|
Man Pages
A man page (short for manual page) is a form of software documentation found on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. Topics covered include programs, system libraries, system calls, and sometimes local system details. The local host administrators can create and install manual pages associated with the specific host. A manual end user may invoke a documentation page by issuing the man command followed by the name of the item for which they want the documentation. These manual pages are typically requested by end users, programmers and administrators doing real time work but can also be formatted for printing. By default, man typically uses a formatting program such as nroff with a macro package or mandoc, and also a terminal pager program such as more or less to display its output on the user's screen. Man pages are often referred to as an ''online'' form of software documentation, even though the man command does not require internet access. The environment variable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sed Stream Editor (cropped)
sed ("stream editor") is a Unix utility that parses and transforms text, using a simple, compact programming language. It was developed from 1973 to 1974 by Lee E. McMahon of Bell Labs, and is available today for most operating systems. sed was based on the scripting features of the interactive editor ed (text editor), ed ("editor", 1971) and the earlier QED (text editor), qed ("quick editor", 1965–66). It was one of the earliest tools to support regular expressions, and remains in use for text processing, most notably with the substitution command. Popular alternative tools for plaintext string manipulation and "stream editing" include AWK and Perl. History First appearing in Version 7 Unix, sed is one of the early Unix commands built for command line processing of data files. It evolved as the natural successor to the popular grep command. The original motivation was an analogue of grep (g/re/p) for substitution, hence "g/re/s". Foreseeing that further special-purpose progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
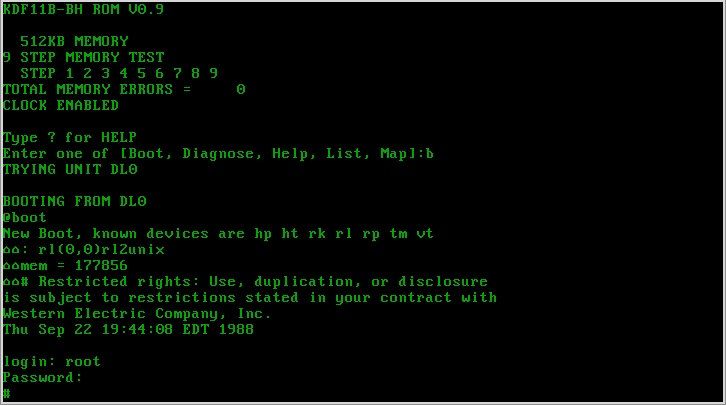
History Of Unix
The history of Unix dates back to the mid-1960s, when the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Bell Labs, and General Electric were jointly developing an experimental time-sharing operating system called Multics for the GE-600 series, GE-645 mainframe. Multics introduced many Multics#Novel ideas, innovations, but also had many problems. Bell Labs, frustrated by the size and complexity of Multics but not its aims, slowly pulled out of the project. Their last researchers to leave Multics – among them Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Douglas McIlroy, Doug McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna – decided to redo the work, but on a much smaller scale. APDF/ref> In 1979, Ritchie described the group's vision for Unix: 1960s Multics In the late 1960s, Bell Labs was involved in a project with Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT and General Electric to develop a time-sharing system, called Multics, allowing multiple users to access a mainframe computer, mainframe simultaneously. A key con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
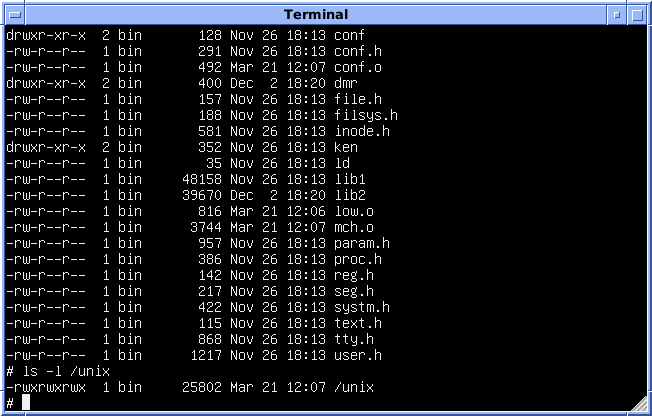
Version 4 Unix
Research Unix refers to the early versions of the Unix operating system for PDP-7, DEC PDP-7, PDP-11, VAX and Interdata 7/32 and 8/32 computers, developed in the Bell Labs Computing Sciences Research Center (CSRC). The term ''Research Unix'' first appeared in the Bell System Technical Journal (Vol. 57, No. 6, Part 2 July/August 1978) to distinguish it from other versions internal to Bell Labs (such as PWB/UNIX and Multi-Environment Real-Time, MERT) whose code-base had diverged from the primary CSRC version. However, that term was little-used until Version 8 Unix (1985), but has been Retroactive continuity, retroactively applied to earlier versions as well. Prior to V8, the operating system was most commonly called simply UNIX (in caps) or the UNIX Time-Sharing System. Ancient UNIX is any early release of the Unix code base prior to Unix System III, particularly the Research Unix releases prior to and including Version 7 (the base for UNIX/32V as well as later developments of AT&T Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 6 Unix
Sixth Edition Unix, also called Version 6 Unix or just V6 is a version of the Unix operating system first released in May 1975 and the first version of the Unix operating system to see wide release outside Bell Labs. Like its direct predecessor, the sixth edition targeted the DEC PDP-11 family of minicomputers. It was superseded by Version 7 Unix in 1978/1979, although V6 systems remained in regular operation until at least 1985. AT&T Corporation licensed Version 5 Unix to educational institutions only, but licensed Version 6 also to commercial users for $20,000, and it remained the most widely used version into the 1980s. An enhanced V6 was the basis of the first ever commercially sold Unix version, INTERACTIVE's IS/1. Bell's own PWB/UNIX 1.0 was also based on V6, where earlier (unreleased) versions were based on V4 and V5. Whitesmiths produced and marketed a (binary-compatible) V6 clone under the name Idris. Source code V6 Unix was released as a distribution including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorinda Cherry
Lorinda Cherry ( Landgraf; November 18, 1944 – February 11, 2022) was an American computer scientist and programmer. Much of her career was spent at Bell Labs, where she was for many years a member of the original Unix Lab. Cherry developed several mathematical tools and utilities for text formatting and analysis, and influenced the creation of others. Early life Cherry was born on November 18, 1944, to John F. and Evelyn K. Landgraf. She had one sister, Carynn Elizabeth. Raised in Verona, New Jersey, she graduated from Verona High School and received a Bachelor of Arts (Mathematics) from the University of Delaware in 1966. Computer science career Cherry started as a Technical Assistant (TA) at Bell Labs in 1966, initially working in Acoustics and Speech Research on vocal tract simulation. She received her Masters in computer science from Stevens Institute of Technology in 1969. At Bell Labs, Cherry was involved in projects with Ken Knowlton and James L. Flanagan related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 3 Unix
Research Unix refers to the early versions of the Unix operating system for DEC PDP-7, PDP-11, VAX and Interdata 7/32 and 8/32 computers, developed in the Bell Labs Computing Sciences Research Center (CSRC). The term ''Research Unix'' first appeared in the Bell System Technical Journal (Vol. 57, No. 6, Part 2 July/August 1978) to distinguish it from other versions internal to Bell Labs (such as PWB/UNIX and MERT) whose code-base had diverged from the primary CSRC version. However, that term was little-used until Version 8 Unix (1985), but has been retroactively applied to earlier versions as well. Prior to V8, the operating system was most commonly called simply UNIX (in caps) or the UNIX Time-Sharing System. Ancient UNIX is any early release of the Unix code base prior to Unix System III, particularly the Research Unix releases prior to and including Version 7 (the base for UNIX/32V as well as later developments of AT&T Unix). History AT&T licensed Version 5 to edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Unix
Research Unix refers to the early versions of the Unix operating system for DEC PDP-7, PDP-11, VAX and Interdata 7/32 and 8/32 computers, developed in the Bell Labs Computing Sciences Research Center (CSRC). The term ''Research Unix'' first appeared in the Bell System Technical Journal (Vol. 57, No. 6, Part 2 July/August 1978) to distinguish it from other versions internal to Bell Labs (such as PWB/UNIX and MERT) whose code-base had diverged from the primary CSRC version. However, that term was little-used until Version 8 Unix (1985), but has been retroactively applied to earlier versions as well. Prior to V8, the operating system was most commonly called simply UNIX (in caps) or the UNIX Time-Sharing System. Ancient UNIX is any early release of the Unix code base prior to Unix System III, particularly the Research Unix releases prior to and including Version 7 (the base for UNIX/32V as well as later developments of AT&T Unix). History AT&T licensed Version 5 to ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
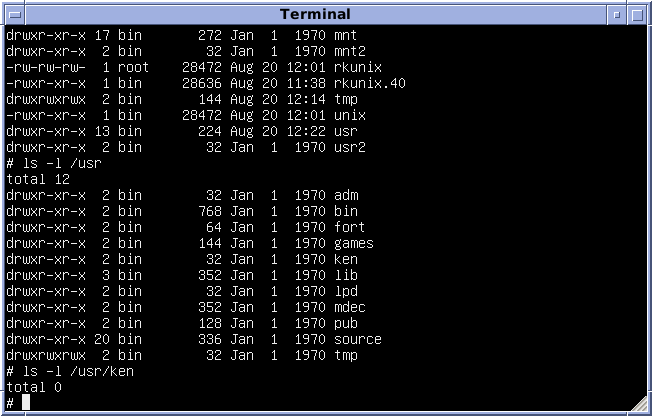
Version 7 Unix
Version 7 Unix, also called Seventh Edition Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicompute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PWB/UNIX
The Programmer's Workbench (PWB/UNIX) was an early, now discontinued, version of the Unix operating system that had been created in the Bell Labs Computer Science Research Group of AT&T. Its stated goal was to provide a time-sharing working environment for large groups of programmers, writing software for larger batch processing computers. Prior to 1973 Unix development at AT&T was a project of a small group of researchers in Department 1127 of Bell Labs. As the usefulness of Unix in other departments of Bell Labs was evident, the company decided to develop a version of Unix tailored to support programmers in production work, not just research. The Programmer's Workbench was started in 1973,John R. Mashey (2004)Languages, Levels, Libraries, and Longevity. ACM Queue 2 (9). by Evan Ivie and Rudd Canaday to support a computer center for a 1000-employee Bell Labs division, which would be the largest Unix site for several years. PWB/UNIX was to provide tools for teams of programmers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yacc
Yacc (Yet Another Compiler-Compiler) is a computer program for the Unix operating system developed by Stephen C. Johnson. It is a lookahead left-to-right rightmost derivation (LALR) parser generator, generating a LALR parser (the part of a compiler that tries to make syntactic sense of the source code) based on a formal grammar, written in a notation similar to Backus–Naur form (BNF). Yacc is supplied as a standard utility on BSD and AT&T Unix. GNU-based Linux distributions include Bison, a forward-compatible Yacc replacement. History In the early 1970s, Stephen C. Johnson, a computer scientist at Bell Labs / AT&T, developed Yacc because he wanted to insert an exclusive or operator into a B language compiler (developed using McIlroy's TMG compiler-compiler), but it turned out to be a hard task. As a result, he was directed by his colleague at Bell Labs Al Aho to Donald Knuth's work on LR parsing, which served as the basis for Yacc. Yacc was influenced by and rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutorial
In education, a tutorial is a method of transferring knowledge and may be used as a part of a learning process. More interactive and specific than a book or a lecture, a tutorial seeks to teach by example and supply the information to complete a certain task. A tutorial can be taken in many forms, ranging from a set of instructions to complete a task to an interactive problem solving session (usually in academia). Academia Tutorial class In British academic parlance, a tutorial is a small class of one, or only a few students, in which the tutor, a lecturer, or other academic staff member, gives individual attention to the students. The tutorial system at Oxford and Cambridge is fundamental to methods of teaching at those universities, but it is by no means particular to them; Heythrop College (University of London), for instance, offers a tutorial system but with one-on-one teaching. Another example is Imperial College London, where tutorials in groups of 3 take pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |