|
Molecular Beam
A molecular beam is produced by allowing a gas at higher pressure to expand through a small orifice into a chamber at lower pressure to form a beam of particles (atoms, free radicals, molecules or ions) moving at approximately equal velocities, with very few collisions between the particles. Molecular beams are useful for fabricating thin films in molecular beam epitaxy and artificial structures such as quantum wells, quantum wires, and quantum dots. Molecular beams have also been applied as crossed molecular beams. The molecules in the molecular beam can be manipulated by electrical fields and magnetic fields. Molecules can be decelerated in a Stark decelerator or in a Zeeman slower. History The first to study atomic beam experiments was Louis Dunoyer de Segonzac 1911, but were simple experiments to confirm that atoms travelled in straight lines when not acted on by external forces. In 1921, Hartmut Kallmann and Fritz Reiche wrote about the deflection of beams of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various #Units, units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the International System of Units, SI unit of pressure, the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton (unit), newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the Pound (force), pound-force per square inch (Pound per square inch, psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial units, imperial and United States customary units, US customary systems. Pressure ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zeeman Slower
In atomic physics, a Zeeman slower is a scientific instrument that is commonly used in atomic, molecular, and optical physics, atomic physics to slow and Cooling, cool a molecular beam, beam of hot atoms to speeds of several meters per second and temperatures below a kelvin. The gas-phase atoms used in atomic physics are often generated in an oven by heating a solid or liquid atomic sample to temperatures where the vapor pressure is high enough that a substantial number of atoms are in the gas phase. These atoms Effusion, effuse out of a hole in the oven with average speeds on the order of hundreds of m/s and large velocity distributions (due to their high temperature). The Zeeman slower is attached close to where the hot atoms exit the oven and are used to slow them to less than 10 m/s (slowing) with a very small velocity spread (cooling). A Zeeman slower consists of a cylinder (geometry), cylinder, through which an atomic beam travels, a Laser pumping, pump laser that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Matter Wave
Matter waves are a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics, being half of wave–particle duality. At all scales where measurements have been practical, matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave. The concept that matter behaves like a wave was proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie () in 1924, and so matter waves are also known as de Broglie waves. The ''de Broglie wavelength'' is the wavelength, , associated with a particle with momentum through the Planck constant, : \lambda = \frac. Wave-like behavior of matter has been experimentally demonstrated, first for electrons in 1927 and for other elementary particles, neutral atoms and molecules in the years since. Matter waves have more complex velocity relations than solid objects and they also differ from electromagnetic waves (light). Collective matter waves are used to model phenomena in solid state physics; standing matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Angular Momentum Operator
In quantum mechanics, the angular momentum operator is one of several related operators analogous to classical angular momentum. The angular momentum operator plays a central role in the theory of atomic and molecular physics and other quantum problems involving rotational symmetry. Being an observable, its eigenfunctions represent the distinguishable physical states of a system's angular momentum, and the corresponding eigenvalues the observable experimental values. When applied to a mathematical representation of the state of a system, yields the same state multiplied by its angular momentum value if the state is an eigenstate (as per the eigenstates/eigenvalues equation). In both classical and quantum mechanical systems, angular momentum (together with linear momentum and energy) is one of the three fundamental properties of motion.Introductory Quantum Mechanics, Richard L. Liboff, 2nd Edition, There are several angular momentum operators: total angular momentum (usually den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spin (physics)
Spin is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic form of angular momentum carried by elementary particles, and thus by List of particles#Composite particles, composite particles such as hadrons, atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, and atoms. Spin is quantized, and accurate models for the interaction with spin require relativistic quantum mechanics or quantum field theory. The existence of electron spin angular momentum is inferred from experiments, such as the Stern–Gerlach experiment, in which silver atoms were observed to possess two possible discrete angular momenta despite having no orbital angular momentum. The relativistic spin–statistics theorem connects electron spin quantization to the Pauli exclusion principle: observations of exclusion imply half-integer spin, and observations of half-integer spin imply exclusion. Spin is described mathematically as a vector for some particles such as photons, and as a spinor or bispinor for other particles such as electrons. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stern–Gerlach Experiment
In quantum physics, the Stern–Gerlach experiment demonstrated that the spatial orientation of angular momentum is quantization (physics), quantized. Thus an Atomic spacing, atomic-scale system was shown to have intrinsically quantum properties. In the original experiment, silver atoms were sent through a spatially-varying magnetic field, which Deflection (physics), deflected them before they struck a detector screen, such as a glass slide. Particles with non-zero magnetic moment were deflected, owing to the magnetic field spatial gradient, gradient, from a straight path. The screen revealed discrete points of accumulation, rather than a continuous distribution, owing to their quantized Spin (physics), spin. Historically, this experiment was decisive in convincing physicists of the reality of angular-momentum quantization in all atomic-scale systems. After its conception by Otto Stern in 1921, the experiment was first successfully conducted with Walther Gerlach in early 1922. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walther Gerlach
Walther Gerlach (1 August 1889 – 10 August 1979) was a German physicist who co-discovered, through laboratory experiment, spin quantization in a magnetic field, the Stern–Gerlach effect. The experiment was conceived by Otto Stern in 1921 and successfully conducted first by Gerlach in early 1922. He was Nazi Germany's plenipotentiary of nuclear physics from December 1943 until his capture by US Army in May 1945. Education Gerlach was born in Biebrich, Hessen-Nassau, German Empire, as son of Dr. med. Valentin Gerlach and his wife Marie Niederhaeuser. He studied at the University of Tübingen from 1908, and received his doctorate in 1912, under Friedrich Paschen. The subject of his dissertation was on the measurement of radiation. After obtaining his doctorate, he continued on as an assistant to Paschen, which he had been since 1911. Gerlach completed his Habilitation at Tübingen in 1916, while serving during World War I. Career World War I and the interwar period F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Frankfurt Am Main
Goethe University Frankfurt () is a public research university located in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It was founded in 1914 as a citizens' university, which means it was founded and funded by the wealthy and active liberal citizenry of Frankfurt. The original name in German was Universität Frankfurt am Main (University of Frankfurt am Main). In 1932, the university's name was extended in honour of one of the most famous native sons of Frankfurt, the poet, philosopher and writer/dramatist Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. The university currently has around 48,000 students, distributed across four major campuses within the city. The university celebrated its 100th anniversary in 2014. The first female president of the university, Birgitta Wolff, was sworn into office in 2015, and was succeeded by Enrico Schleiff in 2021. 20 Nobel Prize winners have been affiliated with the university, including Max von Laue and Max Born. The university is also affiliated with 18 winners of the Gottfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Hamburg
The University of Hamburg (, also referred to as UHH) is a public university, public research university in Hamburg, Germany. It was founded on 28 March 1919 by combining the previous General Lecture System ('':de:Allgemeines Vorlesungswesen, Allgemeines Vorlesungswesen''), the Hamburg Colonial Institute ('':de:Hamburgisches Kolonialinstitut, Hamburgisches Kolonialinstitut''), and the Academic College ('':de:Akademisches Gymnasium (Hamburg), Akademisches Gymnasium''). The main campus is located in the central district of Rotherbaum, with affiliated institutes and research centres distributed around the city-state. Seven Nobel Prize winners and one Wolf Prize winner are affiliated with UHH. History Founding At the beginning of the 20th century, wealthy individuals made several unsuccessful petitions to the Hamburg Senate and Parliament requesting the establishment of a university. Senator Werner von Melle worked towards the merging of existing institutions into one university, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Otto Stern
:''Otto Stern was also the pen name of German women's rights activist Louise Otto-Peters (1819–1895)''. Otto Stern (; 17 February 1888 – 17 August 1969) was a German-American physicist. He is the second most nominated person for a Nobel Prize, with 82 nominations during the years 1925–1945. In 1943, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his contribution to the development of the molecular ray method and his discovery of the magnetic moment of the proton". Biography Otto Stern () was born into a Jewish family in Sohrau (now Żory) in the Province of Silesia, the German Empire's Kingdom of Prussia. His father was Oskar Stern (; 1850–1919), a mill owner, who had been living in Breslau (now Wrocław) since 1892. His mother Eugenia née Rosenthal (; 1863–1907) was from Rawitsch (now Rawicz) in the Prussian Province of Posen. Otto Stern had a brother, Kurt, who became a noted botanist in Frankfurt, and three sisters. He studied in Freiburg im Breisgau, Munich a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electric Dipole Moment
The electric dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative electrical charges within a system: that is, a measure of the system's overall Chemical polarity, polarity. The International System of Units, SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb-metre (C⋅m). The debye (D) is another unit of measurement used in atomic physics and chemistry. Theoretically, an electric dipole is defined by the first-order term of the multipole expansion; it consists of two equal and opposite charges that are infinitesimally close together, although real dipoles have separated charge.Many theorists predict elementary particles can have very tiny electric dipole moments, possibly without separated charge. Such small dipoles make no difference to everyday physics, and have not yet been observed (see ''Electron electric dipole moment''). However, when making measurements at a distance much larger than the charge separation, the dipole gives a good approximation of the actua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
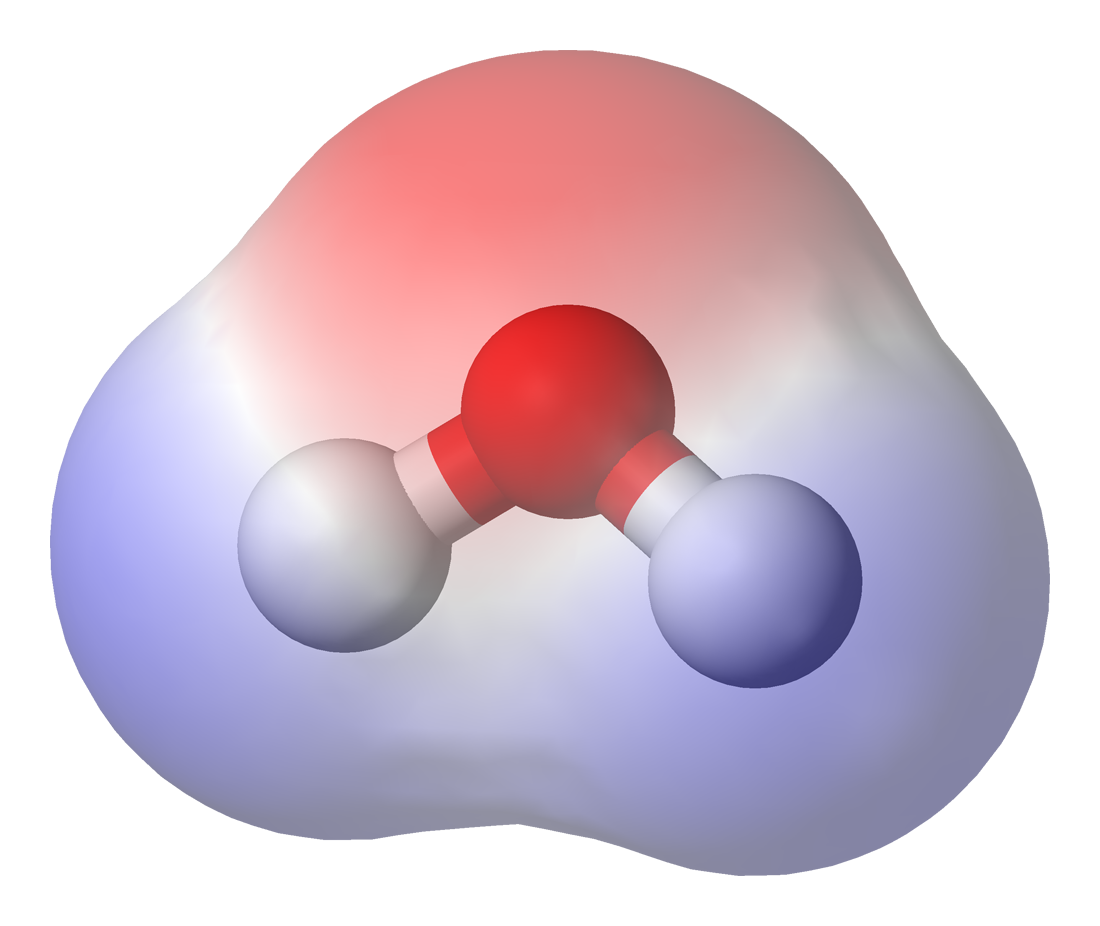
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |