|
Metropolitan Ethernet
A metropolitan-area Ethernet, Ethernet MAN, carrier Ethernet or metro Ethernet network is a metropolitan area network (MAN) that is based on :Ethernet standards, Ethernet standards. It is commonly used to connect subscribers to a larger service network or for internet access. Businesses can also use metropolitan-area Ethernet to connect their own offices to each other. An Ethernet interface is typically more economical than a synchronous digital hierarchy (SONET/SDH) or plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) interface of the same bandwidth. Another distinct advantage of an Ethernet-based access network is that it can be easily connected to the customer network, due to the prevalent use of Ethernet in corporate and residential networks. A typical Internet_service_provider, service provider's network is a collection of Network switch, switches and Router (computing), routers connected through optical fiber. The Network topology, topology could be a Ring network, ring, hub-and-spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Metro-5200
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100 Gigabit Ethernet
40 Gigabit Ethernet (40GbE) and 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) are groups of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at rates of 40 and 100 gigabits per second (Gbit/s), respectively. These technologies offer significantly higher speeds than 10 Gigabit Ethernet. The technology was first defined by the IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3ba-2010 standard and later by the 802.3bg-2011, 802.3bj-2014, 802.3bm-2015, and 802.3cd-2018 standards. The first succeeding Terabit Ethernet specifications were approved in 2017. The standards define numerous port types with different optical and electrical interfaces and different numbers of optical fiber strands per port. Short distances (e.g. 7 m) over twinaxial cable are supported while standards for fiber reach up to 80 km. Standards development On July 18, 2006, a call for interest for a High Speed Study Group (HSSG) to investigate new standards for high speed Ethernet was held at the IEEE 802.3 plenary meeting in Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PBB-TE
Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering (PBB-TE) is a computer networking technology specified in IEEE 802.1Qay, an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q standard. PBB-TE adapts Ethernet to carrier class transport networks. It is based on the layered VLAN tags and MAC-in-MAC encapsulation defined in IEEE 802.1ah (Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB)), but it differs from PBB in eliminating flooding, dynamically created forwarding tables, and spanning tree protocols. Compared to PBB and its predecessors, PBB-TE behaves more predictably and its behavior can be more easily controlled by the network operator, at the expense of requiring up-front connection configuration at each bridge along a forwarding path. PBB-TE Operations, Administration, and Management (OAM) is usually based on IEEE 802.1ag. It was initially based on Nortel's Provider Backbone Transport (PBT). PBB-TE's connection-oriented features and behaviors, as well as its OAM approach, are inspired by SDH/SONET. PBB-TE can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet In The First Mile
Ethernet in the first mile (EFM) refers to using one of the Ethernet family of computer network technologies between a telecommunications company and a customer's premises. From the customer's point of view, it is their first mile, although from the access network's point of view it is known as the last mile. A working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) produced the standards known as IEEE 802.3ah-2004, which were later included in the overall standard IEEE 802.3-2008. EFM is often used in active optical network deployments. Although it is often used for businesses, it can also be known as Ethernet to the home (ETTH). One family of standards known as Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) uses a passive optical network. History With wide, metro, and local area networks using various forms of Ethernet, the goal was to eliminate non-native transport such as Ethernet over Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) from access networks. One early effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
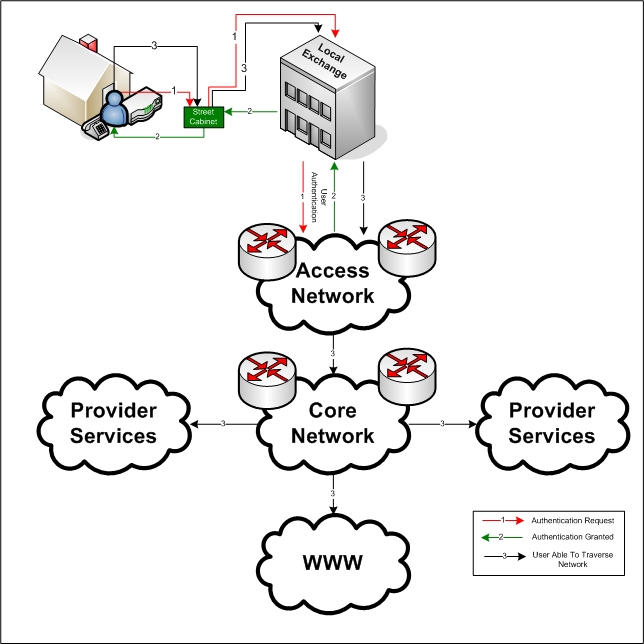
Telephone Exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers. The term "central office" can also refer to a central location for fiber optic equipment for a fiber internet provider. In historical perspective, telecommunication terminology has evolved with time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. A central office is defined as the telephone switch controlling connections for one or more central office prefixes. However, it also often denotes the building used to house the inside plant equipment for multiple telephone exchange areas. In North America, the term ''wire center'' may be used to denote a central office location, indicating a facility that provides a telephone with a dial tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outside Plant
In telecommunications, the term outside plant has the following meanings: *In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure (such as conduit, cabinets, tower or poles), and any associated hardware (such as repeaters) located between a demarcation point in a switching facility and a demarcation point in another switching center or customer premises. *In the United States, the DOD defines outside plant as the communications equipment located between a main distribution frame (MDF) and a user end instrument. The CATV industry divides its fixed assets between head end or inside plant, and outside plant. The electrical power industry also uses the term outside plant to refer to electric power distribution systems. Context Network connections between devices such as computers, printers, and phones require a physical infrastructure to carry and process signals. Typically, this infrastructure will consist o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Line Terminal
An optical line termination (OLT), also called an optical line terminal, is a device which serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network. It provides two main functions: # to perform conversion between the electrical signals used by the service provider's equipment and the fiber optic signals used by the passive optical network. # to coordinate the multiplexing between the conversion devices on the other end of that network (called either optical network terminals or optical network units). In general, an OLT is akin to a Network Switch where each port represents one or more client ONT or a node. Each port may be attached to the boards or network/line cards via a SFP module which must be a OLT module for it to have its Tx and Rx wavelengths swapped, but not all OLTs use SFP modules as shown in the image to the left. OLTs are either found at the ISP level inside a cabinet or distribution point, or customer level for connecting ONTs locally, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber To The X
Fiber to the ''x'' (FTTX; also spelled "fibre") or fiber in the loop is a generic term for any broadband network architecture using optical fiber to provide all or part of the local loop used for last mile telecommunications. As fiber optic cables are able to carry much more data than copper cables, especially over long distances, copper telephone networks built in the 20th century are being replaced by fiber. The carrier equipment for FTTx is often housed in a "fiber hut", point of presence or central office. FTTX is a generalization for several configurations of fiber deployment, arranged into two groups: FTTP/FTTH/FTTB (fiber laid all the way to the premises/home/building) and FTTC/N (fiber laid to the cabinet/node, with copper wires completing the connection). Residential areas already served by balanced pair distribution plant call for a trade-off between cost and capacity. The closer the fiber head, the higher the cost of construction and the higher the channel capa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Subscriber Line
Digital subscriber line (DSL; originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology, for Internet access. In ADSL, the data throughput in the upstream (networking), upstream direction (the direction to the service provider) is lower, hence the designation of ''asymmetric'' service. In symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL) services, the downstream and upstream data rates are equal. DSL service can be delivered simultaneously with plain old telephone service, wired telephone service on the same telephone line since DSL uses higher frequency bands for data transmission. On the customer premises, a DSL filter is installed on each telephone to prevent undesirable interaction between DSL and telephone service. The bit rate of consumer ADSL services typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Optical Network
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications network that uses only ''unpowered'' devices to carry signals, as opposed to electronic equipment. In practice, PONs are typically used for the '' last mile'' between Internet service providers (ISP) and their customers. In this use, a PON has a point-to-multipoint topology in which an ISP uses a single device to serve many end-user sites using a system such as 10G-PON or GPON. In this one-to-many topology, a single fiber serving many sites branches into multiple fibers through a passive splitter, and those fibers can each serve multiple sites through further splitters. The light from the ISP is divided through the splitters to reach all the customer sites, and light from the customer sites is combined into the single fiber. Many fiber ISPs prefer this system. Components and characteristics A passive optical network consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Distribution Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Network Terminal
upTwo simple NIDs, carrying six lines each, on the outside of a building upA German copper phone line termination box called '':de:Abschlusspunkt Linientechnik, Abschlusspunkt LinienTechnik'' (APL, "Demarcation point") In telecommunications, a network interface device (NID; also known by several other names) is a device that serves as the demarcation point between the carrier's local loop and the customer's premises wiring. Outdoor telephone NIDs also provide the subscriber with access to the station wiring and serve as a convenient test point for verification of loop integrity and of the subscriber's inside wiring. Naming Generically, an NID may also be called a network interface unit (NIU), telephone network interface (TNI), system network interface (SNI), or telephone network box. Australia's National Broadband Network uses the term '' network termination device'' or NTD. A smartjack is a type of NID with capabilities beyond simple electrical connection, such as diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |