|
Mepronil
Mepronil is a fungicide used as a seed treatment or Pesticide application, foliar spray in agriculture to protect crops from fungal diseases. It was first marketed by Kumiai Chemical Industries in 1981 using their brand name Basitac. The compound is a benzanilide which combines 2-methylbenzoic acid with the O-isopropyl derivative of 3-aminophenol to give an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase (SDHI). History Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase, the complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain, has been known as a fungicidal mechanism of action since the first examples were marketed in the 1960s. The first compound in this class was carboxin, which had a narrow spectrum of useful biological activity, mainly on basidiomycetes and was used as a seed treatment. Many further examples of this mechanism of action were developed by crop protection companies seeking compounds with improved properties and mepronil was developed owing to its effectiveness as a foliar application and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinate Dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Histochemical analysis showing high succinate dehydrogenase in muscle demonstrates high mitochondrial content and high oxidative potential. In step 6 of the citric acid cycle, SQR catalyzes the oxidation of succinate to fumarate with the reduction of ubiquinone to ubiquinol. This occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane by coupling the two reactions together. Structure Subunits Mitochondrial and many bacterial SQRs are composed of four structurally different subunits: two hydrophilic and two hydrophobic. The first two subunits, a flavoprotein (SDHA) and an iron-sulfur protein (SDHB), form a hydrophilic head where enzymatic activity of the complex takes place. SD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Treatment
A seed treatment is a treatment of the seed with either chemical agents or biological or by physical methods. Usually done to provide protection to the seed and improve the establishment of healthy crops. Not to be confused with a seed coating. In agriculture and horticulture, coating of the seed is the process of applying exogenous materials to the seed. Also referred to as seed dressing. A seed coating is the layer of material added to the seed, which may or may not contain a "protectant" (biological or chemical pesticide) or biostimulant applied to the seed and possibly some color... By the amount of material added, it can be divided into: * A Film coating, a layer of thin film applied to the seed typically less than 10% of the mass of the original seed. * Encrustment, where the applied material is typically 100%–500% of the original seed mass, but the shape is still discernible. * Pellet, where the applied material is so thick that the seed's original shape is not dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoctonia Solani
''Rhizoctonia solani'' is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name ''Rhizoctonia solani'' is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, ''Rhizoctonia solani'' is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids. Taxonomy In 1858, the German plant pathologist Julius Kühn observed and described a fungus on diseased potato tubers and named it ''Rhizoctonia solani'', the species epithet referring to ''Solanum tuberosum'' (potato). The disease caused was well known before the discovery and description of the fungus. In 1956, Dutch mycologist M.A. Donk published the new name ''Thanatephorus cucume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicides
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
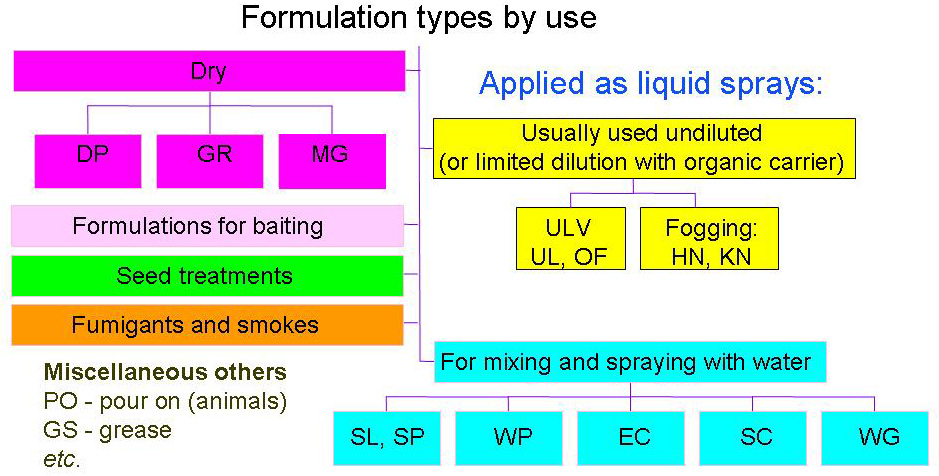
Pesticide Formulation
The biological activity of a pesticide, be it chemical or biological in nature, is determined by its active ingredient (AI - also called the ''active substance''). Pesticide products very rarely consist of the pure active ingredient. The AI is usually formulated with other materials (adjuvents and co-formulants) and this is the product as sold, but it may be further diluted in use. Formulations improve the properties of a chemical for handling, storage, application and may substantially influence effectiveness and safety. Formulation terminology follows a 2-letter convention: (''e.g.'' GR: granules) listed by CropLife International (formerly GIFAP then GCPF) in the ''Catalogue of Pesticide Formulation Types'' (Monograph 2); see download page Some manufacturers do not follow these industry standards, which can cause confusion for users. Water-miscible formulations By far the most frequently used products are formulations for mixing with water then applying as sprays. Water miscibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trivial Name
In chemistry, a trivial name is a non-systematic name for a chemical substance. That is, the name is not recognized according to the rules of any formal system of chemical nomenclature such as IUPAC inorganic or IUPAC organic nomenclature. A trivial name is not a formal name and is usually a common name. Generally, trivial names are not useful in describing the essential properties of the thing being named. Properties such as the molecular structure of a chemical compound are not indicated. And, in some cases, trivial names can be ambiguous or will carry different meanings in different industries or in different geographic regions (for example, a trivial name such as '' white metal'' can mean various things). Trivial names are simpler. As a result, a limited number of trivial chemical names are retained names, an accepted part of the nomenclature. Trivial names often arise in the common language; they may come from historic usages in, for example, alchemy. Many trivial name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Organization For Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and () it has published over 25,000 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has over 800 technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees (SCs) to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes international standards in technical and nontechnical fields, including everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, transport, IT, agriculture, and healthcare. More specialized topics like electrical and electronic engineering are instead handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms." Entomologists and ecologists have urged the adoption of IPM pest control since the 1970s. IPM is a safer pest control framework than reliance on the use of chemical pesticides, mitigating risks such as: insecticide-induced resurgence, pesticide resistance and (especially food) crop residues.Bateman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide Resistance
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Puccinia Species
This is a list of the fungus species in the genus ''Puccinia''. Members of this genus are plant pathogen, pathogens on all major cereal crop species except rice, and some cause large economic losses. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the widespread genus contains about 4000 species. There were an estiamated 3300 species as accepted by Wijayawardene et al. 2020. , the GBIF lists up to 3,259 species, while Species Fungorum lists about 3251 species (with many former species). The Encyclopedia of Life lists 3,192 species. This list is based on the Species Fungorum list in 2023. A *''Puccinia abchazica'' *''Puccinia abei'' *''Puccinia aberrans'' *''Puccinia abnormis'' *''Puccinia abramoviana'' *''Puccinia abramsii'' *''Puccinia abrepta'' *''Puccinia abrotani'' *''Puccinia abrupta'' *''Puccinia absicca'' *''Puccinia abundans'' *''Puccinia abutiloides'' *''Puccinia abutilonis'' *''Puccinia abyssinica'' *''Puccinia acalyphae'' *''Puccinia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |