|
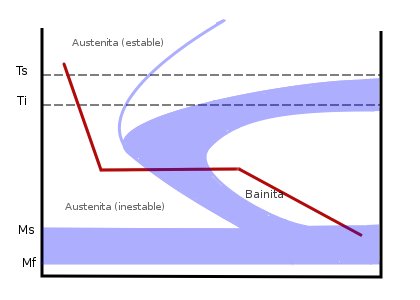
Martempering
Martempering is also known as stepped quenching or interrupted quenching. In this process, steel is heated above the upper critical point (above the transformation range) and then quenched in a salt, oil, or lead bath kept at a temperature of 150-300 °C. The workpiece is held at this temperature above martensite start (Ms) point until the temperature becomes uniform throughout the cross-section of workpiece. After that it is cooled in air or oil to room temperature. The steel is then tempered. In this process, Austenite is transformed to martensite by step quenching, at a rate fast enough to avoid the formation of ferrite, pearlite or bainite. In the martempering process, austenitized metal part is immersed in a bath at a temperature just above the martensite start temperature (Ms). By using interrupted quenching, the cooling is stopped at a point above the martensite transformation region to ensure sufficient time for the center to cool to the same temperature as the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempering (metallurgy)
Tempering is a process of heat treating, which is used to increase the toughness of iron-based alloys. Tempering is usually performed after hardening, to reduce some of the excess hardness, and is done by heating the metal to some temperature below the critical point for a certain period of time, then allowing it to cool in still air. The exact temperature determines the amount of hardness removed, and depends on both the specific composition of the alloy and on the desired properties in the finished product. For instance, very hard tools are often tempered at low temperatures, while springs are tempered at much higher temperatures. Introduction Tempering is a heat treatment technique applied to ferrous alloys, such as steel or cast iron, to achieve greater toughness by decreasing the hardness of the alloy. The reduction in hardness is usually accompanied by an increase in ductility, thereby decreasing the brittleness of the metal. Tempering is usually performed after quen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. It does this by reducing the window of time during which these undesired reactions are both thermodynamically favorable, and kinetically accessible; for instance, quenching can reduce the crystal grain size of both metallic and plastic materials, increasing their hardness. In metallurgy, quenching is most commonly used to harden steel by inducing a martensite transformation, where the steel must be rapidly cooled through its eutectoid A eutectic system or eutectic mixture ( ) is a homogeneous mixture that has a melting point lower than those of the constituents. The lowest possible melting point over all of the mixing ratios of the constituents is called the ''eutectic tempe ... point, the temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition At the phase transition point for a substance, for instance the boiling point, the two phases involved - liquid and vapor, have id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austenite
Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron with an alloying element. In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1000 K (727 °C); other alloys of steel have different eutectoid temperatures. The austenite allotrope is named after Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen (1843–1902); it exists at room temperature in some stainless steels due to the presence of nickel stabilizing the austenite at lower temperatures. Allotrope of iron From alpha iron undergoes a phase transition from body-centered cubic (BCC) to the face-centered cubic (FCC) configuration of gamma iron, also called austenite. This is similarly soft and ductile but can dissolve considerably more carbon (as much as 2.03% by mass at ). This gamma form of iron is present in the most commonly used type of stainless steel for making hospital and food-service equipment. Material Austenitiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martensite
Martensite is a very hard form of steel crystalline structure. It is named after German metallurgist Adolf Martens. By analogy the term can also refer to any crystal structure that is formed by diffusionless transformation. Properties Martensite is formed in carbon steels by the rapid cooling (quenching) of the austenite form of iron at such a high rate that carbon atoms do not have time to diffuse out of the crystal structure in large enough quantities to form cementite (Fe3C). Austenite is gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), a solid solution of iron and alloying elements. As a result of the quenching, the face-centered cubic austenite transforms to a highly strained body-centered tetragonal form called martensite that is supersaturated with carbon. The shear deformations that result produce a large number of dislocations, which is a primary strengthening mechanism of steels. The highest hardness of a pearlitic steel is 400 Brinell, whereas martensite can achieve 700&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotropes Of Iron
At atmospheric pressure, three allotropic forms of iron exist, depending on temperature: alpha iron (α-Fe), gamma iron (γ-Fe), and delta iron (δ-Fe). At very high pressure, a fourth form exists, called epsilon iron (ε-Fe). Some controversial experimental evidence suggests the existence of a fifth high-pressure form that is stable at very high pressures and temperatures. The phases of iron at atmospheric pressure are important because of the differences in solubility of carbon, forming different types of steel. The high-pressure phases of iron are important as models for the solid parts of planetary cores. The inner core of the Earth is generally assumed to consist essentially of a crystalline iron-nickel alloy with ε structure. The outer core surrounding the solid inner core is believed to be composed of liquid iron mixed with nickel and trace amounts of lighter elements. Standard pressure allotropes Alpha iron (α-Fe) Below 912 °C (1,674 °F), iron has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearlite
Pearlite is a two-phased, lamellar (or layered) structure composed of alternating layers of ferrite (87.5 wt%) and cementite (12.5 wt%) that occurs in some steels and cast irons. During slow cooling of an iron-carbon alloy, pearlite forms by a eutectoid reaction as austenite cools below (the eutectoid temperature). Pearlite is a microstructure occurring in many common grades of steels. The eutectoid composition of austenite is approximately 0.8% carbon; steel with less carbon content ( hypoeutectoid steel) will contain a corresponding proportion of relatively pure ferrite crystallites that do not participate in the eutectoid reaction and cannot transform into pearlite. Likewise steels with higher carbon content ( hypereutectoid steels) will form cementite before reaching the eutectoid point. The proportion of ferrite and cementite forming above the eutectoid point can be calculated from the iron/iron—carbide equilibrium phase diagram using the lever rule. Steels wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bainite
Bainite is a plate-like microstructure that forms in steels at temperatures of 125–550 °C (depending on alloy content). First described by E. S. Davenport and Edgar Bain, it is one of the products that may form when austenite (the face-centered cubic crystal structure of iron) is cooled past a temperature where it is no longer thermodynamically stable with respect to ferrite, cementite, or ferrite and cementite. Davenport and Bain originally described the microstructure as being similar in appearance to tempered martensite. A fine non-lamellar structure, bainite commonly consists of cementite and dislocation-rich ferrite. The large density of dislocations in the ferrite present in bainite, and the fine size of the bainite platelets, makes this ferrite harder than it normally would be. The temperature range for transformation of austenite to bainite (125–550 °C) is between those for pearlite and martensite. In fact, there is no fundamental lower limit to the bai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austempering
Austempering is heat treatment that is applied to ferrous metals, most notably steel and ductile iron. In steel it produces a bainite microstructure whereas in cast irons it produces a structure of acicular ferrite and high carbon, stabilized austenite known as ''ausferrite''. It is primarily used to improve mechanical properties or reduce / eliminate distortion. Austempering is defined by both the process and the resultant microstructure. Typical austempering process parameters applied to an unsuitable material will not result in the formation of bainite or ausferrite and thus the final product will not be called austempered. Both microstructures may also be produced via other methods. For example, they may be produced as-cast or air cooled with the proper alloy content. These materials are also not referred to as austempered. History The austempering of steel was first pioneered in the 1930s by Edgar C. Bain and Edmund S. Davenport, who were working for the United States Stee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |