|
Myśl Zachodnia
Western Thought (''Myśl zachodnia'') was a school of thought in Polish historical and political science. In the 1920s and 1930s Myśl zachodnia was organized in opposition to Ostforschung. A main center of Western Thought was the association Polski Związek Zachodni (PZZ; ''Polish Western Union''), founded in 1921. Unlike Germann Ostforschung, Polish western thought was not institutionalized and didn't constitute any real threat. Its influence was exaggerated by German scholars in order to fund and justify their own work. Before 1945 At the time of 10th century the Western border of Poland was located on the line of the Odra and Nysa Luzycka In partitioned Poland, historians developed a romanticized view of the Piast kingdom of the early Middle Ages, extending to the Oder. Polish historians have construed a continuous Polish-German clash caused by Germans' drive of territorial and ethnic expansion, alleging that assimilation of Slavic inhabitants to German language and cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Umiastowski
Roman Umiastowski, who was born on January 29, 1893, in Warsaw and died on December 29, 1982, in London, has been a colonel in the Polish Army, a patriot and a bibliophile. Biography World War II When the Germans invaded Poland, Umiastowski was the head of the propaganda department in the Polish High Staff. On the night of 6/7 September 1939 he aired a message on the radio, urging all able men of Warsaw to go to the front; the idea was to man a defense line east of the Vistula. The result is said to have been one of the most legendary traffic jams in history.O. Gingerich, The book nobody read, Heinemann, London, 2004 Umiastowki continued his work after arriving in England after the military collapse in 1939 and published ("with the assistance of Joanna Mary Aldridge"): Russia and the Polish Republic 1918 - 1941 (London, 1945?, pp 320 ) and Poland, Russia and Great Britain 1941 - 1945. A Study of Evidence(London, 1946, pp 544). The first in memory of his son, lieutenant Jan Kaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recovered Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands () are the lands east of the Oder–Neisse line, Oder-Neisse line that over the centuries were gradually lost by Poland and colonized by the Germans, and that returned to Poland after World War II. This term includes Western Pomerania, Lower Silesia, the western part of Upper Silesia, Warmia, Masuria, Lubusz Land and Kłodzko Land. Sometimes the city of Gdańsk is also included. The rationale for the term "Recovered" was that these territories formed part of the Polish state, and were lost by Poland in different periods of time. It also referred to the Piast Concept that these territories were part of the traditional Polish homeland under the Piast dynasty (there were their small parts under Poland even after the Piast dynasty ended), after the establishment of the Polish state in 966. Over the centuries, however, they had become predominantly German-speaking through the processes of German eastward settlement (), political expansion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propaganda In The Polish People's Republic
Communist propaganda played an important role in the Polish People's Republic, one of the largest and most important satellite states of the Soviet Union following WWII. Together with the use of force and terror it was instrumental in keeping the country's communist government in power and was designed to shape Polish society into a communist one. Starting from the 1970s, Polish propaganda was significantly altered and then dominated by the form known as " propaganda of success". Themes Allies Polish diaspora PZPR propaganda usually expressed a positive view of Polish Americans and tried to convince them to immigrate back to Poland. The PZPR criticized the Polish diaspora as a whole for not joining the Polish Armed Forces during the 1939 Invasion of Poland. Enemies United States The propagandists of the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR) declared the United States to be the "foremost capitalist" of the capitalist countries and criticized it extensively. Accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polonization
Polonization or Polonisation ()In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэяй. Польскі рух на беларускіх і літоўскіх землях. 1864–1917 г. / Пад рэд. С. Куль-Сяльверставай. – Гродна: ГрДУ, 2001. – 322 с. (2004). Pp.24, 28.), an additional distinction between the Polonization () and self-Polonization () has been being made, however, most modern Polish researchers do not use the term ''polszczenie się''. is the acquisition or imposition of elements of Polish culture, in particular the Polish language. This happened in some historic periods among non-Polish populations in territories controlled by or substantially under the influence of Poland. Like other examples of cultural assimilation, Polonization could be either voluntary or forced. It was most vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight And Expulsion Of Germans From Poland During And After World War II
The flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland was the largest of a series of Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), flights and expulsions of Germans in Europe during and after World War II. The German population fled or was expelled from all regions which are Territorial changes of Poland after World War II, currently within the territorial boundaries of Poland: including the former eastern territories of Germany annexed by Poland after the war and parts of Second Polish Republic, pre-war Poland; despite acquiring territories from Germany, the Poles themselves were also expelled from the former eastern territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. West Germany, West German government figures of those evacuated, migrated, or expelled by 1950 totaled 8,129,800 (6,981,000 from the former eastern territories of Germany; 290,800 from Free City of Danzig, Danzig, 688,000 from pre-war Poland and 170,000 Baltic Germans resettled in Poland during the war). Research by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Leszczycki
Stanisław Leszczycki (8 May 1907, in Mielec – 17 June 1996, in Warsaw) was a Polish geographer. He was a professor at the University of Warsaw since 1948 and the Polish Academy of Sciences since 1952 (in each of them he created an Institute of Geography). He was President of the International Geographical Union in 1968–1972, as well as a member of many learned societies and the author of 200 scientific publication Scientific literature encompasses a vast body of academic papers that spans various disciplines within the natural and social sciences. It primarily consists of academic papers that present original empirical research and theoretical co ...s on various subdisciplines. ReferencesEncyklopedia PWN 1907 births 1996 deaths People from Mielec People from the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria Polish Socialist Party politicians Polish United Workers' Party members Members of the State National Council Members of the Polish Sejm 1947–1952 Polish g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
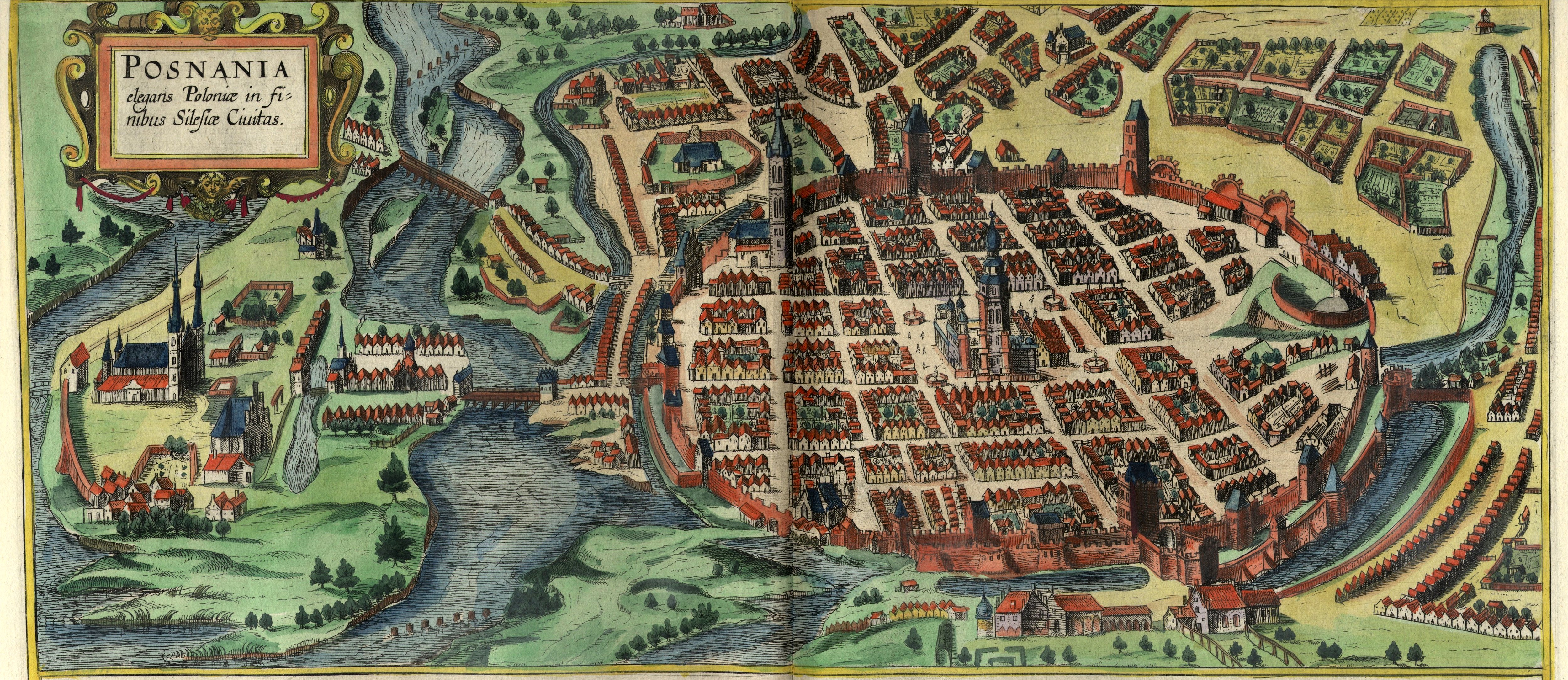
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the Armistice with Germany (Compiègne), armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, and agreed certain principles and conditions including the payment of reparations, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. Germany was not allowed to participate in the negotiations before signing the treaty. The treaty German disarmament, required Germany to disarm, make territorial concessions, extradite alleged war criminals, agree to Kaiser Wilhelm being p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole '' Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, and his word became the highest law. The government was not a coordinated, coopera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |