|
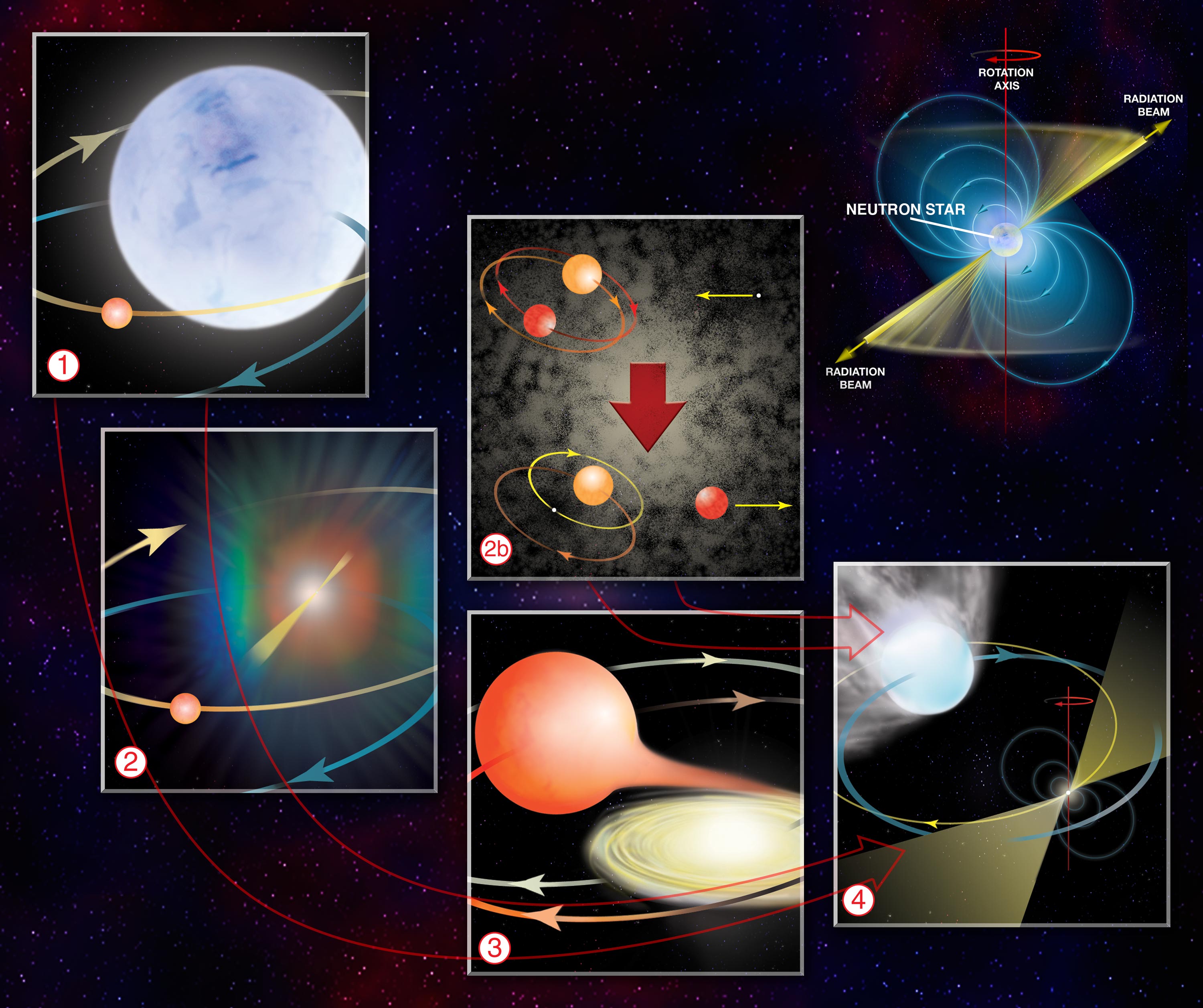
Millisecond Pulsar
A millisecond pulsar (MSP) is a pulsar with a rotational period less than about 10 milliseconds. Millisecond pulsars have been detected in radio pulsar, radio, X-ray pulsar, X-ray, and gamma ray portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The leading hypothesis for the origin of millisecond pulsars is that they are old, rapidly rotating neutron stars that have been spun up or "recycled" through Accretion (astrophysics), accretion of matter from a companion star in a close binary system. For this reason, millisecond pulsars are sometimes called recycled pulsars. Origins Millisecond pulsars are thought to be related to low-mass X-ray binary systems. It is thought that the X-rays in these systems are emitted by the accretion disk of a neutron star produced by the outer layers of a companion star that has overflowed its Roche lobe. The transfer of angular momentum from this accretion event can increase the rotation rate of the pulsar to hundreds of times per second, as is observed in mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Santa Cruz
The University of California, Santa Cruz (UC Santa Cruz or UCSC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Santa Cruz, California, United States. It is one of the ten campuses in the University of California system. Located in Monterey Bay, on the edge of the coastal community of Santa Cruz, the main campus lies on of rolling, forested hills overlooking the Pacific Ocean. As of Fall 2024, its ten residential colleges enroll some 17,940 undergraduate and 1,998 graduate students. Satellite facilities in other Santa Cruz locations include the Coastal Science Campus and the Westside Research Park and the Silicon Valley Center in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, along with administrative control of the Lick Observatory near San Jose, California, San Jose in the Diablo Range and the W. M. Keck Observatory, Keck Observatory near the summit of Mauna Kea in Hawaii. Founded in 1965, UC Santa Cruz uses a residential college system consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Radiation
Gravitational waves are oscillations of the gravitational field that travel through space at the speed of light; they are generated by the relative motion of gravitating masses. They were proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves. In 1916, Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, instead asserting that gravity has instantaneous effect everywhere. Gravitational waves therefore stand as an important relativistic phenomenon that is absent from Newtonian physics. Gravitational-wave astronomy has the advantage that, unlike electromagnetic radiation, gravitational waves are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSR J1748-2446ad
PSR may refer to: Organizations * Pacific School of Religion, Berkeley, California, US * Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research * Payment Systems Regulator in the United Kingdom * Physicians for Social Responsibility, US Political parties * Revolutionary Socialist Party (Portugal) (''Partido Socialista Revolucionário'') * Romanian Socialist Party (present-day) * Polish Reason of State Places * Abruzzo Airport (IATA airport code), near Pescara, Italy * Pasir Ris MRT station (MRT station abbreviation), Singapore * Pioneer Scout Reservation, a Boy Scout camp in Ohio, US Science and technology * Pulsar, a kind of star * Primary radar * Perimeter surveillance radar * Posthumous sperm retrieval, from dead men Computing * PHP Standard Recommendation * Predictive state representation of a system * Problem Steps Recorder, psr.exe, a Microsoft utility * Panel self-refresh, in Embedded DisplayPort Law enforcement and military * US Precision Sniper Rifle * PSR-9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Backer
Donald Charles Backer (November 9, 1943 – July 25, 2010) was an American astrophysicist who primarily worked in radio astronomy. Backer made important contributions to the understanding and study of pulsars (including the discovery of the first millisecond pulsar), black holes, and the epoch of reionization. Biography Backer was born in Plainfield, New Jersey. He attended Cornell University, where he earned a Bachelor's degree in engineering physics (B.E.P.) from Cornell University in 1966. He received a Master of Science degree in radio astronomy from Manchester University in 1968, and then returned to Cornell to earn his doctorate in astronomy in 1971. Backer then took post-doctoral positions first at NRAO in Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia (1971–1973), and then at NASA/GSFC in Greenbelt, Maryland, Greenbelt, Maryland (1973–1975). In 1975, Backer moved to the University of California, Berkeley as a research astronomer in the Radio Astronomy Laboratory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Star Cluster Terzan 5
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 15
Messier 15 or M15 (also designated NGC 7078 and sometimes known as the Great Pegasus Cluster) is a globular cluster in the constellation Pegasus (constellation), Pegasus. It was discovered by Jean-Dominique Maraldi in 1746 and included in Charles Messier's catalogue of comet-like objects in 1764. At an estimated billion years old, it is one of the oldest known globular clusters. Characteristics M 15 is about 35,700 light-years from Earth, and 175 light-years in diameter. It has an absolute magnitude of −9.2, which translates to a total luminosity of 360,000 times that of the Sun. Messier 15 is one of the most densely packed globulars known in the Milky Way galaxy. Its core has undergone a contraction known as "Core collapse (cluster), core collapse" and it has a central density cusp with an enormous number of stars surrounding what may be a central black hole. Home to over 100,000 stars,the cluster is notable for containing a large number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier 28
Messier 28 or M28, also known as NGC 6626, is a globular cluster of stars in the center-west of Sagittarius. It was discovered by French astronomer Charles Messier in 1764. He briefly described it as a "nebula containing no star... round, seen with difficulty in 3-foot telescope; Diam 2′." In the sky it is less than a degree to the northwest of the 3rd magnitude star Kaus Borealis (Lambda ). This cluster is faintly visible as a hazy patch with a pair of binoculars and can be readily found in a small telescope with an aperture, showing as a nebulous feature spanning 11.2 arcminutes. Using an aperture of , the core becomes visible and a few distinct stars can be resolved, along the periphery. Larger telescopes will provide greater resolution, one of revealing a dense 2′ core, with more density within. It is about 18,300 light-years away from Earth. It is about and its metallicity (averaging −1.32 which means more than 10 times less than our own star), coherency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae or 47 Tuc (also designated as NGC 104 and Caldwell 106) is a globular cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It is about from Earth, and 120 light years in diameter. 47 Tuc can be seen with the naked eye, with an apparent magnitude of 4.1. It appears about 44 arcminutes across including its far outreaches. Due to its far southern location, 18° from the south celestial pole, it was not catalogued by European astronomers until the 1750s, when the cluster was first identified by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille from South Africa. 47 Tucanae is the second brightest globular cluster after Omega Centauri, and telescopically reveals about ten thousand stars, many appearing within a small dense central core. The cluster may contain an intermediate-mass black hole. Early history The cluster was recorded in 1751-2 by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille, who initially thought it was the nucleus of a bright comet. Lacaille then listed it as "Lac I-1", the first object listed in his dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terzan 5
Terzan 5 is a heavily obscured globular cluster belonging to the bulge (the central star concentration) of the Milky Way galaxy. It was one of six globulars discovered by French astronomer Agop Terzan in 1968 and was initially labeled ''Terzan 11''. The cluster was cataloged by the Two-Micron Sky Survey as IRC–20385. It is situated in the Sagittarius constellation in the direction of the Milky Way's center. Terzan 5 probably follows an unknown complicated orbit around the center of the galaxy, but currently it is moving towards the Sun with a speed of around 90 km/s. Physical properties The absolute magnitude of Terzan 5 is at least . Its bolometric luminosity is about 800,000 times that of the Sun, while its mass is about 2 million solar masses. The small core of Terzan 5—about 0.5 pc in size—has one of the highest star densities in the galaxy. Its volume mass density exceeds , while its volume luminosity density exceeds , where and are the Sun's mass and lum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science Foundation (NSF). The observatory's main instrument was the Arecibo Telescope, a spherical reflector dish built into a natural sinkhole, with a cable-mount steerable receiver and several radar transmitters for emitting signals mounted above the dish. Completed in 1963, it was the world's largest single-aperture telescope for 53 years, surpassed in July 2016 by the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) in China. On August 10 and November 6, 2020, two of the receiver's support cables broke and the NSF announced that it would decommission the telescope. The telescope collapsed on December 1, 2020. In 2022, the NSF announced the telescope will not be rebuilt, with an educational facility to be established on the site. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |