|
Mausolea
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from the ) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Mausolea were historically, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres outside Rome. When Christianity became dominant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum At Halicarnassus At The Bodrum Museum Of Underwater Archaeology
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the Chamber tomb, burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's Cadaver, remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from the ) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Achaemenid Empire, Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Mausolea were historically, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in Necropolis, necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb
A tomb ( ''tumbos'') or sepulchre () is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called '' immurement'', although this word mainly means entombing people alive, and is a method of final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial. Overview The word is used in a broad sense to encompass a number of such types of places of interment or, occasionally, burial, including: * Architectural shrines – in Christianity, an architectural shrine above a saint's first place of burial, as opposed to a similar shrine on which stands a reliquary or feretory into which the saint's remains have been transferred * Burial vault – a stone or brick-lined underground space for multiple burials, originally vaulted, often privately owned for specific family groups; usually beneath a religious building such as a * Church * Cemetery * Churchyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum At Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus (; ) was a tomb built between 353 and 351 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Persian Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed , such as the Nereid Monument. The Mausoleum was approximately in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors: Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros, and Timotheus. The Mausoleum contained 400 freestanding sculptures. The mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 12th to the 15th century; it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchyard
In Christian countries, a churchyard is a patch of land adjoining or surrounding a church (building), church, which is usually owned by the relevant church or local parish itself. In the Scots language and in both Scottish English and Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster Scots, this can also be known as a kirkyard. While churchyards can be any patch of land on church grounds, historically, they were often used as graveyards (burial places). Use of churchyards as a place of burial After the establishment of the parish as the centre of the Christian spiritual life, the possession of a cemetery, as well as the baptismal font, was a mark of parochial status. During the Middle Ages, religious orders also constructed cemeteries around their churches. Thus, the most common use of churchyards was as a consecration, consecrated burial ground known as a graveyard. Graveyards were usually established at the same time as the building of the relevant place of worship (which can date back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite, graveyard, or a green space called a memorial park or memorial garden, is a place where the remains of many death, dead people are burial, buried or otherwise entombed. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek language, Greek ) implies that the land is specifically designated as a burial ground and originally applied to the Ancient Rome, Roman catacombs. The term ''graveyard'' is often used interchangeably with cemetery, but a graveyard primarily refers to a burial ground within a churchyard. The intact or cremated remains of people may be interred in a grave, commonly referred to as burial, or in a tomb, an "above-ground grave" (resembling a sarcophagus), a mausoleum, a columbarium, a niche, or another edifice. In Western world, Western cultures, funeral ceremonies are often observed in cemeteries. These ceremonies or rites of passage differ according to culture, cultural practices and religion, religious beliefs. Modern cemeteries often inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbarium
A columbarium (; pl. columbaria), also called a cinerarium, is a structure for the reverential and usually public storage of funerary urns holding cremated remains of the dead. The term comes from the Latin ''columba'' (dove) and originally solely referred to compartmentalized housing for doves and pigeons, also called dovecotes. Background Roman columbaria were often built partly or completely underground. The Columbarium of Pomponius Hylas is an ancient Roman example, rich in frescoes, decorations, and precious mosaics. Today's columbaria can be free-standing units or part of a mausoleum or another building. Some manufacturers produce columbaria built entirely offsite and brought to a cemetery by large truck. Many modern crematoria have columbaria. Examples of these are the columbaria in Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris and Golders Green Crematorium in London. In other cases, columbaria are built into church structures. One example is the Cathedral of Our Lady of the Ange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:σάρξ, σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and wikt:φαγεῖν, φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' (wikt:λίθος, λίθος wikt:σαρκοφάγος, σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the corpse decomposition, decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 BC. The Hagia Triada sarcoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Vault (tomb)
A burial vault is a structural stone or brick-lined underground tomb or 'burial chamber' for the interment of a single body or multiple bodies underground. The main difference between entombment in a subterranean vault and a traditional in-ground burial is that the coffin is not placed directly in the earth, but is placed in a burial chamber specially built for this purpose. A burial vault refers to an underground chamber, in contrast to an above-ground, freestanding mausoleum. These underground burial tombs were originally and are still often vault (architecture), vaulted and usually have stone slab entrances. They are often privately owned and used for specific family or other groups, but usually stand beneath a public religious building, such as a church architecture, church, or in a churchyard or cemetery. A crypt may be used as a burial vault and a freestanding mausoleum may contain a burial vault beneath the ground. History and description After the Christianization of Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
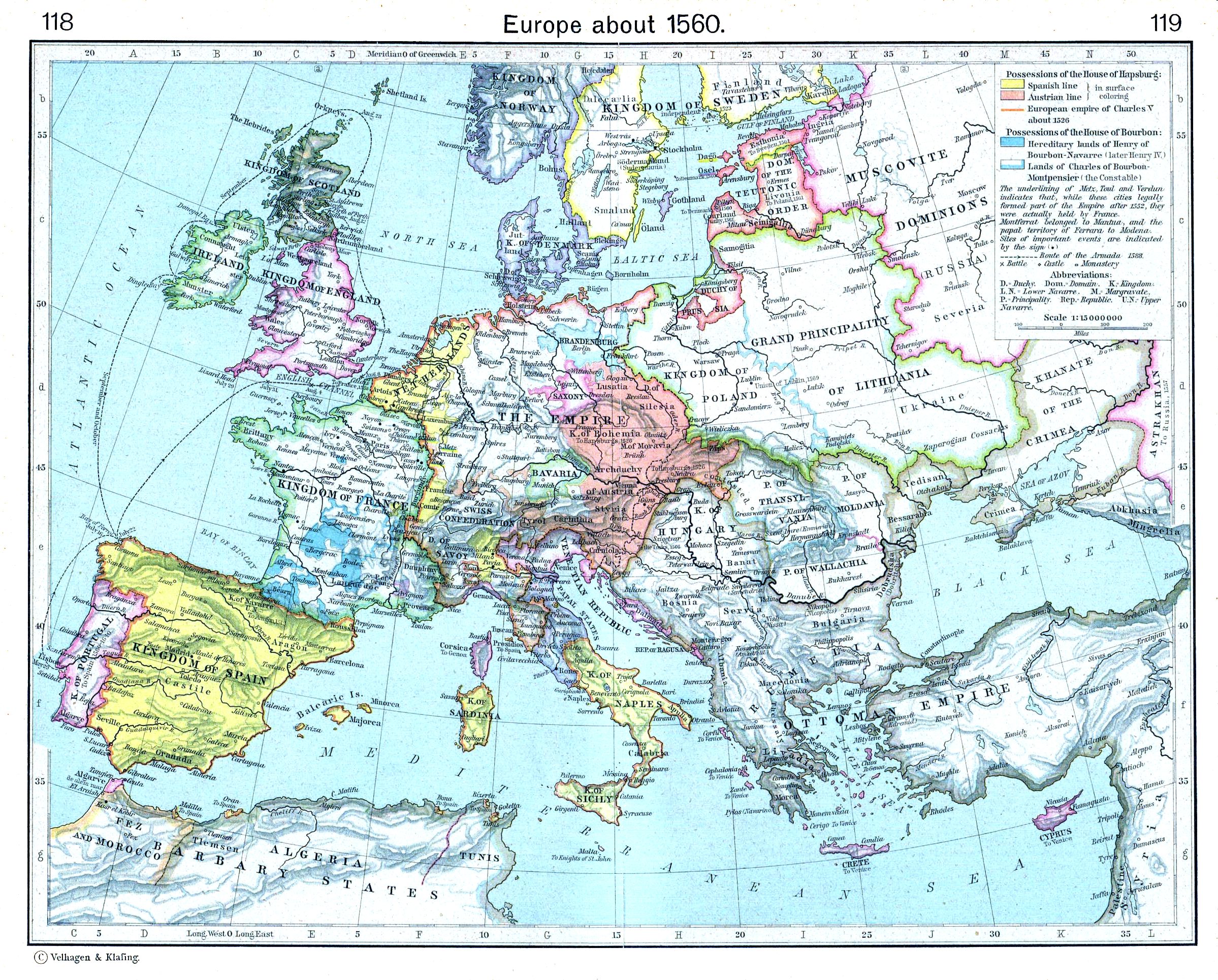
History Of Europe
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500–1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500). The first early European modern humans appear in the fossil record about 48,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic era. Settled agriculture marked the Neolithic era, which spread slowly across Europe from southeast to the north and west. The later Neolithic period saw the introduction of early metallurgy and the use of copper-based tools and weapons, and the building of megalithic structures, as exemplified by Stonehenge. During the Indo-European migrations, Europe saw migrations from the east and southeast. The period known as classical antiquity began with the emergence of the city state, city-states of ancient Greece. Later, the Roman Empire came to dominate the entire Mediterranean Basin. The Migration Period of the Germanic people began in the late 4th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Europe
Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of European history between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the mid 15th century to the late 18th century. Historians variously mark the beginning of the early modern period with the invention of moveable type printing in the 1450s, the Fall of Constantinople and end of the Hundred Years' War in 1453, the end of the Wars of the Roses in 1485, the beginning of the High Renaissance in Italy in the 1490s, the end of the Reconquista and subsequent voyages of Christopher Columbus to the Americas in 1492, or the start of the Protestant Reformation in 1517. The precise dates of its end point also vary and are usually linked with either the start of the French Revolution in 1789 or with the more vaguely defined beginning of the Industrial Revolution in late 18th century England. Some of the more notable trends and events of the early modern period included th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony
A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule, which rules the territory and its indigenous peoples separated from the foreign rulers, the colonizer, and their ''metropole'' (or "mother country"). This separated rule was often organized into colonial empires, with their metropoles at their centers, making colonies neither annexation, annexed or even Territorial integration, integrated territories, nor client states. Particularly new imperialism and its colonialism advanced this separated rule and its lasting coloniality. Colonies were most often set up and colonized for exploitation and possibly settlement by colonists. The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman , a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colonus'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'. Furthermore, the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were Greek colonisation, overseas settlements by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |