|
Mesothelial
The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura (pleural cavity around the lungs), peritoneum (abdominopelvic cavity including the mesentery, omenta, falciform ligament and the perimetrium) and pericardium (around the heart). Mesothelial tissue also surrounds the male testis (as the tunica vaginalis) and occasionally the spermatic cord (in a patent processus vaginalis). Mesothelium that covers the internal organs is called visceral mesothelium, while one that covers the surrounding body walls is called the parietal mesothelium. The mesothelium that secretes serous fluid as a main function is also known as a serosa. Origin Mesothelium derives from the embryonic mesoderm cell layer, that lines the coelom (body cavity) in the embryo. It develops into the layer of cells that covers and protects most of the internal organs of the body. Structure The mesothelium forms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Cavity
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient. The serous membrane that covers the surface of the lung is the visceral pleura and is separated from the outer membrane, the parietal pleura, by just the film of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity. The visceral pleura follows the fissures of the lung and the root of the lung structures. The parietal pleura is attached to the mediastinum, the upper surface of the diaphragm, and to the inside of the ribcage. Structure In humans, the left and right lungs are completely separated by the mediastinum, and there is no communication between their pleural cavities. Therefore, in cases of a unilateral pneumothorax, the contralateral lung will remain functioning n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
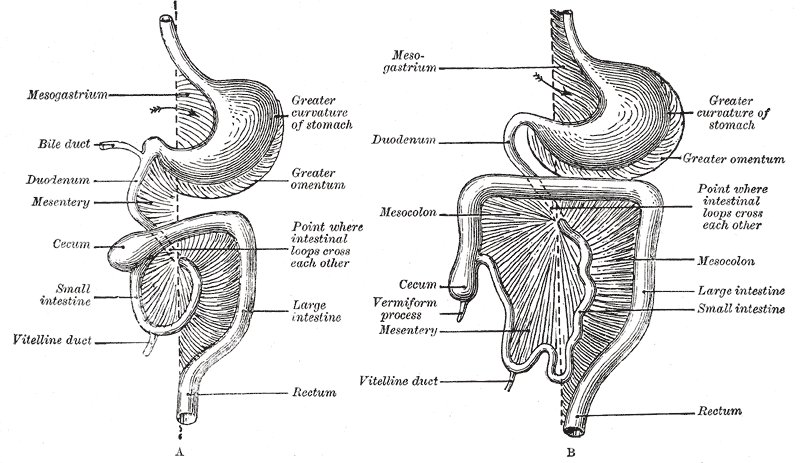
Mesentery
In human anatomy, the mesentery is an Organ (anatomy), organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall, consisting of a double fold of the peritoneum. It helps (among other functions) in storing Adipose tissue, fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines. The (the part of the mesentery that attaches the colon to the abdominal wall) was formerly thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopy, microscopic and electron microscope, electron microscopic histology, examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdomen#Contents, abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intrape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleura
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane. The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of each lung is often called the visceral pleura. This can lead to some confusion, as the lung is not the only visceral organ covered by the pleura. The pleura typically dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each thoracic sac during embryonic development. The portion of the pleura seen as the outer layer covers the chest wall, the diaphragm and the mediastinum and is often also misleadingly called the parieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organ (anatomy), organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal Tissue (biology), tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix ''peri-'' (περί) 'around' and the suffix ''-cardion'' (κάρδιον) 'heart'. Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of the transcription facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica (biology)
In biology, a tunica (, ; : tunicae) is a layer, coat, sheath, or similar covering. The word came to English from the Neo-Latin of science and medicine. Its literal sense is about the same as that of the word ''tunic'', with which it is cognate. In biology, one of its senses used to be the taxonomic name of a genus of plants, but the nomenclature has been revised and those plants are now included in the genus '' Petrorhagia''. In modern biology in general, ''tunica'' occurs as a technical or anatomical term mainly in botany and zoology. It usually refers to membranous structures that line or cover particular organs. In many such contexts, ''tunica'' is used interchangeably with ''tunic'' according to preference. An organ or organism that has a tunic(a) may be said to be ''tunicate'', as in a ''tunicate bulb''. This adjective ''tunicate'' is not to be confused with the noun ''tunicate'', which refers to a member of the subphylum '' Tunicata''. Botanical and related usages In botany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visceral
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processus Vaginalis
The vaginal process (or processus vaginalis) is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the parietal peritoneum. It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching. Sex differences In males, it precedes the testes in their descent down within the gubernaculum, and closes. This closure (also called ''fusion'') occurs at any point from a few weeks before birth, to a few weeks after birth. The remaining portion around the testes becomes the tunica vaginalis. If it does not close in females, it forms the canal of Nuck. Clinical significance Failure of closure of the vaginal process leads to the propensity to develop a number of abnormalities. Peritoneal fluid can travel down a patent vaginal process leading to the formation of a hydrocele. Persistent patent processus vaginalis is more common on the right than the left. Accumulation of blood in a persistent processus vaginalis could result in a hematocele. There is the potential for an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |