|
Membrane Protrusion
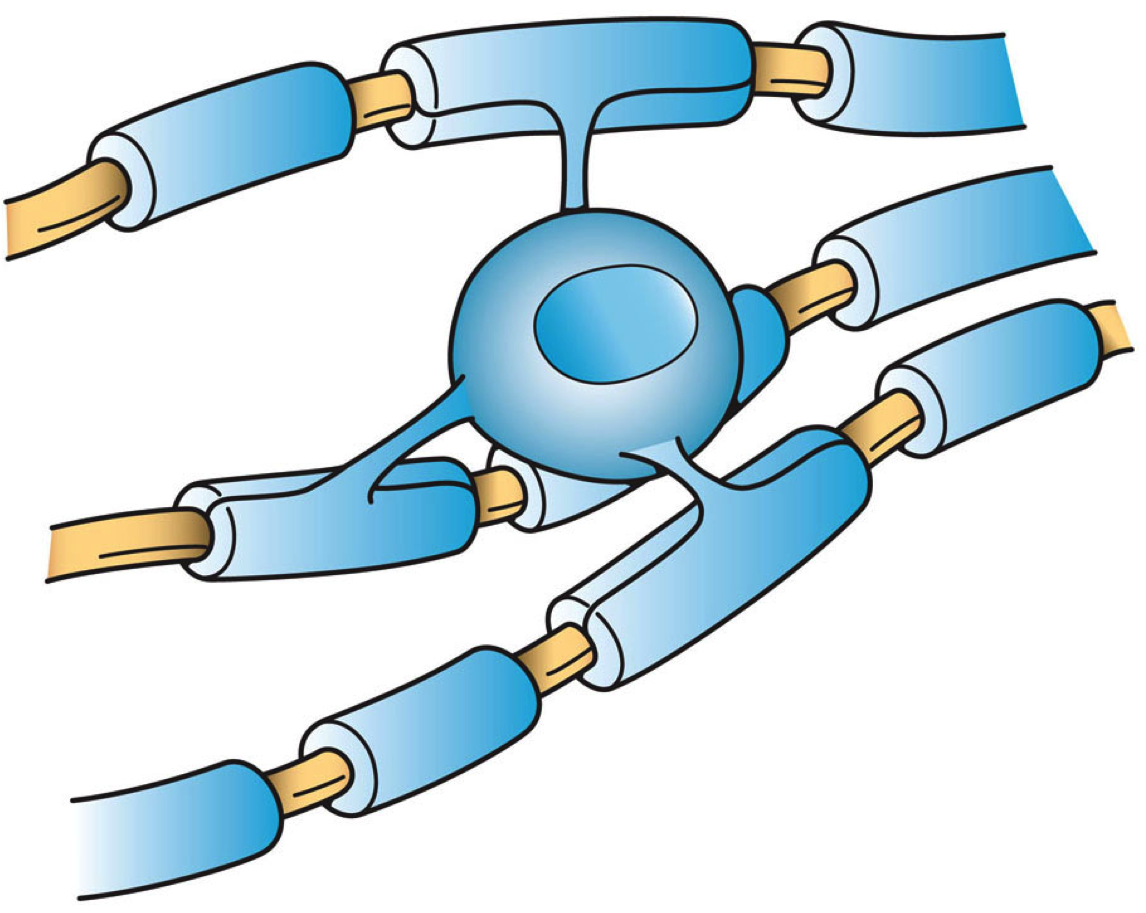
Cellular extensions also known as cytoplasmic protrusions and cytoplasmic processes are those structures that project from different cells, in the body, or in other organisms. Many of the extensions are cytoplasmic protrusions such as the axon and dendrite of a neuron, known also as cytoplasmic processes. Different glial cells project cytoplasmic processes. In the brain, the processes of astrocytes form terminal endfeet, foot processes that help to form protective barriers in the brain. In the kidneys specialised cells called podocytes extend processes that terminate in podocyte foot processes that cover capillaries in the nephron. End-processes may also be known as ''vascular footplates'', and in general may exhibit a pyramidal or finger-like morphology. Mural cells such as pericytes extend processes to wrap around capillaries. Foot-like processes are also present in Müller glia (modified astrocytes of the retina), pancreatic stellate cells, dendritic cells, oligodendro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in the human body. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes (that produce myelin), astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells (that produce myelin), and satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: * to surround neurons and hold them in place * to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons * to insulate one neuron from another * to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and synaptic connections, and in physiological processes such as breathing. While glia we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podocyte Foot Processes
Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus. Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine. Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes, which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule. The podocytes have long primary processes called ''trabeculae'' that form secondary processes known as ''pedicels'' or foot processes (for which the cells are named '' podo-'' + '' -cyte''). The pedicels wrap around the capillaries and leave slits between them. Blood is filtered through these slits, each known as a filtration slit, slit diaphragm, or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocyte Endfeet
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to around 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) and in the peripheral nervous system that do not produce Action potential, electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural Tissue (biology), tissue in the human body. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes (that produce myelin), astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells (that produce myelin), and Satellite glial cell, satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: * to surround neurons and hold them in place * to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons * to Myelination, insulate one neuron from another * to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and Synapse, synaptic con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the CNS. Microglia originate in the yolk sac under tightly regulated molecular conditions. These cells (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenancethey are constantly scavenging the CNS for senile plaques, plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular pota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main function is to provide the myelin sheath to neuronal axons in the central nervous system (CNS). Myelination gives metabolic support to, and insulates the axons of most vertebrates. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its Cellular extensions, processes to cover up to 40 axons, that can include multiple adjacent axons. The myelin sheath is segmented along the axon's length at gaps known as the nodes of Ranvier. In the peripheral nervous system the myelination of axons is carried out by Schwann cells. Oligodendrocytes are found exclusively in the CNS, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. They are the most widespread cell lineage, including oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, pre-myelinating cells, and mature myelinating oligodendrocytes in the CNS white matter. Non-myelinating oligodendrocytes are found in the grey matter surrounding and lying next to neuronal cell bodies. They are known as neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Stellate Cell
Pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are classified as myofibroblast-like cells that are located in exocrine regions of the pancreas. PaSCs are mediated by paracrine and autocrine stimuli and share similarities with the hepatic stellate cell. Pancreatic stellate cell activation and expression of matrix molecules constitute the complex process that induces pancreatic fibrosis. Synthesis, deposition, maturation and remodelling of the fibrous connective tissue can be protective, however when persistent it impedes regular pancreatic function. Structure PaSCs are located within the peri-acinar spaces of the pancreas and extrude long cytoplasmic processes that surround the base of the acinus. PaSCs compose 4% of the total cell mass in the gland Stellate cells derive their name from their star shape and are located in other organs such as the kidney and lungs. The cells are located in periductal and perivascular regions of the pancreas and contain vitamin A lipid droplets in their cytoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the photographic film, film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by Chemical synapse, synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rod cell, rods and cone cell, cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Müller Glia
Müller glia, or Müller cells, are a type of retinal glial cells, first recognized and described by Heinrich Müller (physiologist), Heinrich Müller. They are found in the vertebrate retina, where they serve as support cells for the neurons, as all glial cells do. They are the most common type of glial cell found in the retina. While their cell bodies are located in the inner nuclear layer of the retina, they span across the entire retina. The major role of the Müller cells is to maintain the structural and functional stability of retinal cells. This includes regulation of the extracellular environment via uptake of neurotransmitters, removal of debris, regulation of K+ levels, storage of glycogen, electrical insulation of receptors and other neurons, and mechanical support of the neural retina. Development Müller glia are derived developmentally from two distinct populations of cells. The Müller glia cell is the only retinal glial cell that shares a common cell lineage w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
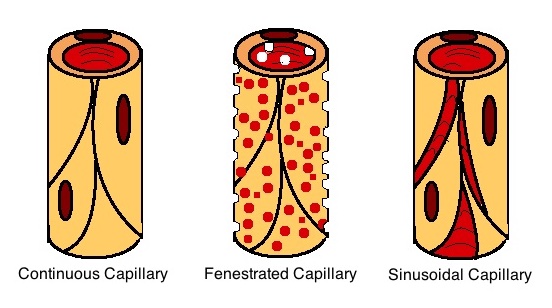
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericyte
Pericytes (formerly called Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood capillaries, where they communicate with endothelial cells by means of both direct physical contact and paracrine signaling. The morphology, distribution, density and molecular fingerprints of pericytes vary between organs and vascular beds. Pericytes help in the maintainenance of homeostatic and hemostatic functions in the brain, where one of the organs is characterized with a higher pericyte coverage, and also sustain the blood–brain barrier. These cells are also a key component of the neurovascular unit, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons. Pericytes have been postulated to regulate capillary blood flow and the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris ''in vitro.'' Pericytes stabilize and monitor the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |