|
Marattioid Fern
Marattiaceae is the only family of extant (living) ferns in the order Marattiales. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), Marattiales is the only order in the subclass Marattiidae. The family has six genera and about 110 species. Many are different in appearance from other ferns, having large fronds and fleshy rootstocks. Description The Marattiaceae diverged from other ferns very early in their evolutionary history and are quite different from many plants familiar to people in temperate zones. Many of them have massive, fleshy rootstocks and the largest known fronds of any fern. The Marattiaceae is one of two groups of ferns traditionally known as eusporangiate ferns, meaning that the sporangium is formed from a group of cells as opposed to a leptosporangium in which there is a single initial cell. The large fronds characteristic of the group are most readily found in the genus ''Angiopteris'', native to Australasia, Madagascar and Oceania. These fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link (2 February 1767 – 1 January 1851) was a German natural history, naturalist and botanist. Biography Link was born at Hildesheim as a son of the minister August Heinrich Link (1738–1783), who taught him love of nature through collection of 'natural objects'. He studied medicine and natural sciences at the Hannoverschen Landesuniversität of Göttingen, and graduated as MD in 1789, promoting on his thesis ''"Flora der Felsgesteine rund um Göttingen"'' (Flora of the rocky beds around Göttingen). One of his teachers was the famous natural scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840). He became a private tutor (''Privatdozent'') in Göttingen. In 1792 he became the first professor of the new department of chemistry, zoology and botany at the University of Rostock. During his stay at Rostock, he became an early follower of the antiphlogistic theory of Lavoisier, teaching about the existence of oxygen instead of phlogiston. He was also a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food webfor example the purple sea urchin ('' Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'') which has decimated kelp forests along the northern California coast due to overharvesting of its natural predator, the California sea otter ('' Enhydra lutris''). Since the 20th century, invasive species have become a serious economic, social, and environmental threat. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million as of 2021. When compared with (and sometimes described as being one of) the continents, the region of Oceania is the smallest in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second least populated after Antarctica. Its major population centres are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, Adelaide, Honolulu, and Christchurch. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries, less developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's Capital of New Zealand, capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptisana Salicina
''Ptisana salicina'', or king fern, is a species of fern native to Norfolk Island, New Zealand and the South Pacific. Large and robust with a distinctive tropical appearance, it has fronds up to 5 metres (16 feet +/-) tall that arise from a starchy base that was a traditional food for the Maori. It has several other common names including para, tawhiti-para, and horseshoe fern. Distribution King fern is indigenous to Norfolk Island (the type locality), New Zealand, New Caledonia, Cook Islands, Austral Islands, Society Islands and the Marquesas. It is closely related to ''Ptisana smithii'' of Vanuatu, Fiji, the Solomon Islands, Samoa and Tonga. In New Zealand it is found in lowland areas on the north-western half of the North Island from inland Wanganui northwards. It is most abundant in the western Waikato, where it is found in forests and forest remnants. It prefers limestone-rich soils, including the entrances to caves and shady stream sides. It often grows in New Zeala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
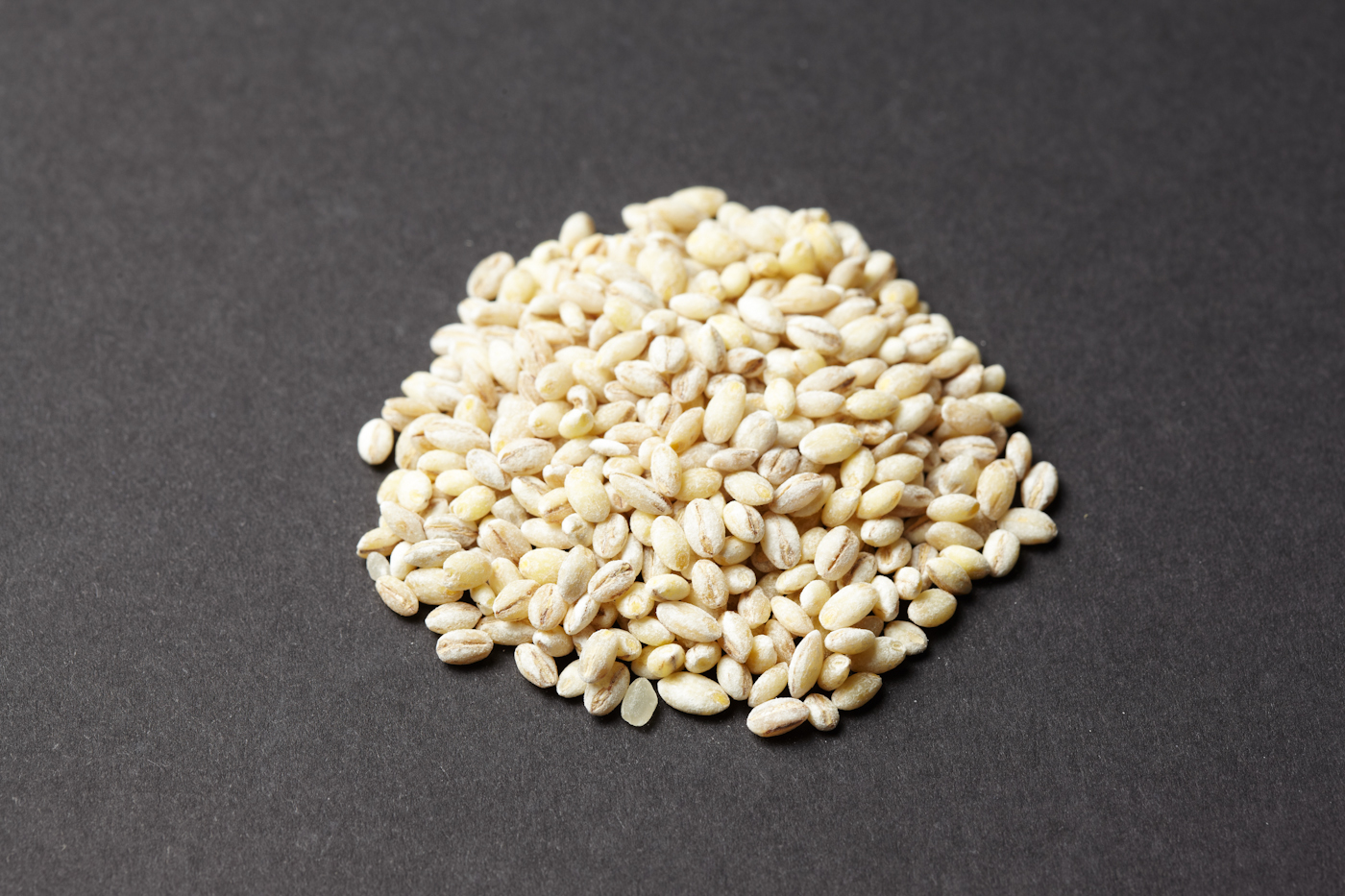
Pearl Barley
Pearl barley, or pearled barley, is barley that has been processed to remove its fibrous outer hull and polished to remove some or all of the bran layer. It is the most common form of barley for human consumption because it cooks faster and is less chewy than other, less-processed forms of the grainBarley from The Cook's Thesaurus (foodsubs.com) such as "hulled barley" (or "barley groats", also known as "pot barley" and "Scotch barley"). Fine barley flour is prepared from milled pearl barley. Pearl barley is similar to wheat in its caloric, protein, vitamin and mineral content, though some varieties are higher in |
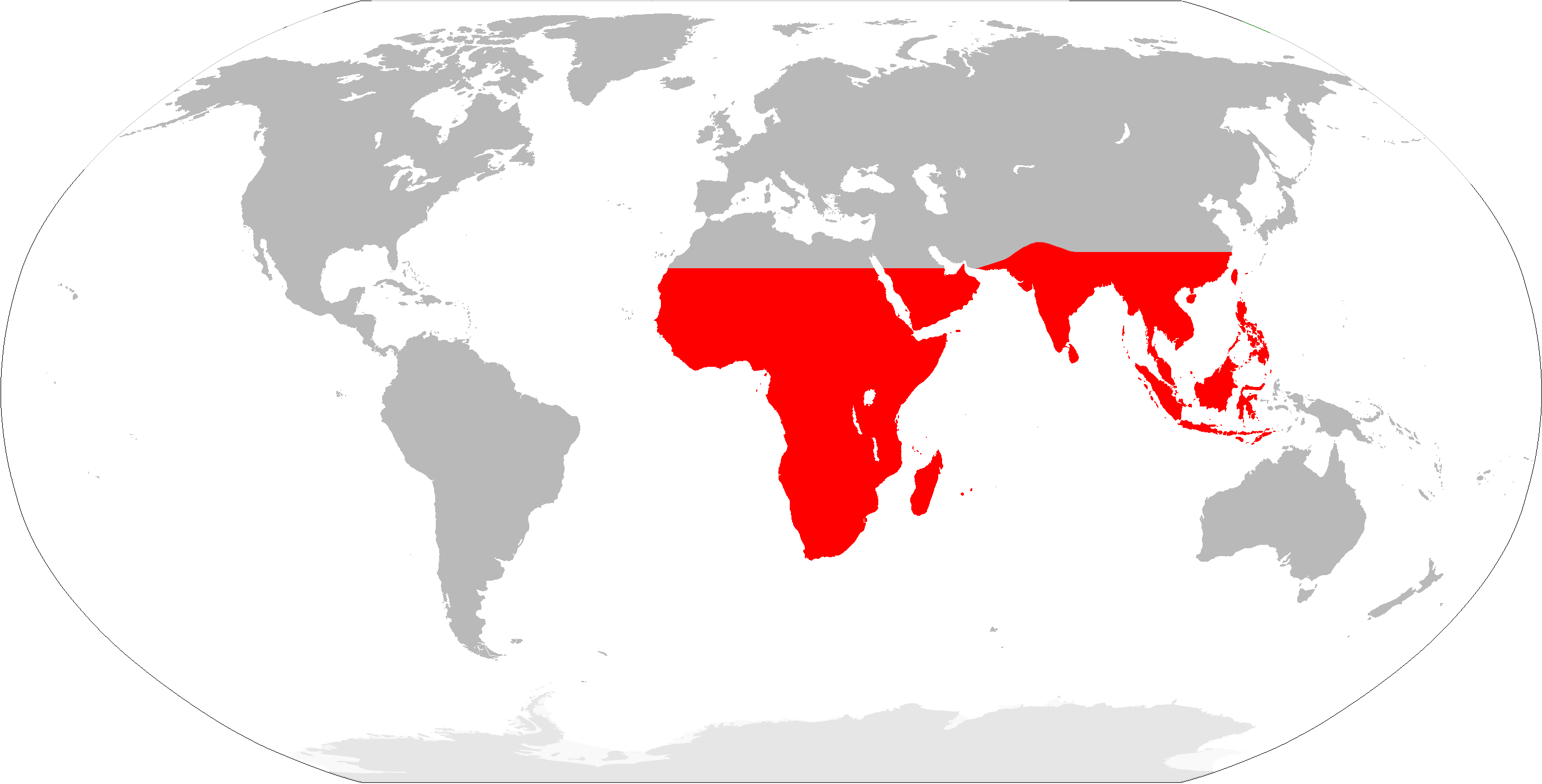
Paleotropics
The Paleotropical Kingdom (Paleotropis) is a floristic kingdom comprising tropical areas of Africa, Asia and Oceania (excluding Australia and New Zealand), as proposed by Ronald Good and Armen Takhtajan. Part of its flora, inherited from the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana or exchanged later (e.g. Piperaceae with pantropical distribution and but few warm temperate representatives), is shared with the Neotropical Kingdom, comprising tropical areas of Central and South America. Moreover, the Paleotropical flora influenced the tropical flora of the Australian Kingdom. The Paleotropical Kingdom is subdivided into five floristic subkingdoms according to Takhtajan (or three, according to Good) and about 13 floristic regions. In this article the floristic subkingdoms and regions are given as delineated by Takhtajan. Origin A distinct community of vascular plants evolved millions of years ago, and are now found on several separate areas. Millions of years ago, the warmer and wetter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptisana
Sori of ''Ptisana fraxinea'' ''Ptisana'' is a genus in the eusporangiate fern family Marattiaceae, comprising species historically treated in the genus ''Marattia''. The establishment of this genus follows the 2008 work by Andrew G. Murdock, which supported recognition of this group on the basis of genetic analysis and morphology. ''Ptisana'' can be distinguished from ''Marattia'' by the presence of distinct sutures at the point of leaflet attachment, deeply cut synangia, and the absence of labiate sporangial apertures. The name ''Ptisana'' is derived from the Latin word for pearl barley, an allusion to the shape of the synangia. ''Ptisana'' has a palaeotropical distribution, with the westernmost extreme of the range in Ascension Island and extending eastward through tropical Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Ferns in this genus are generally quite large, with fronds often reaching 2-3 meters in length; the one known exception to this is ''Ptisana rolandi-principis'', a dwarf speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotropics
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone. Definition In biogeography, the Neotropic or Neotropical realm is one of the eight terrestrial realms. This realm includes South America, Central America, the Caribbean islands, and southern North America. In Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula and southern lowlands, and most of the east and west coastlines, including the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula are Neotropical. In the United States southern Florida and coastal Central Florida are considered Neotropical. The realm also includes temperate southern South America. In contrast, the Neotropical Floristic Kingdom excludes southernmost South America, which instead is placed in the Antarctic kingdom. The Neotropic is delimited by similarities in fauna or flora. Its fauna and flora are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupodium
''Eupodium'' is a genus of ferns in the family Marattiaceae native to the Neotropics. Traditionally, many taxonomists have included ''Eupodium'' within the genus ''Marattia'' (along with ''Ptisana''). However, molecular phylogenetic studies and morphological studies of extant and fossil taxa support the recognition of ''Eupodium'' as a lineage distinct from ''Marattia''. Morphologically, ''Eupodium'' was thought to be distinct among the Marattiaceae in only having one frond at a time (occasionally two), bearing awns along veins, and having stalked synangia (clusters of sporangia that have become fused in development). However, recent phylogenetic work found that an additional species native to Brazil, '' Eupodium cicutifolium'', which lacks these characters, is also genetically in ''Eupodium'', making the genus challenging to distinguish morphologically. ''Eupodium cicutifolium'' does occasionally have short-stalked synangia, and has spinulose spores like the other ''Eupodium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marattia
''Marattia'' is a small genus of primitive, large, fleshy eusporangiate ferns. It is the type genus of the family Marattiaceae, order Marattiales and class Marattiopsida. Formerly considered to be a much larger genus, genetic analysis has shown that ''Marattia'' in the broad sense was paraphyletic, and subsequently the genera '' Ptisana'' and ''Eupodium'' were split off. Except for one species in Hawaii, the genus is neotropical. The plants are large and terrestrial, with more or less erect rhizomes and fronds being 2-5 times pinnate. Sporangia are fused into synangia, and spores are monolete. Basal chromosome count is ''2n=80''. The type species is ''M. alata''. Species list *'' Marattia alata'' Sw. – Jamaica and Cuba *'' Marattia douglasii'' (C. Presl) Baker – pala, kapua ilio, or Hawaii potato fern; Hawaii *'' Marattia excavata'' Underw. – Mexico to Panama *'' Marattia interposita'' Christ – Guatemala to Panama *'' Marattia laxa'' Kunze – Mexico to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castleton Botanical Garden
Castleton Botanical Garden is a horticultural site of interest established in 1862 and located 19 miles from Kingston, Jamaica Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ....Postcard, undated. Text "Greetings from Jamaica. Castleton Gardens, 19 miles from Kingston".Postcard, undated. Text "Castleton Gardens. Greetings from Jamaica.". Soon after their creation the gardens were "the most richly stocked in the Caribbean, boasting over 180 species of palm and at least 400 specimens of other flora". References External links * Botanical gardens in Jamaica Geography of Saint Mary Parish, Jamaica 1862 establishments in Jamaica {{garden-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |