|
Maculopapular Rash
A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: '' macules'' are small, flat discolored spots on the surface of the skin; and ''papules'' are small, raised bumps. It is also described as erythematous, or red. This type of rash is common in several diseases and medical conditions, including scarlet fever, measles, Ebola virus disease, rubella, HIV, secondary syphilis (Congenital syphilis, which is asymptomatic, the newborn may present this type of rash), erythrovirus ( parvovirus B19), chikungunya (alphavirus), zika, smallpox (which has been eradicated), varicella (when vaccinated persons exhibit symptoms from the modified form), heat rash, and sometimes in Dengue fever. It is also a common manifestation of a skin reaction to the antibiotic amoxicillin or chemotherapy drugs. Cutaneous infiltration of leu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morbillivirus Measles Infection
''Morbillivirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales'', in the family ''Paramyxoviridae''. Humans, dogs, cats, cattle, seals, and cetaceans serve as natural hosts. This genus contains 10 species, one of which is extinct. Diseases in humans associated with viruses classified in this genus include measles; in animals, they include acute febrile respiratory tract infection and Canine distemper. In 2013, a wave of increased death among the Common bottlenose dolphin population was attributed to morbillivirus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species, listed by scientific name and followed by the exemplar virus of the species: * ''Morbillivirus canis'', Canine distemper virus * ''Morbillivirus caprinae'', Peste-des-petits-ruminants virus * ''Morbillivirus ceti'', Cetacean morbillivirus * ''Morbillivirus felis'', Feline morbillivirus * ''Morbillivirus hominis'', Measles virus * ''Morbillivirus myotis'', Myotis bat morbillivirus * †''Morbillivirus peco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into severe dengue (previously known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome) with bleeding, low levels of blood platelets, blood plasma leakage, and dangerously low blood pressure. Dengue virus has four confirmed serotypes; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications, so-called Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE). The symptoms of dengue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Manual
''The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'', referred to as ''The Merck Manual'', is the world's best-selling medical textbook, and the oldest continuously published English language medical textbook. First published in 1899, the current print edition of the book, the 20th Edition, was published in 2018. In 2014, Merck decided to move ''The Merck Manual'' to digital-only, online publication, available in both professional and consumer versions; this decision was reversed in 2017, with the publication of the 20th edition the following year. ''The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'' is one of several medical textbooks, collectively known as '' The Merck Manuals'', which are published by Merck Publishing, a subsidiary of the pharmaceutical company Merck Co., Inc. in the United States and Canada, and MSD (as ''The MSD Manuals'') in other countries in the world. Merck also formerly published '' The Merck Index'', ''An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals.'' History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linuche
''Linuche'' is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Linuchidae. The species of this genus are found in America and Southeastern Asia. Species: *'' Linuche aquila'' *'' Linuche lamarckii'' *'' Linuche unguiculata'' *''Linuche vesiculata ''Linuche'' is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Linuchidae. The species of this genus are found in America and Southeastern Asia. Species: *''Linuche aquila'' *''Linuche lamarckii'' *''Linuche unguiculata'' *''Linuche vesiculat ...'' *'' Linuche draco'' References Scyphozoan genera Linuchidae {{Scyphozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwardsiella (Edwardsiidae)
''Edwardsiella'' is a genus of sea anemones in the family Edwardsiidae. It is named in honour of Henri Milne-Edwards, an eminent French zoologist. Species The following species are listed by the World Register of Marine Species The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive catalogue and list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scien .... * '' Edwardsiella andrillae'' (Daly, Rack & Zook, 2013) * '' Edwardsiella carnea'' (Gosse, 1856) * '' Edwardsiella ignota'' (Carlgren, 1959) * '' Edwardsiella janthina'' (Andrès, 1881) * '' Edwardsiella lineata'' (Verrill in Baird, 1873) * '' Edwardsiella loveni'' (Carlgren, 1892) References Edwardsiidae Hexacorallia genera Taxa named by Angelo Andres {{Actiniaria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Bather's Eruption
Seabather's eruption is an itching dermatitis caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to the immature nematocysts of larval-stage thimble jellyfish (''Linuche unguiculata''), sea anemones ('' Edwardsiella lineata'') and other larval cnidarians. The eruption is sometimes attributed to "sea lice" or "sea ants", but sea lice (Caligidae) are crustacean parasites of fish only. It should not be confused with swimmer's itch. Symptoms and signs Symptoms generally arise later after showering. It is unusual to notice the eruptions immediately. Symptoms can last from a few days up to, exceptionally, two weeks. The reaction is identified by severe itching around small red papules 1mm to 1.5 cm in size on areas of skin that were covered by water-permeable clothing or hair during ocean swimming. Initial swimmer exposure to the free-floating larvae produces no effects, as each organism possesses only a single undeveloped nematocyst which is inactive while suspended in seawater. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niacin (substance)
Nicotinic acid, or niacin, is an organic compound and a vitamer of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It is produced by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Nicotinic acid is also a prescription medication. Amounts far in excess of the recommended dietary intake for vitamin functions will lower blood triglycerides and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and raise blood high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C, often referred to as "good" cholesterol). There are two forms: immediate-release and sustained-release nicotinic acid. Initial prescription amounts are 500 mg/day, increased over time until a therapeutic effect is achieved. Immediate-release doses can be as high as 3,000 mg/day; sustained-release as high as 2,000 mg/day. Despite the proven lipid changes, nicotinic acid has not been found useful for decreasing the risk of cardiovascular disease in those already prescribed a statin drug. A 2010 review had concluded that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filovirus
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known relatives, cause severe disease in humans and nonhuman primates in the form of viral hemorrhagic fevers. All filoviruses are classified by the US as select agents, by the World Health Organization as Risk Group 4 Pathogens (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases as Category A Priority Pathogens, and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as Category A Bioterrorism Agents, and are listed as Biological Agents for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The family ''Filoviridae'' is a virological taxon that was defined in 1982 and emended in 1991, 1998, 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2011. The family currently includes the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever
Marburg (; ) is a university town in the German federal state () of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf district (). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has a population of approximately 76,000. Having been awarded town privileges in 1222, Marburg served as capital of the landgraviate of Hessen-Marburg during periods of the 15th to 17th centuries. The University of Marburg was founded in 1527 and dominates the public life in the town to this day. Marburg is a historic centre of the pharmaceutical industry in Germany, and there is a plant in the town (by BioNTech) to produce vaccines to tackle Covid-19. History Founding and early history Like many settlements, Marburg developed at the crossroads of two important early medieval highways: the trade route linking Cologne and Prague and the trade route from the North Sea to the Alps and on to Italy, the former crossing the river Lahn here. A first mention of the settlement dates from 822 in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
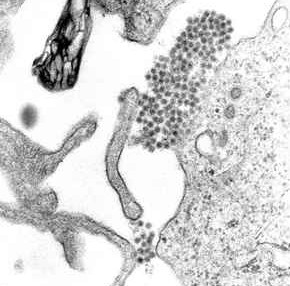
Ebola Virus
''Orthoebolavirus zairense'' or Zaire ebolavirus, more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the Western African Ebola virus epidemic, 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was List of Ebola outbreaks, first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
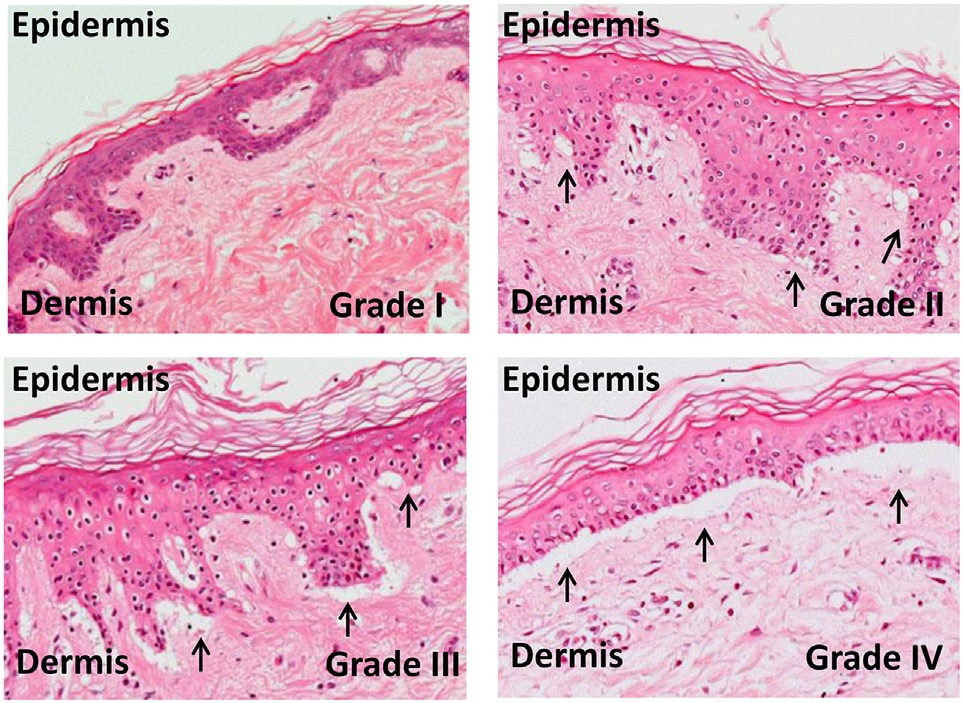
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), also known as Lyell's syndrome, is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) it forms a spectrum of disease, with TEN being more severe. Early symptoms include fever and flu-like symptoms. A few days later the skin begins to blister and peel forming painful raw areas. Mucous membranes, such as the mouth, are also typically involved. Complications include dehydration, sepsis, pneumonia, and multiple organ failure. The most common cause is certain medications such as lamotrigine, carbamazepine, allopurinol, sulfonamide antibiotics, and nevirapine. Other causes can include infections such as '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' and cytomegalovirus or the cause may remain unknown. Risk factors include HIV/AIDS and systemic lupus erythematosus. Diagnosis is based on a skin biopsy and involvement of more than 30% of the skin. TEN is a type of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs), together with SJS, a SJS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graft-versus-host Disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. White blood cells of the donor's immune system which remain within the donated tissue (the graft) recognize the recipient (the host) as foreign (non-self). The white blood cells present within the transplanted tissue then attack the recipient's body's cells, which leads to GvHD. This should not be confused with a transplant rejection, which occurs when the immune system of the transplant recipient rejects the transplanted tissue; GvHD occurs when the donor's immune system's white blood cells reject the recipient. The underlying principle ( alloimmunity) is the same, but the details and course may differ. GvHD can also occur after a blood transfusion, known as ''Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease'' or TA-GvHD if the blood products used have not been gamma irradiated or treated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |