|
Mu'amalat
''Muamalat'' (also ''muʿāmalāt,'' , literally "transactions" TBE, "CHAPTER A1, INTRODUCTION TO ISLAMIC MUAMALAT", 2012: p.6 or "dealings") is a part of Islamic jurisprudence, or ''fiqh''. Sources agree that ''muamalat'' includes Islamic "rulings governing commercial transactions" and Majallah al-Ahkam al-Adliyyah). JALIL, et. al., ''FOUR INTRODUCTORY THEORIES OF FIQH MUAMALAT'': p.8 However, other sources (Oxford Islamic Studies Online, Brian Kettell, and Wahbah al-Zuhayli’) give it a broader definition including civil acts and in general all aspects of fiqh that are not ''Ibadat'' (acts of ritual worship such as prayer or fasting). (See organizational chart of the structure of Islam below in "Principles" section.) Chik, ''Shariah in Islamic Finance'': p.5 Lee, "Islamic Banking Law", 2015: p.29 ''Mu'amalat'' provides much of the basis for Islamic economics, and the instruments of Islamic financing, and deals not only with Islamic legality but also social and economic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Economics
Islamic economics () refers to the knowledge of economics or economic activities and processes in terms of Islamic principles and teachings. Islam has a set of specific moral norms and values about individual and social economic behavior. Therefore, it has its own economic system, which is based on its philosophical views and is compatible with the Islamic organization of other aspects of human behavior: social and political systems. Islamic economics is a broad field, related to the more specific subset of Islamic commercial jurisprudence (, '' fiqh al-mu'āmalāt''). It is also an ideology of economics similar to the labour theory of value, which is "labour-based exchange and exchange-based labour".. While there are differences between the two, Islamic economics still tends to be closer to labor theory rather than subjective theory. Islamic commercial jurisprudence entails the rules of transacting finance or other economic activity in a ''Shari'a'' compliant manner, i.e., a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gharar
''Gharar'' () literally means uncertainty, hazard, chance or risk. It is a negative element in ''mu'amalat'' ''fiqh'' (transactional Islamic jurisprudence), like ''riba'' (usury) and '' maisir'' (gambling). One Islamic dictionary (''A Concise Dictionary of Islamic Terms'') describes it as "the sale of what is not present" — such as fish not yet caught, crops not yet harvested. Similarly, author Muhammad Ayub says that "in the legal terminology of jurists", ''gharar'' is "the sale of a thing which is not present at hand, or the sale of a thing whose ''aqibah'' (consequence) is not known, or a sale involving hazard in which one does not know whether it will come to be or not". Definitions, fiqh According to Sami Al-Suwailem, "researchers in Islamic finance" do not agree on the "precise meaning" of gharar, although there is not necessarily great difference among the Islamic schools of jurisprudence ( madhab) in the term's definition. The ''Hanafi'' legal school defines ''gharar'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maqasid
''Maqasid'' (, ) or ''maqāṣid al-sharīʿa'' (goals or objectives of ''sharia'') is an Islamic legal doctrine. Together with another related classical doctrine, '' maṣlaḥa'' (), it has come to play an increasingly prominent role in modern times. The notion of ''maqasid'' was first clearly articulated by al-Ghazali (died 1111), who argued that ''maslaha'' was God's general purpose in revealing the divine law, and that its specific aim was preservation of five essentials of human well-being: religion, life, intellect, lineage, and property. Although most classical-era jurists recognized ''maslaha'' and ''maqasid'' as important legal principles, they held different views regarding the role they should play in Islamic law. Some jurists viewed them as auxiliary rationales constrained by scriptural sources (Quran and hadith) and ''qiyas Qiyas (, , ) is the process of deductive analogy in which the teachings of the hadith are compared and contrasted with those of the Quran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Words And Phrases
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the world and is used to varying degrees in workplaces, governments and the media. During the Middle Ages, Arabic was a major vehicle of culture and learning, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Practices
Islam is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number 2 billion worldwide and are the world's second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier prophets and messengers, including Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous revelations, such as the Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad is the main and final of God's prophets, through whom the religion was completed. The teachings and normative examples of Muhammad, called the Sunnah, documented in accounts called the hadith, provide a constitutional model for Muslims. Islam is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Banking
Islamic banking, Islamic finance ( ''masrifiyya 'islamia''), or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or financing activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law) and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic finance include '' mudarabah'' (profit-sharing and loss-bearing), '' wadiah'' (safekeeping), '' musharaka'' (joint venture), '' murabahah'' (cost-plus), and '' ijarah'' (leasing). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, generally defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haram'' ("sinful and prohibited"). These prohibitions have been applied historically in varying degrees in Muslim countries/communities to prevent un-Islamic practices. In the late 20th century, as part of the revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
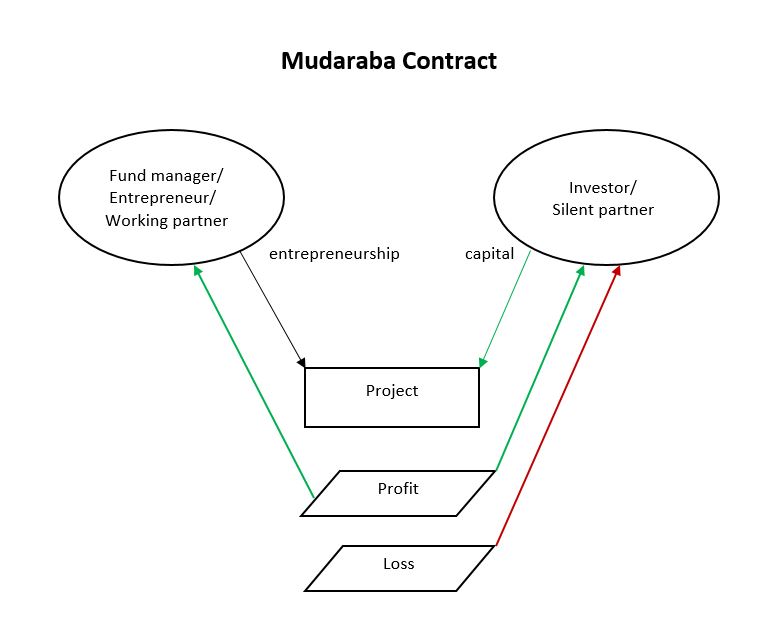
Profit And Loss Sharing
Profit and Loss Sharing (also called PLS or participatory banking) refers to Sharia-compliant forms of equity financing such as mudarabah and musharakah. These mechanisms comply with the religious prohibition on interest on loans that most Muslims subscribe to. ''Mudarabah'' (مضاربة) refers to "trustee finance" or passive partnership contract, while ''Musharakah'' (مشاركة or مشركة) refers to equity participation contract. Other sources include sukuk (also called "Islamic bonds") and direct equity investment (such as purchase of common shares of stock) as types of PLS. Khan, ''Islamic Banking in Pakistan'', 2015: p.91 The profits and losses shared in PLS are those of a business enterprise or person which/who has obtained capital from the Islamic bank/financial institution (the terms "debt", "borrow", "loan" and "lender" are not used). As financing is repaid, the provider of capital collects some agreed upon percentage of the profits (or deducts if there are losses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murabahah
''Murabaḥah'', ''murabaḥa'', or ''murâbaḥah'' (, derived from ''ribh'' , meaning profit) was originally a term of ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence) for a sales contract where the buyer and seller agree on the markup (profit) or " cost-plus" price for the item(s) being sold. In recent decades it has become a term for a very common form of Islamic (i.e., " shariah compliant") financing, where the price is marked up in exchange for allowing the buyer to pay over time—for example with monthly payments (a contract with deferred payment being known as ''bai-muajjal''). ''Murabaha'' financing is basically the same as a rent-to-own arrangement in the non-Muslim world, with the intermediary (e.g., the lending bank) retaining ownership of the item being sold until the loan is paid in full. There are also Islamic investment funds and ''sukuk'' (Islamic bonds) that use ''murabahah'' contracts. Jamaldeen, ''Islamic Finance For Dummies'', 2012:188-9, 220-1 The purpose of ''murabaha' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maisir
In Islam, gambling ( or ''qimâr'') is forbidden (). ''Maisir'' is totally prohibited by Islamic law () on the grounds that "the agreement between participants is based on immoral inducement provided by entirely wishful hopes in the participants' minds that they will gain by mere chance, with no consideration for the possibility of loss". Definitions Both ''qimar'' and ''maisir'' refer to games of chance, but ''qimar'' is a kind (or subset) of ''maisir''. Author Muhammad Ayub defines ''maisir'' as "wishing something valuable with ease and without paying an equivalent compensation for it or without working for it, or without undertaking any liability against it by way of a game of chance", Another source, Faleel Jamaldeen, defines it as "the acquisition of wealth by chance (not by effort)". Ayub defines ''qimar'' as "also mean ngreceipt of money, benefit or usufruct at the cost of others, having entitlement to that money or benefit by resorting to chance"; Jamaldeen as "any game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riba
''Riba'' (, or , ) is an Arabic word used in Islamic law and roughly translated as " usury": unjust, exploitative gains made in trade or business. ''Riba'' is mentioned and condemned in several different verses in the Qur'an3:130 and most commonl 2:275-2:280 . It is also mentioned in many '''' (reports of the life of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haram
''Haram'' (; ) is an Arabic term meaning 'taboo'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowledge; or, in direct contrast, to an evil and thus " sinful action that is forbidden to be done". The term also denotes something "set aside", thus being the Arabic equivalent of the Hebrew concept () and the concept of (cf. sacred) in Roman law and religion. In Islamic jurisprudence, ''haram'' is used to refer to any act that is forbidden by Allah and is one of the five Islamic commandments ( ) that define the morality of human action. Acts that are haram are typically prohibited in the religious texts of the Quran and the category of haram is the highest status of prohibition. Something that is considered haram remains prohibited no matter how good the intention is or how honorable the purpose is. Sins, good, and meritorious acts are placed on the (weighin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |