|
Lament Bass
In music, the lament bass is a ground bass, built from a descending perfect fourth from tonic to dominant, with each step harmonized.Brover-Lubovsky, Bella (2008). ''Tonal Space in the Music of Antonio Vivaldi'', p.151-52. . The diatonic version is the upper tetrachord from the natural minor scale, known as the Phrygian tetrachord, while the chromatic version, the chromatic fourth, has all semitones filled in. It is often used in music to denote tragedy or sorrow. However, "A common misperception exists that the 'lament bass' of Venetian opera became so prevalent that it immediately swept away all other possible affective associations with this bass pattern...To cite but one example, Peter Holman, writing about Henry Purcell, once characterized the minor tetrachord as 'the descending ground that was associated with love in seventeenth-century opera'." Compositional form There exists a short, free musical form of the Romantic Era, called complaint or "complainte" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament Bass
In music, the lament bass is a ground bass, built from a descending perfect fourth from tonic to dominant, with each step harmonized.Brover-Lubovsky, Bella (2008). ''Tonal Space in the Music of Antonio Vivaldi'', p.151-52. . The diatonic version is the upper tetrachord from the natural minor scale, known as the Phrygian tetrachord, while the chromatic version, the chromatic fourth, has all semitones filled in. It is often used in music to denote tragedy or sorrow. However, "A common misperception exists that the 'lament bass' of Venetian opera became so prevalent that it immediately swept away all other possible affective associations with this bass pattern...To cite but one example, Peter Holman, writing about Henry Purcell, once characterized the minor tetrachord as 'the descending ground that was associated with love in seventeenth-century opera'." Compositional form There exists a short, free musical form of the Romantic Era, called complaint or "complainte" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
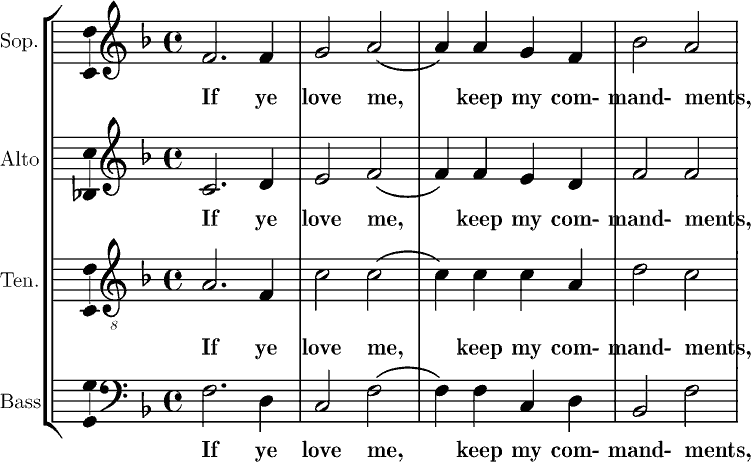
Lament Bass Harmonized
A lament or lamentation is a passionate expression of grief, often in music, poetry, or song form. The grief is most often born of regret, or mourning. Laments can also be expressed in a verbal manner in which participants lament about something that they regret or someone that they have lost, and they are usually accompanied by wailing, moaning and/or crying. Laments constitute some of the oldest forms of writing, and examples exist across human cultures. History Many of the oldest and most lasting poems in human history have been laments. The Lament for Sumer and Ur dates back at least 4000 years to ancient Sumer, the world's first urban civilization. Laments are present in both the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', and laments continued to be sung in elegiacs accompanied by the aulos in classical and Hellenistic Greece. Elements of laments appear in ''Beowulf'', in the Hindu Vedas, and in ancient Near Eastern religious texts. They are included in the Mesopotamian City Laments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band of all time and were integral to the development of counterculture of the 1960s, 1960s counterculture and popular music's recognition as an art form. Rooted in skiffle, beat music, beat and 1950s rock and roll, rock 'n' roll, their sound incorporated elements of classical music and traditional pop in innovative ways; the band also explored music styles ranging from folk music, folk and Music of India, Indian music to Psychedelic music, psychedelia and hard rock. As Recording practices of the Beatles, pioneers in recording, songwriting and artistic presentation, the Beatles revolutionised many aspects of the music industry and were often publicised as leaders of the era's Baby boomers, youth and sociocultural movements. Led by primary songwriter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Any Time At All
"Any Time at All" is a song by the English rock band the Beatles. Credited to the Lennon–McCartney partnership, it was mainly composed by John Lennon, with an instrumental middle eight by Paul McCartney. It first appeared on the Beatles' '' A Hard Day's Night'' album. Origin In his 1980 interview with ''Playboy'', Lennon described the song as "An effort at writing 'It Won't Be Long'. Same ilk: C to A minor, C to A minor—with me shouting." Lyrically, the song appears similar to the 1963, song, " All I've Got to Do" off the album, With the Beatles. Lennon's handwritten lyrics for "Any Time at All" were sold for £6,000 to an unidentified individual at an auction held at Sotheby's in London, on 8 April 1988. Recording Incomplete when first brought into EMI Studios on Tuesday 2 June 1964, Paul McCartney suggested an idea for the middle eight section based solely on chords, which was recorded with the intention of adding lyrics later. But by the time it was needed to be mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodgers And Hart
Rodgers and Hart were an American songwriting partnership between composer Richard Rodgers (1902–1979) and the lyricist Lorenz Hart (1895–1943). They worked together on 28 stage musicals and more than 500 songs from 1919 until Hart's death in 1943.Rodgers and Hart Biography Guide to Musical Theatre, accessed April 5, 2009 History Richard Rodgers and Lorenz Hart were introduced in 1919; Rodgers was still in high school while Hart had already graduated from . Their first collaboration together was at Columbia, and resulted in the 1920 Varsi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
My Funny Valentine
"My Funny Valentine" is a show tune from the 1937 Richard Rodgers and Lorenz Hart coming of age musical '' Babes in Arms'' in which it was introduced by teenaged star Mitzi Green. The song became a popular jazz standard, appearing on over 1300 albums performed by over 600 artists. One of them was Chet Baker, for whom it became his signature song. In 2015, it was announced that the Gerry Mulligan quartet featuring Chet Baker's version of the song was inducted into the Library of Congress's National Recording Registry for the song's "cultural, artistic and/or historical significance to American society and the nation’s audio legacy". Mulligan also recorded the song with his Concert Jazz Band in 1960. History '' Babes in Arms'' opened at the Shubert Theatre on Broadway, in New York City on April 14, 1937 and ran for 289 performances. In the original play, a character named Billie Smith (played by Mitzi Green) sings the song to Valentine "Val" LaMar (played by Ray Heatherton) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Bass
In music, an ostinato (; derived from Italian word for ''stubborn'', compare English ''obstinate'') is a motif or phrase that persistently repeats in the same musical voice, frequently in the same pitch. Well-known ostinato-based pieces include classical compositions such as Ravel's ''Boléro'' and the ''Carol of the Bells'', and popular songs such as Donna Summer and Giorgio Moroder's "I Feel Love" (1977), Henry Mancini's theme from ''Peter Gunn'' (1959), The Who's "Baba O'Riley" (1971), and The Verve's "Bitter Sweet Symphony" (1997). Both ''ostinatos'' and ''ostinati'' are accepted English plural forms, the latter reflecting the word's Italian etymology. The repeating idea may be a rhythmic pattern, part of a tune, or a complete melody in itself. Kamien, Roger (1258). ''Music: An Appreciation'', p. 611. . Strictly speaking, ostinati should have exact repetition, but in common usage, the term covers repetition with variation and development, such as the alteration of an ostin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Scale
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, which st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh out the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variation (music)
In music, variation is a formal technique where material is repeated in an altered form. The changes may involve melody, rhythm, harmony, counterpoint, timbre, orchestration or any combination of these. Variation techniques Mozart's Twelve Variations on "Ah vous dirai-je, Maman" (1785), known in the English-speaking world as " Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star" exemplifies a number of common variation techniques. Here are the first eight bars of the theme: Melodic variation Mozart's first variation decorates and elaborates the plain melodic line: Rhythmic variation The fifth variation breaks up the steady pulse and creates syncopated off-beats: Harmonic variation The seventh variation introduces powerful new chords, which replace the simple harmonies originally implied by the theme with a prolongational series of descending fifths: Minor mode In the elaborate eighth variation, Mozart changes from the major to the parallel minor mode, while combining three techniques: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romantic Music
Romantic music is a stylistic movement in Western Classical music associated with the period of the 19th century commonly referred to as the Romantic era (or Romantic period). It is closely related to the broader concept of Romanticism—the intellectual, artistic and literary movement that became prominent in Western culture from approximately 1798 until 1837. Romantic composers sought to create music that was individualistic, emotional, dramatic and often programmatic; reflecting broader trends within the movements of Romantic literature, poetry, art, and philosophy. Romantic music was often ostensibly inspired by (or else sought to evoke) non-musical stimuli, such as nature, literature, poetry, super-natural elements or the fine arts. It included features such as increased chromaticism and moved away from traditional forms. Background The Romantic movement was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |