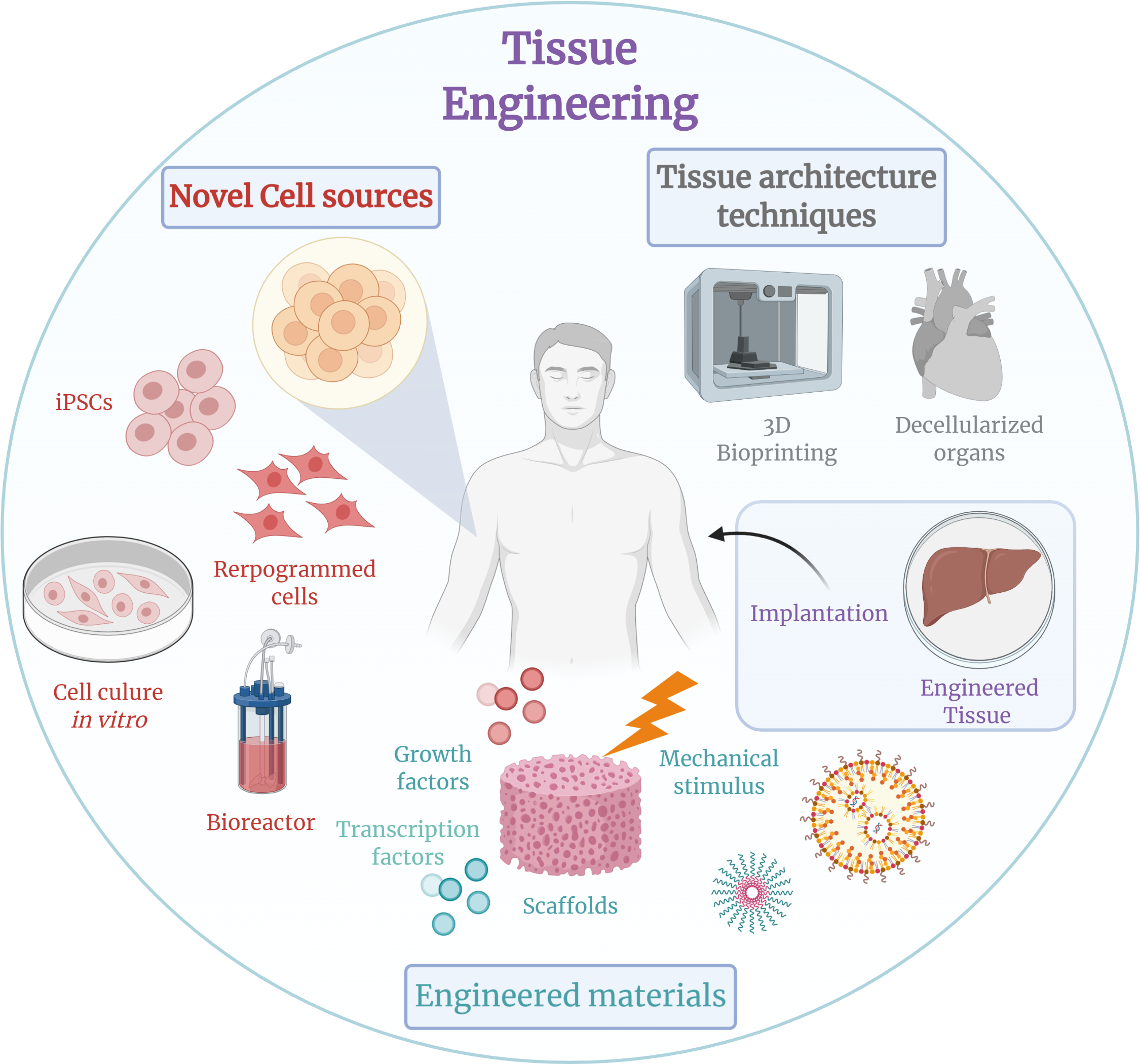
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biology, biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, Autologous chondrocyte implantation, cartilage, blood vessels, Urinary bladder, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Delivery
Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury. Drug deliv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Nanoparticle
Silver nanoparticles are nanoparticles of silver of between 1 nm and 100 nm in size. While frequently described as being 'silver' some are composed of a large percentage of silver oxide due to their large ratio of surface to bulk silver atoms. Numerous shapes of nanoparticles can be constructed depending on the application at hand. Commonly used silver nanoparticles are spherical, but diamond, octagonal, and thin sheets are also common. Their extremely large surface area permits the coordination of a vast number of ligands. The properties of silver nanoparticles applicable to human treatments are under investigation in laboratory and animal studies, assessing potential efficacy, biosafety, and biodistribution. Synthesis methods Wet chemistry The most common methods for nanoparticle synthesis fall under the category of wet chemistry, or the nucleation of particles within a solution. This nucleation occurs when a silver ion complex, usually AgNO3 or AgClO4, is reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)