|
Metrizamide
Metrizamide is a non-ionic iodine-based radiocontrast agent. It is also a density gradient medium for the centrifugation of biological particles. Historically metrizamide replaced iofendylate (trade names: Pantopaque, Myodil) as the contrast agent of choice for myelography (an X-ray study of the spine now largely replaced by MRI). The radio opacity characteristics are such that finer detail is displayed with metrizamide, as well as the advantage of reabsorption from spinal fluid and excretion from the body – since unlike iofendylate, metrizamide is a water-soluble substance. Both agents are administered by lumbar puncture (also referred to as a spinal tap or cisternal puncture), at the cervicocranial junction. The human patient is rolled from the lateral decubitus (lying on the side) to prone. Ankles are strapped to the end of a hard X-ray, CT, or MRI table. To obtain images of the cervical region the patient is then carefully tilted in the Trendelenberg position (head d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iofendylate
Iofendylate is a molecule that was used as a radiocontrast agent, typically for performing myelography studies. It was marketed under the trade names Pantopaque (in North America) and Myodil (rest of the world). Iofendylate is a highly lipophilic (oily) substance and as such it was recommended that the physician remove it from the patient at the end of the myelography study, which was a difficult and painful part of the procedure. Moreover, because complete removal could not always be achieved (or even attempted by some physicians), iofendylate's persistence in the body might sometimes lead to arachnoiditis, a potentially painful and debilitating lifelong disorder of the spine. As a result, the substance, which was used extensively for over three decades, became the subject of multiple lawsuits filed around the world. Iofendylate's use ceased when water-soluble agents suitable for spinal imaging (such as metrizamide) became available in the late 1970s. With those substances it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
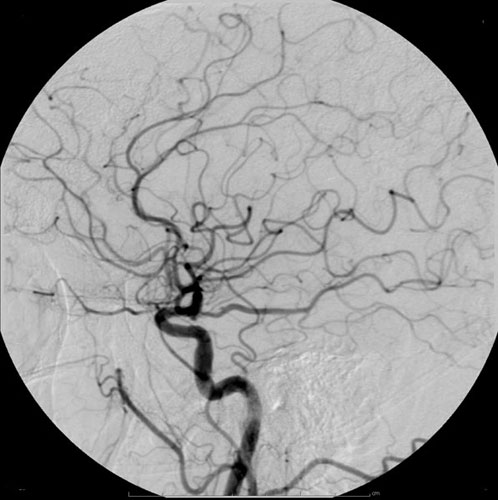
Myelography
Myelography is a type of radiographic examination that uses a contrast medium to detect pathology of the spinal cord, including the location of a spinal cord injury, cysts, and tumors. Historically the procedure involved the injection of a radiocontrast agent into the cervical or lumbar spine, followed by several X-ray projections. Today, myelography has largely been replaced by the use of MRI scans, although the technique is still sometimes used under certain circumstances – though now usually in conjunction with CT rather than X-ray projections. Types Cervical myelography This procedure is used to look for the level of where spinal cord disease occurs or compression of the spinal cord at the neck region for those who are unable or unwilling to undergone MRI scan of the spine. Lumbar myelography This procedure is to look for the level of spinal cord disease such as lumbar nerve root compression, cauda equina syndrome, conus medullaris lesions, and spinal stenosis. This is do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocontrast Agents
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocontrast Agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-ionic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Brain Barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the Cell (biology), cells, and transports Metabolic waste, metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in the Global North. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's speech or language must be significantly impaired in one (or more) of the four aspects of communication following acquired brain injury. Alternatively, in the case of progressive aphasia, it must have significantly declined over a short period of time. The four aspects of communication are auditory comprehension, verbal expression, reading and writing, and functional communication. The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble finding words, to losing the ability to speak, read, or write; intelligence, however, is unaffected. Expressive lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystonic
Dystonia is a neurological hyperkinetic movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions result in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures. The movements may resemble a tremor. Dystonia is often intensified or exacerbated by physical activity, and symptoms may progress into adjacent muscles. The disorder may be hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth-related or other physical trauma, infection, poisoning (e.g., lead poisoning) or reaction to pharmaceutical drugs, particularly neuroleptics, or stress. Treatment must be highly customized to the needs of the individual and may include oral medications, chemodenervation botulinum neurotoxin injections, physical therapy, or other supportive therapies, and surgical procedures such as deep brain stimulation. Classification There are multiple types of dystonia, and many diseases and conditions may cause dystonia. Dystonia is classified by: # Clinical characteristics such as age o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or neural oscillation, synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness (tonic-clonic seizure), to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness (focal seizure), to a subtle momentary loss of awareness (absence seizure). Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Urinary incontinence, Loss of bladder control may occur. Seizures may be provoked and unprovoked. Provoked seizures are due to a temporary event such as low blood sugar, alcohol withdrawal, abusing alcohol together with prescription medication, low blood sodium, fever, brain infection, or concussion. Unprovoked seizures occur without a known or fixable cause such that ongoing seizures are likely. Unprovoked seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herniation
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal type but may also be femoral. Other types of hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowel is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness in the area. Hiatus, or hiatal hernias often result in heartbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)