|
Megagametogenesis
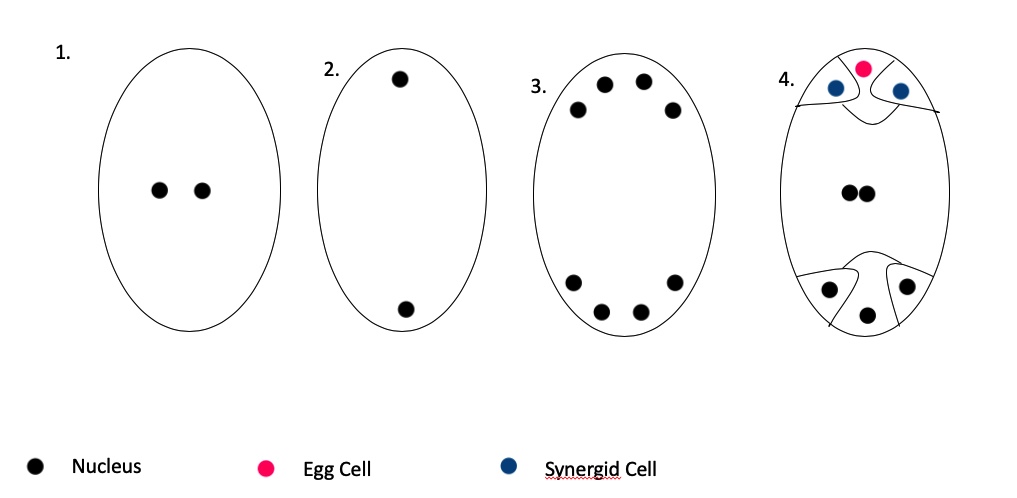
Megagametogenesis is the process of maturation of the female gametophyte, or megagametophyte, in plants During the process of megagametogenesis, the megaspore, which arises from megasporogenesis, develops into the embryo sac, which is where the female gamete is housed. These megaspores then develop into the haploid female gametophytes. This occurs within the ovule, which is housed inside the ovary. The Process Prior to megagametogenesis, a developing embryo undergoes meiosis during a process called megasporogenesis. Next, three out of four megaspores disintegrate, leaving only the megaspore that will undergo the megagametogenesis. The following steps are shown in Figure 1, and detailed below. # The remaining megaspore undergoes a round of mitosis. This results in a structure with two nuclei, also called a binucleate embryo sac. # The two nuclei migrate to opposite sides of the embryo sac. # Each haploid nucleus then undergoes two rounds of mitosis which creates 4 haploid nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaspore
Megaspores, also called macrospores, are a type of spore that is present in heterosporous plants. These plants have two spore types, megaspores and microspores. Generally speaking, the megaspore, or large spore, germinates into a female gametophyte, which produces egg cells. These are fertilized by sperm produced by the male gametophyte developing from the microspore. Heterosporous plants include seed plants (gymnosperms and flowering plants), water ferns (Salviniales), spikemosses (Selaginellaceae) and quillworts (Isoetaceae). Megasporogenesis In gymnosperms and flowering plants, the megaspore is produced inside the nucellus of the ovule. During megasporogenesis, a diploid precursor cell, the megasporocyte or megaspore mother cell, undergoes meiosis to produce initially four haploid cells (the megaspores). Angiosperms exhibit three patterns of megasporogenesis: monosporic, bisporic, and tetrasporic, also known as the ''Polygonum'' type, the ''Alisma'' type, and the ''Drusa'' ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image 3-28-19 At 7
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image 5-3-19 At 11
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicot
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the female gametophyte (formed from a haploid megaspore) in its center. The female gametophyte — specifically termed a ''megagametophyte''— is also called the ''embryo sac'' in angiosperms. The megagametophyte produces an egg cell for the purpose of fertilization. The ovule is a small structure present in the ovary. It is attached to the placenta by a stalk called a funicle. The funicle provides nourishment to the ovule. Location within the plant In flowering plants, the ovule is located inside the portion of the flower called the gynoecium. The ovary of the gynoecium produces one or more ovules and ultimately becomes the fruit wall. Ovules are attached to the placenta in the ovary through a stalk-like structure known as a ''funiculus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiotic
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microspore
Microspores are land plant spores that develop into male gametophytes, whereas megaspores develop into female gametophytes. The male gametophyte gives rise to sperm cells, which are used for fertilization of an egg cell to form a zygote. Megaspores are structures that are part of the alternation of generations in many seedless vascular cryptogams, all gymnosperms and all angiosperms. Plants with heterosporous life cycles using microspores and megaspores arose independently in several plant groups during the Devonian period. Microspores are haploid, and are produced from diploid microsporocytes by meiosis. Morphology The microspore has three different types of wall layers. The outer layer is called the perispore, the next is the exospore, and the inner layer is the endospore. The perispore is the thickest of the three layers while the exospore and endospore are relatively equal in width. Seedless vascular plants In heterosporous seedless vascular plants, modified leaves call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the Sexual reproduction of plants, sexual phase in the life cycle of plants and algae. It develops sex organs that produce gametes, haploid sex cells that participate in fertilization to form a diploid zygote which has a double set of chromosomes. Cell division of the zygote results in a new diploid multicellular organism, the second stage in the life cycle known as the sporophyte. The sporophyte can produce haploid spores by meiosis that on germination produce a new generation of gametophytes. Algae In some multicellular green algae (''Ulva lactuca'' is one example), red algae and brown algae, sporophytes and gametophytes may be externally indistinguishable (isomorphic). In ''Ulva (genus), Ulv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |