|
Microenvironment (biology)
The tumor microenvironment is a complex ecosystem surrounding a tumor, composed of cancer cells, stromal tissue (including blood vessels, immune cells, fibroblasts and signaling molecules) and the extracellular matrix. Mutual interaction between cancer cells and the different components of the tumor microenvironment support its growth and invasion in healthy tissues which correlates with tumor resistance to current treatments and poor prognosis. The tumor microenvironment is in constant change because of the tumor's ability to influence the microenvironment by releasing extracellular signals, promoting tumor angiogenesis and inducing peripheral immune tolerance, while the immune cells in the microenvironment can affect the growth and evolution of cancerous cells. History The concept of the tumor microenvironment (TME) dates back to 1863 when Rudolf Virchow established a connection between inflammation and cancer. However, it was not until 1889 that Stephen Paget's seed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs; "innate T cell-like" cells involved in mucosal immunity and homeostasis), of which natural killer cells are an important subtype (which functions in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte" (with ''cyte'' meaning cell). Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. They can also be classified as small lymphocytes and large lymphocytes based on their size and appearance. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
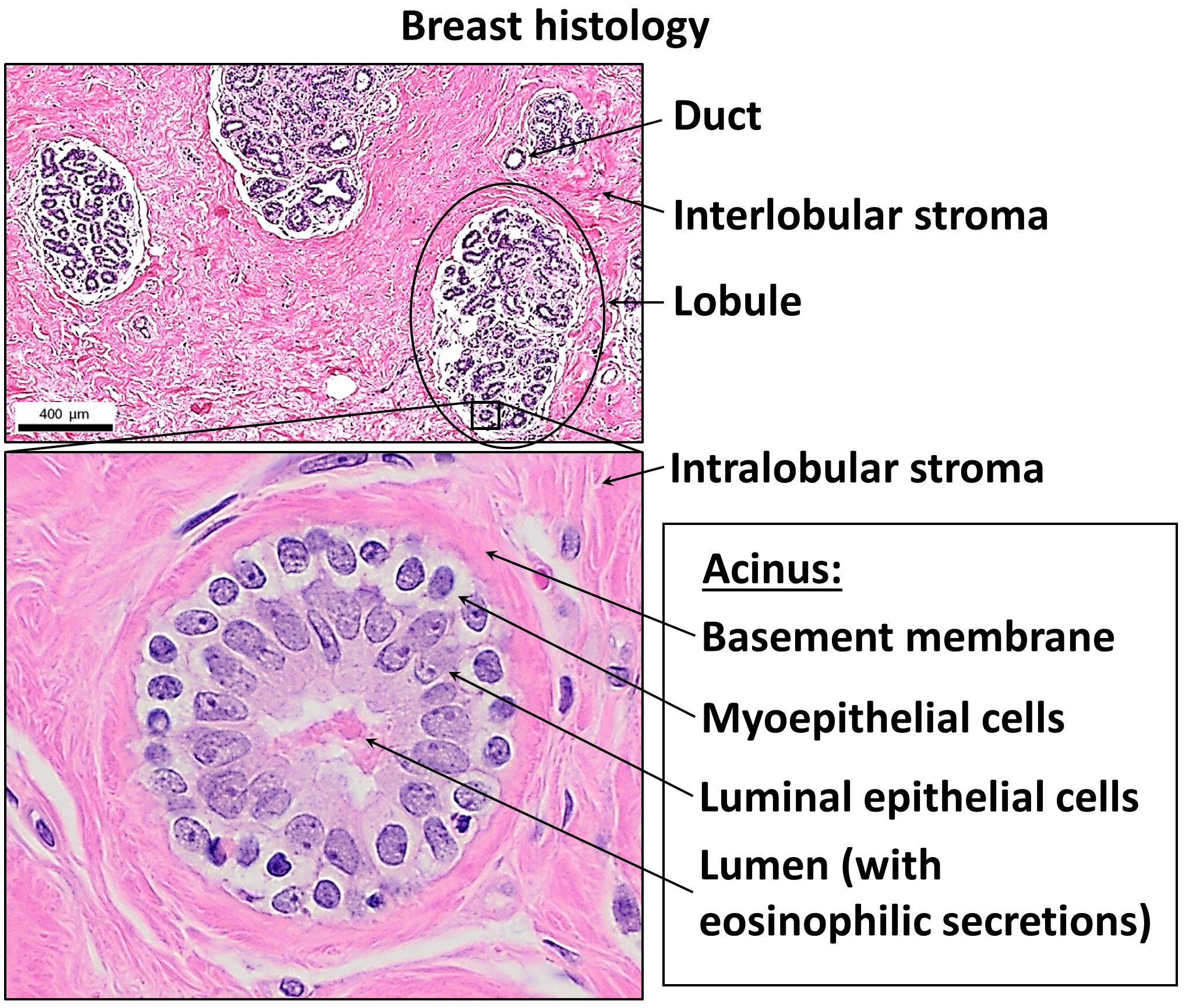
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericytes
Pericytes (formerly called Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood capillaries, where they communicate with endothelial cells by means of both direct physical contact and paracrine signaling. The morphology, distribution, density and molecular fingerprints of pericytes vary between organs and vascular beds. Pericytes help in the maintainenance of homeostatic and hemostatic functions in the brain, where one of the organs is characterized with a higher pericyte coverage, and also sustain the blood–brain barrier. These cells are also a key component of the neurovascular unit, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons. Pericytes have been postulated to regulate capillary blood flow and the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris ''in vitro.'' Pericytes stabilize and monitor the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymph is a clear fluid carried by the lymphatic vessels back to the heart for re-circulation. The Latin word for lymph, , refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha". Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through Starling equation, capillary filtration, which removes blood plasma, plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of Cystine knot, cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the ''De novo synthesis, de novo'' formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). It is part of the system that restores the oxygen supply to tissues when blood circulation is inadequate such as in hypoxic conditions. Serum concentration of VEGF is high in bronchial asthma and diabetes mellitus. VEGF's normal function is to create new blood vessels during embryonic development, new blood vessels after injury, muscle following exercise, and new vessels (collateral circulation) to bypass blocked vessels. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia-inducible Factor
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are transcription factors that respond to decreases in available oxygen in the cellular environment, or hypoxia. They also respond to instances of pseudohypoxia, such as thiamine deficiency. Both hypoxia and pseudohypoxia leads to impairment of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production by the mitochondria. Discovery The HIF transcriptional complex was discovered in 1995 by Gregg L. Semenza and postdoctoral fellow Guang Wang. In 2016, William Kaelin Jr., Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza were presented the Lasker Award for their work in elucidating the role of HIF-1 in oxygen sensing and its role in surviving low oxygen conditions. In 2019, the same three individuals were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work in elucidating how HIF senses and adapts cellular response to oxygen availability. Structure Oxygen-breathing species express the highly conserved transcriptional complex HIF-1, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Transport
Passive transport is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes. Instead of using cellular energy, like active transport, passive transport relies on the second law of thermodynamics to drive the movement of substances across cell membranes. Fundamentally, substances follow Fick's first law, and move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration because this movement increases the entropy of the overall system. The rate of passive transport depends on the permeability of the cell membrane, which, in turn, depends on the organization and characteristics of the membrane lipids and proteins. The four main kinds of passive transport are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, filtration, and/or osmosis. Passive transport follows Fick's first law. Diffusion Diffusion is the net movement of material from an area of high concentration to an area with lower concentration. The difference of concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |