|
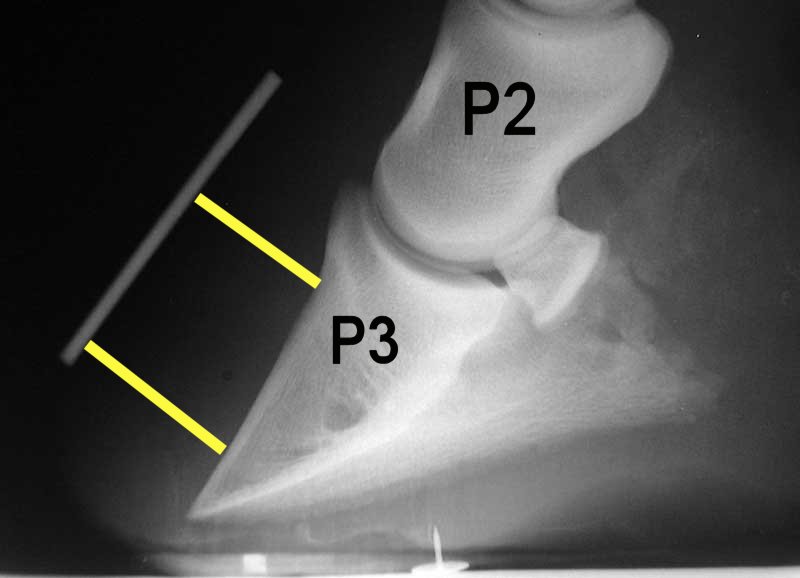
Navicular Disease
Navicular syndrome, often called navicular disease, is a syndrome of lameness problems in horses. It most commonly describes an inflammation or degeneration of the navicular bone and its surrounding tissues, usually on the front feet. It can lead to significant and even disabling lameness. Description of the navicular area Knowledge of equine forelimb anatomy is especially useful for understanding navicular syndrome. The navicular bone lies behind the coffin bone and under the small pastern bone (middle phalanx). The deep digital flexor (DDF) tendon runs down the back of the cannon and soft tissue in that area and under the navicular bone before attaching to the underside of the coffin bone. The DDF tendon flexes the coffin joint, and the navicular bone acts as a fulcrum that the DDF tendon runs over. The navicular bone is stabilized by the impar ligament distally at its attachment to the coffin bone (distal phalanx), and by the collateral ligaments of the navicular bone extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that disease#Terminology, the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of heredity, inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe
A horseshoe is a product designed to protect a horse hoof from wear. Shoes are attached on the palmar surface (ground side) of the hooves, usually nailed through the insensitive hoof wall that is anatomically akin to the human toenail, although much larger and thicker. However, there are also cases where shoes are glued. Horseshoes are available in a wide variety of materials and styles, developed for different types of horses and for the work they do. The most common materials are steel and aluminium, but specialized shoes may include use of rubber, plastic, magnesium, titanium, or copper.Price, Steven D. (ed.) ''The Whole Horse Catalog: Revised and Updated'' New York:Fireside 1998 , pp. 84–87. Steel tends to be preferred in sports in which a strong, long-wearing shoe is needed, such as polo, eventing, show jumping, and western riding events. Aluminium shoes are lighter, making them common in horse racing where a lighter shoe is desired, and often facilitate certain ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic acid, uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan sulfate, keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidosis, Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of Stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, another class of anti-inflammatory drugs, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isozyme, isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. Warfarin may sometimes be prescribed following a ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and orthopedic surgery. It is usually taken by mouth, but may also be administered intravenously. The common side effect, a natural consequence of reduced clotting, is bleeding. Less common side effects may include areas of tissue necrosis, tissue damage, and purple toes syndrome. Use is not recommended during pregnancy. The effects of warfarin are typically monitored by checking prothrombin time (INR) every one to four weeks. Many other medications and Diet (nutrition), dietary factors can interact with warfarin, either increasing or decreasing its effectiveness. The effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentoxifylline
Pentoxifylline, also known as oxpentifylline, is a xanthine derivative used as a drug to treat muscle pain in people with peripheral artery disease. It is generic and sold under many brand names worldwide like Trental.Drugs.codrugs.com international listings for Pentoxifylline Page accessed Feb 1, 206 Medical uses Its primary use in medicine is to reduce pain, cramping, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs which occurs due to intermittent claudication, a form of muscle pain resulting from peripheral artery diseases. This is its only FDA, MHRA and TGA-labelled indication. However, pentoxifylline is also recommended for off-label use as an adjunct to compression bandaging for the treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) as this has been shown to improve healing rates. Pentoxifylline has been tested for use in sarcoidosis patients as an alternative or complement to prednisone and other steroids, as the drug can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoxsuprine
Isoxsuprine (used as isoxsuprine hydrochloride) is a drug used as a vasodilator in humans (under the trade name Duvadilan) and equines. Isoxsuprine is a β2 adrenoreceptor agonist that causes direct relaxation of uterine and vascular smooth muscle via β2 receptors. Use In humans Isoxsuprine is used in humans for treatment of premature labor, i.e. a tocolytic, and as a vasodilator for the treatment of cerebral vascular insufficiency, Raynaud's phenomenon, and other conditions. Isoxsuprine may increase the heart rate, cause changes in blood pressure, and irritate the GI tract. It should therefore be used with caution if combined with other drugs that affect blood pressure, such as sedatives and anesthetic drugs. In horses Isoxsuprine is most commonly used to treat hoof-related problems in the horse, most commonly for laminitis Laminitis is a disease of the feet of ungulates, found mostly in horses and cattle involving inflammation of the laminae. Clinical signs include fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adjusting metal shoes) with some veterinarian's skills (knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the lower limb) to care for horses' feet. Traditionally an occupation for men, in a number of countries women have now become farriers. History While the practice of putting protective hoof coverings on horses dates back to the first century, evidence suggests that the practice of nailing iron shoes into a horse's hoof is a much later invention. One of the first archaeological discoveries of an iron horseshoe was found in the tomb of Merovingian king Childeric I, who reigned from 458 to 481 or 482. The discovery was made by Adrien Quinquin in 1653, and the findings were written about by Jean-Jacques Chifflet in 1655. Chifflet wrote that the iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminitis
Laminitis is a disease of the feet of ungulates, found mostly in horses and cattle involving inflammation of the laminae. Clinical signs include foot tenderness progressing to inability to walk, increased digital pulses, and increased temperature in the hooves. Severe cases with outwardly visible clinical signs are known by the colloquial term ''#Rotation, sinking, and founder, founder'', and progression of the disease will lead to perforation of the coffin bone through the sole of the hoof or being unable to stand up, requiring Animal euthanasia, euthanasia. Laminae The bones of the hoof are suspended within the Anatomical terms of location#Other directional terms, axial hooves of ungulates by layers of modified skin cells, known as laminae or lamellae, which suspend the bony column from the hoof wall, contributing to shock absorption during locomotion. In horses, there are about 550–600 pairs of primary epidermis (zoology), epidermal laminae, each with 150–200 secondary la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lameness (equine)
Lameness is an abnormal gait or stance of an animal that is the result of dysfunction of the Animal locomotion, locomotor system. In the horse, it is most commonly caused by pain, but can be due to neurologic or mechanical dysfunction. Lameness is a common veterinary problem in racehorses, sport horses, and Pleasure riding, pleasure horses. It is one of the most costly health problems for the Horse industry, equine industry, both monetarily for the cost of diagnosis and treatment, and for the cost of time off resulting in loss-of-use. Causes of lameness Lameness is most commonly caused by pain, but may also be the result of neuromuscular disease or mechanical restriction. Lameness itself is a clinical sign, and not a diagnosis. Pain Pain is the most common cause of lameness in the horse. It is usually the result of trauma or orthopedic disease, but other causes such as metabolic dysfunction, circulatory disease, and infection can also cause pain and subsequent lameness. Orthopedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian (horse)
The Arabian or Arab horse ( , DIN 31635, DMG ''al-ḥiṣān al-ʿarabī'') is a horse breed, breed of horse with historic roots on the Arabian Peninsula. With a distinctive head shape and high tail carriage, the Arabian is one of the most easily recognizable horse breeds in the world. It is also one of the oldest modern breeds. Although modern DNA cannot trace breed purity in the modern population beyond 200 years, there is archaeological evidence of horses in the Middle East with landrace characteristics that resemble modern Arabians dating back 3,500 years. Arabian horses have spread around the world by both war and trade, being used to improve other breeds by adding speed, refinement, endurance, and strong bone. Today, Arabian bloodlines are found in almost every modern breed of riding horse. The Arabian developed in a desert climate and was prized by the nomadic Bedouin people, often being brought inside the family tent for shelter and protection from theft. Selective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pony
A pony is a type of small horse, usually measured under a specified height at maturity. Ponies often have thicker coats, manes and tails, compared to larger horses, and proportionally shorter legs, wider barrels, heavier , thicker necks and shorter heads. In modern use, breed registries and horse shows may define a pony as measuring at the withers below a certain height; height limits varying from about to . Some distinguish between horse or pony based on its breed or phenotype, regardless of its height. The word ''pony'' derives from the old French ''poulenet'', a diminutive of meaning foal, a young, immature horse. A full-sized horse may sometimes be called a pony as a term of endearment. Definition For many forms of competition, the official definition of a pony is a horse that measures up to at the withers. Standard horses are taller than 14.2. The International Federation for Equestrian Sports defines the official cutoff point at without shoes and with shoes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |