|
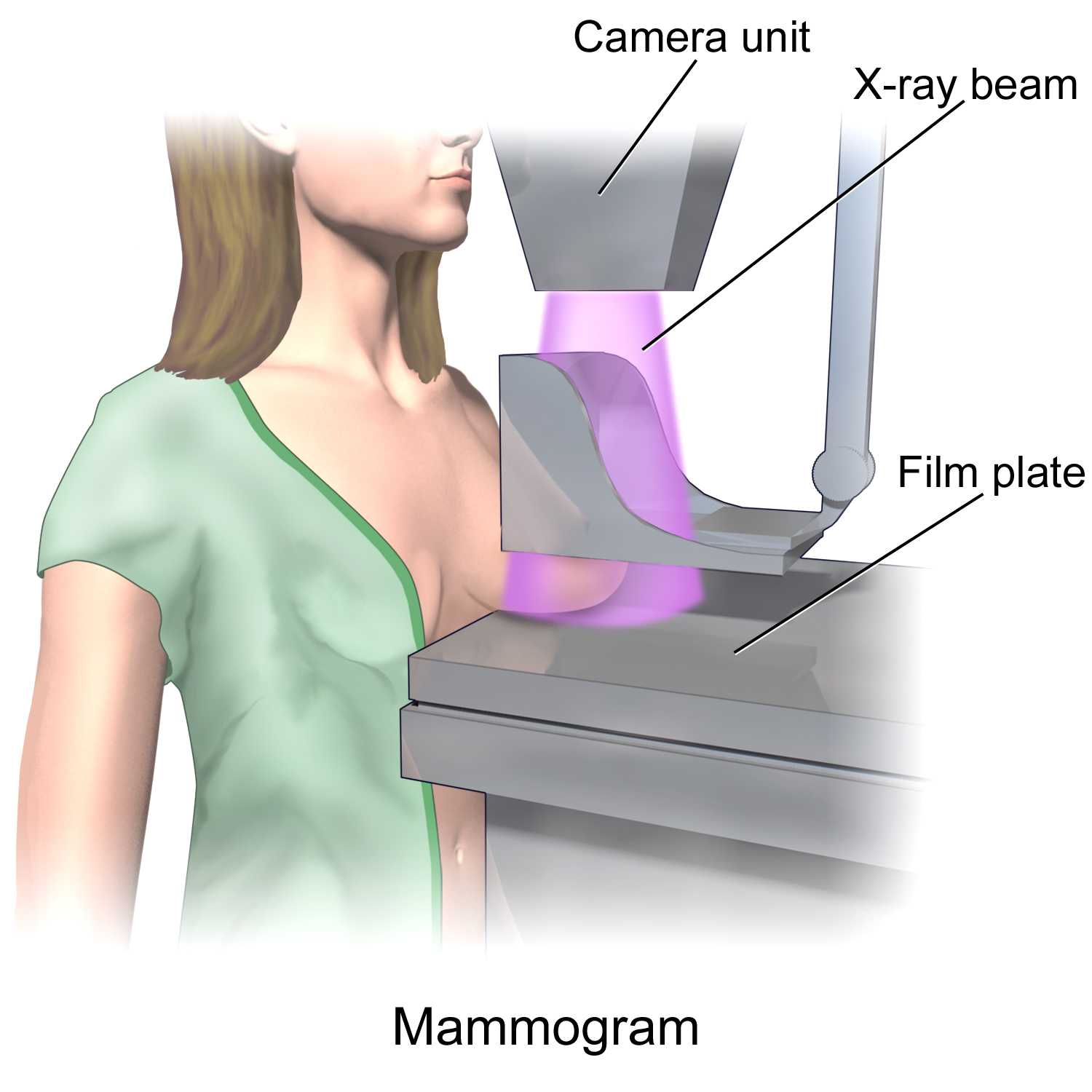
Mammograms
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment and/or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable masses that may or may not be seen on mammo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Preventive Services Task Force
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) is "an independent panel of experts in primary care and prevention that systematically reviews the evidence of effectiveness and develops recommendations for clinical preventive services". The task force, a volunteer panel of primary care clinicians (including those from internal medicine, pediatrics, family medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, nursing, and psychology) with methodology experience including epidemiology, biostatistics, health services research, decision sciences, and health economics, is funded, staffed, and appointed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Intent The USPSTF evaluates scientific evidence to determine whether medical screenings, counseling, and preventive medications work for adults and children who have no symptoms. Methods The methods of evidence synthesis used by the Task Force have been described in detail. In 2007, their methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Breast Tissue
Dense breast tissue, also known as dense breasts, is a condition of the breasts where a higher proportion of the breasts are made up of glandular tissue and fibrous tissue than fatty tissue. Around 40–50% of women have dense breast tissue and one of the main medical components of the condition is that mammograms are unable to differentiate tumorous tissue from the surrounding dense tissue. This increases the risk of late diagnosis of breast cancer in women with dense breast tissue. Additionally, women with such tissue have a higher likelihood of developing breast cancer in general, though the reasons for this are poorly understood. Definition Dense breast tissue is defined based on the amount of glandular and fibrous tissue as compared to the percentage of fatty tissue. The current mammography classifications split up the density of breasts into four categories. Approximately 10% of women have almost entirely fatty breasts, 40% with small pockets of dense tissue, 40% with even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastectomy
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operation as a preventive measure. Alternatively, some women can choose to have a wide local excision, also known as a lumpectomy, an operation in which a small volume of breast tissue containing the tumor and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue is removed to conserve the breast. Both mastectomy and lumpectomy are referred to as "local therapies" for breast cancer, targeting the area of the tumor, as opposed to systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, or immunotherapy. The decision to perform a mastectomy is based on various factors, including breast size, the number of lesions, biologic aggressiveness of a breast cancer, the availability of adjuvant radiation, and the willingness of the patient to accept higher rates of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastectomies
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operation as a preventive measure. Alternatively, some women can choose to have a wide local excision, also known as a lumpectomy, an operation in which a small volume of breast tissue containing the tumor and a surrounding margin of healthy tissue is removed to conserve the breast. Both mastectomy and lumpectomy are referred to as "local therapies" for breast cancer, targeting the area of the tumor, as opposed to systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, or immunotherapy. The decision to perform a mastectomy is based on various factors, including breast size, the number of lesions, biologic aggressiveness of a breast cancer, the availability of adjuvant radiation, and the willingness of the patient to accept higher rates of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stafford L
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It lies about north of Wolverhampton, south of Stoke-on-Trent and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 70,145 in the 2021 census, It is the main settlement within the larger borough of Stafford which had a population of 136,837 (2021). History Stafford means " ford" by a staithe (landing place). The original settlement was on a dry sand and gravel peninsula that offered a strategic crossing point in the marshy valley of the River Sow, a tributary of the River Trent. There is still a large area of marshland north-west of the town, which is subject to flooding and did so in 1947, 2000, 2007 and 2019. Stafford is thought to have been founded about AD 700 by a Mercian prince called Bertelin, who, legend has it, founded a hermitage on a peninsula named Betheney. Until recently it was thought that the remains of a wooden preaching cross from the time had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Röntgen
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (; ; 27 March 184510 February 1923) was a German mechanical engineer and physicist, who, on 8 November 1895, produced and detected electromagnetic radiation in a wavelength range known as X-rays or Röntgen rays, an achievement that earned him the inaugural Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.Novelize, Robert. ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. 1997. p. 1. In honour of Röntgen's accomplishments, in 2004 the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) named element 111, roentgenium, a radioactive element with multiple unstable isotopes, after him. The unit of measurement roentgen was also named after him. Biographical history Education He was born to Friedrich Conrad Röntgen, a German merchant and cloth manufacturer, and Charlotte Constanze Frowein. At age three his family moved to the Netherlands where his family lived. Röntgen attended high school at Utrecht Technical School in Utrecht, Netherl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Salomon (surgeon)
Albert Salomon (1883–1976)Creativity and Its Imprint: Three Jewish Artists and Some Books About Them: Philip Guston, Charlotte Salomon, R. B. Kitaj , Leonard Gold, Rosaline and Myer Feinstein Lecture Series, 2001. Hosted by www.jewishlibraries.org. Retrieved 11 Jul 2011. was a Jewish-German surgeon at the Royal Surgical University Clinic in . He is best known for his study of early mastectom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscopic
Stereoscopy (also called stereoscopics, or stereo imaging) is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Journal Of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one. History In September 1811, John Collins Warren, a Boston physician, along with James Jackson, submitted a formal prospectus to establish the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and Collateral Branches of Science'' as a medical and philosophical journal. Subsequently, the first issue of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' was published in January 1812. The journal was published quarterly. In 1823, another publication, the ''Boston Medical Intelligencer'', appeared under the editorship of Jerome V. C. Smith. The editors of the ''New England Journal of Medicine and Surgery and the Collateral Branches of Medical Science'' purchased the weekly ''Intelligencer'' for $600 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |