|
Late Onset Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (LOCAH), also known as nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH or NCAH), is a milder form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis that leads to variable degrees of postnatal androgen excess. The causes of LOCAH are the same as of classic CAH, and in the majority of the cases are the mutations in the ''CYP21A2'' gene resulting in corresponding activity changes in the associated P450c21 (21-hydroxylase) enzyme which ultimately leads to excessive androgen production. Other causes, albeit less frequent, are mutations in genes affecting other enzymes involved in steroid metabolism, like 11β-hydroxylase or 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. It has a prevalence between 0.1% and 2% depending on population, and is one of the most common autosomal recessive genetic diseases in humans. The pathophysiology is complex and not all individuals are symptomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex. Most of these disorders involve excessive or deficient production of hormones such as glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, or sex steroids, and can alter development of primary or secondary sex characteristics in some affected infants, children, or adults. It is one of the most common autosomal recessive disorders in humans. Types CAH can occur in various forms. The clinical presentation of each form is different and depends to a large extent on the underlying enzyme defect, its precursor retention, and deficient products. Classical forms appear in infancy, and nonclassical forms appear in late childhood. The presentation in patients with classic CAH can be further subdivided into two forms: salt-wasting and simple-virilizing, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
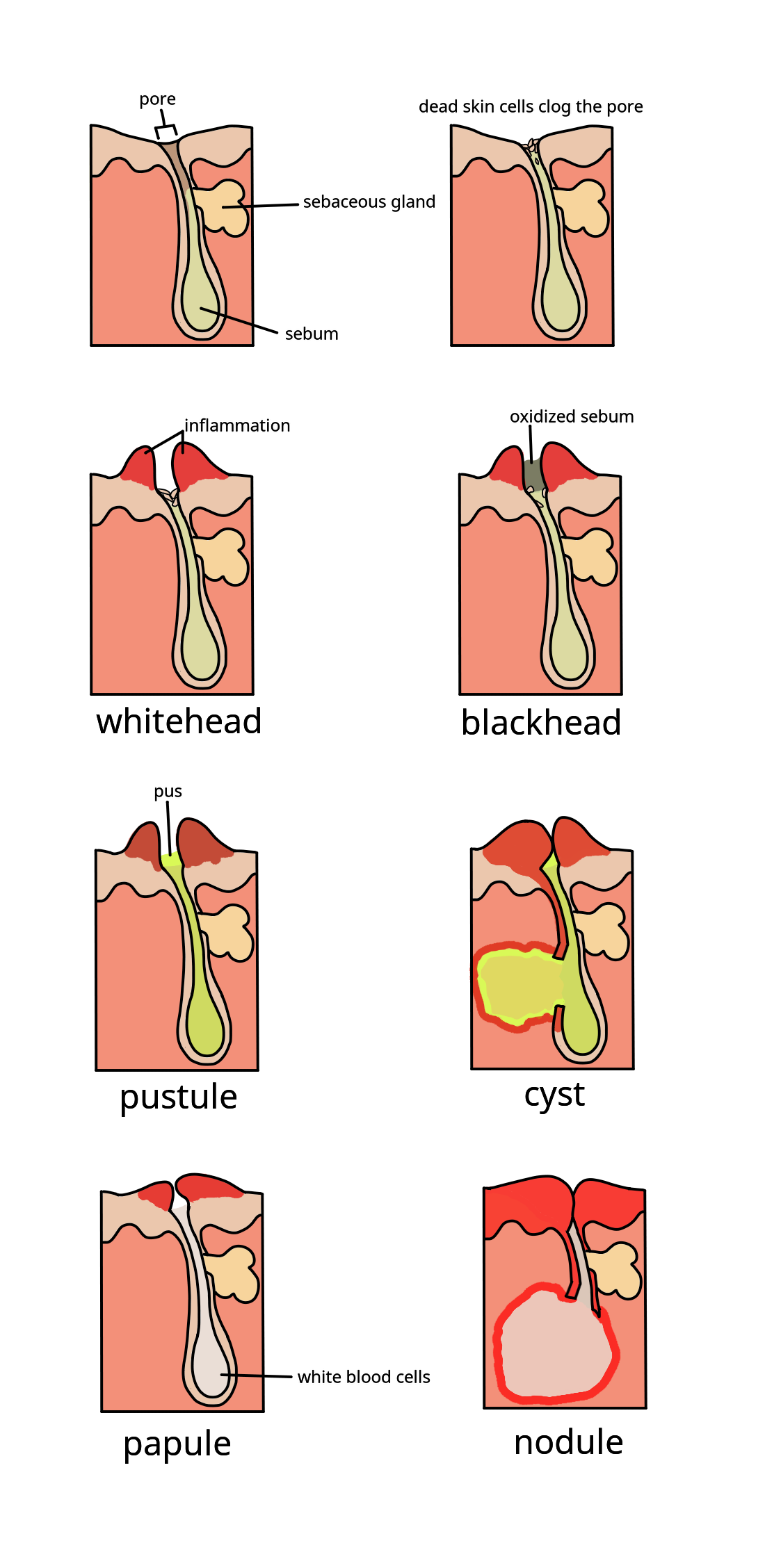
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring is not usually present. Hair loss in some people causes psychological distress. Common types include male- or female-pattern hair loss, alopecia areata, and a thinning of hair known as telogen effluvium. The cause of male-pattern hair loss is a combination of genetics and male hormones; the cause of female pattern hair loss is unclear; the cause of alopecia areata is autoimmune; and the cause of telogen effluvium is typically a physically or psychologically stressful event. Telogen effluvium is very common following pregnancy. Less common causes of hair loss without inflammation or scarring include the pulling out of hair, certain medications including chemotherapy, HIV/AIDS, hypothyroidism, and malnutrition including iron defici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Tumor
An adrenal tumor or adrenal mass is any benign or malignant neoplasms of the adrenal gland, several of which are notable for their tendency to overproduce endocrine hormones. Adrenal cancer is the presence of malignant adrenal tumors, and includes neuroblastoma, adrenocortical carcinoma and some adrenal pheochromocytomas. Most adrenal pheochromocytomas and all adrenocortical adenomas are benign tumors, which do not metastasize or invade nearby tissues, but may cause significant health problems by unbalancing hormones. Metastasis to the adrenals Metastasis to one or both adrenal glands is the most common form of malignant adrenal lesion, and the second most common adrenal tumor after benign adenomas. Last Update: January 20, 2019. Primary tumors in such cases are most commonly from lung cancer (39%), breast cancer (35%), malignant melanoma, gastrointestinal tract cancer, pancreas cancer, and renal cancer. Tumors of the adrenal cortex The adrenal cortex is composed of three dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Tumor
Ovarian tumors, or ovarian neoplasms, are tumors arising from the ovary. They can be benign or malignant (ovarian cancer). They consist of mainly solid tissue, while ovarian cysts contain fluid. Histopathologic classification Ovarian tumors are classified according to the histology of the tumor, obtained in a pathology report. Histology dictates many aspects of clinical treatment, management, and prognosis. The most common forms are: ''Mixed tumors'' contain elements of more than one of the above classes of tumor histology. History An 1882 article appearing in Scientific American mentions the case of a patient at University of Pennsylvania The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ... Hospital when Dr. William Goodell removed a 112 lbs tumor from a 31 year old patien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological stress (along with its precursor corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus). Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol by the cortex of the adrenal gland. ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms. Deficiency of ACTH is an indicator of secondary adrenal insufficiency (suppressed production of ACTH due to an impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, cf. hypopituitarism) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (disease of the hypothalamus, with a decrease in the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)). Conversely, chronically elevated ACTH levels occur in primary ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and not the underlying cause of the disorder. Women with PCOS may experience irregular menstrual periods, heavy periods, excess hair, acne, pelvic pain, difficulty getting pregnant, and patches of thick, darker, velvety skin. The primary characteristics of this syndrome include: hyperandrogenism, anovulation, insulin resistance, and neuroendocrine disruption. A review of the international evidence found that the prevalence of PCOS could be as high as 26% among some populations, though ranges between 4% and 18% are reported for general populations. Despite its high prevalence, the exact cause of PCOS remains uncertain and there is no known cure. Definition Two definitions are commonly used: * NIH : In 1990 a consensus workshop sponsore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17α-hydroxyprogesterone
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OHP), also known as 17-OH progesterone (17-OHP), or hydroxyprogesterone (OHP), is an endogenous progestogen steroid hormone related to progesterone. It is also a chemical intermediate in the biosynthesis of many other endogenous steroids, including androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids, as well as neurosteroids. Biological activity 17α-OHP is an agonist of the progesterone receptor (PR) similarly to progesterone, albeit weakly in comparison. In addition, it is an antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) as well as a partial agonist of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), albeit with very low potency ( EC50 >100-fold less relative to cortisol) at the latter site, also similarly to progesterone. Biochemistry Biosynthesis 17α-OHP is derived from progesterone via 17α-hydroxylase (encoded by CYP17A1) 17α-OHP increases in the third trimester of pregnancy primarily due to fetal adrenal production. This steroid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTH Stimulation Test
The ACTH test (also called the cosyntropin, tetracosactide, or Synacthen test) is a medical test usually requested and interpreted by endocrinologists to assess the functioning of the adrenal glands' stress response by measuring the adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; corticotropin) or another corticotropic agent such as tetracosactide (cosyntropin, tetracosactrin; Synacthen) or alsactide (Synchrodyn). ACTH is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), and aldosterone. During the test, a small amount of synthetic ACTH is injected, and the amount of cortisol (and sometimes aldosterone) that the adrenals produce in response is measured. This test may cause mild side effects in some individuals. This test is used to diagnose or exclude primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency, Addison's disease, and related conditions. In addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massive Parallel Sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation sequencing. Some of these technologies emerged between 1994 and 1998 and have been commercially available since 2005. These technologies use miniaturized and parallelized platforms for sequencing of 1 million to 43 billion short reads (50 to 400 bases each) per instrument run. Many NGS platforms differ in engineering configurations and sequencing chemistry. They share the technical paradigm of massive parallel sequencing via spatially separated, clonally amplified DNA templates or single DNA molecules in a flow cell. This design is very different from that of Sanger sequencing—also known as capillary sequencing or first-generation sequencing—which is based on electrophoretic separation of chain-termination products produced in individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Conversion
Gene conversion is the process by which one DNA sequence replaces a homologous sequence such that the sequences become identical after the conversion event. Gene conversion can be either allelic, meaning that one allele of the same gene replaces another allele, or ectopic, meaning that one paralogous DNA sequence converts another. Allelic gene conversion Allelic gene conversion occurs during meiosis when homologous recombination between heterozygotic sites results in a mismatch in base pairing. This mismatch is then recognized and corrected by the cellular machinery causing one of the alleles to be converted to the other. This can cause non-Mendelian segregation of alleles in germ cells. Nonallelic/ectopic gene conversion Recombination occurs not only during meiosis, but also as a mechanism for repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) caused by DNA damage. These DSBs are usually repaired using the sister chromatid of the broken duplex and not the homologous chromosome, so they wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)