|
Log-convex
In mathematics, a function ''f'' is logarithmically convex or superconvex if \circ f, the composition of the logarithm with ''f'', is itself a convex function. Definition Let be a convex subset of a real vector space, and let be a function taking non-negative values. Then is: * Logarithmically convex if \circ f is convex, and * Strictly logarithmically convex if \circ f is strictly convex. Here we interpret \log 0 as -\infty. Explicitly, is logarithmically convex if and only if, for all and all , the two following equivalent conditions hold: :\begin \log f(tx_1 + (1 - t)x_2) &\le t\log f(x_1) + (1 - t)\log f(x_2), \\ f(tx_1 + (1 - t)x_2) &\le f(x_1)^tf(x_2)^. \end Similarly, is strictly logarithmically convex if and only if, in the above two expressions, strict inequality holds for all . The above definition permits to be zero, but if is logarithmically convex and vanishes anywhere in , then it vanishes everywhere in the interior of . Equivalent conditions If is a dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Logarithmically Concave Function
In convex analysis, a non-negative function is logarithmically concave (or log-concave for short) if its domain is a convex set, and if it satisfies the inequality : f(\theta x + (1 - \theta) y) \geq f(x)^ f(y)^ for all and . If is strictly positive, this is equivalent to saying that the logarithm of the function, , is concave; that is, : \log f(\theta x + (1 - \theta) y) \geq \theta \log f(x) + (1-\theta) \log f(y) for all and . Examples of log-concave functions are the 0-1 indicator functions of convex sets (which requires the more flexible definition), and the Gaussian function. Similarly, a function is '' log-convex'' if it satisfies the reverse inequality : f(\theta x + (1 - \theta) y) \leq f(x)^ f(y)^ for all and . Properties * A log-concave function is also quasi-concave. This follows from the fact that the logarithm is monotone implying that the superlevel sets of this function are convex. * Every concave function that is nonnegative on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gamma Function
In mathematics, the gamma function (represented by Γ, capital Greek alphabet, Greek letter gamma) is the most common extension of the factorial function to complex numbers. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, the gamma function \Gamma(z) is defined for all complex numbers z except non-positive integers, and for every positive integer z=n, \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\,.The gamma function can be defined via a convergent improper integral for complex numbers with positive real part: \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^ e^\textt, \ \qquad \Re(z) > 0\,.The gamma function then is defined in the complex plane as the analytic continuation of this integral function: it is a meromorphic function which is holomorphic function, holomorphic except at zero and the negative integers, where it has simple Zeros and poles, poles. The gamma function has no zeros, so the reciprocal gamma function is an entire function. In fact, the gamma function corresponds to the Mellin transform of the negative exponential functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative denoted is the Product (mathematics), product of all positive integers less than or equal The factorial also equals the product of n with the next smaller factorial: \begin n! &= n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times (n-3) \times \cdots \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 \\ &= n\times(n-1)!\\ \end For example, 5! = 5\times 4! = 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1 = 120. The value of 0! is 1, according to the convention for an empty product. Factorials have been discovered in several ancient cultures, notably in Indian mathematics in the canonical works of Jain literature, and by Jewish mystics in the Talmudic book ''Sefer Yetzirah''. The factorial operation is encountered in many areas of mathematics, notably in combinatorics, where its most basic use counts the possible distinct sequences – the permutations – of n distinct objects: there In mathematical analysis, factorials are used in power series for the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set (mathematics), set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the Domain of a function, domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. History of the function concept, Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable function, differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Function Composition
In mathematics, the composition operator \circ takes two function (mathematics), functions, f and g, and returns a new function h(x) := (g \circ f) (x) = g(f(x)). Thus, the function is function application, applied after applying to . (g \circ f) is pronounced "the composition of and ". Reverse composition, sometimes denoted f \mapsto g , applies the operation in the opposite order, applying f first and g second. Intuitively, reverse composition is a chaining process in which the output of function feeds the input of function . The composition of functions is a special case of the composition of relations, sometimes also denoted by \circ. As a result, all properties of composition of relations are true of composition of functions, such as #Properties, associativity. Examples * Composition of functions on a finite set (mathematics), set: If , and , then , as shown in the figure. * Composition of functions on an infinite set: If (where is the set of all real numbers) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , then is the logarithm of to base , written , so . As a single-variable function, the logarithm to base is the inverse of exponentiation with base . The logarithm base is called the ''decimal'' or ''common'' logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The ''natural'' logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics because of its very simple derivative. The ''binary'' logarithm uses base and is widely used in computer science, information theory, music theory, and photography. When the base is unambiguous from the context or irrelevant it is often omitted, and the logarithm is written . Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
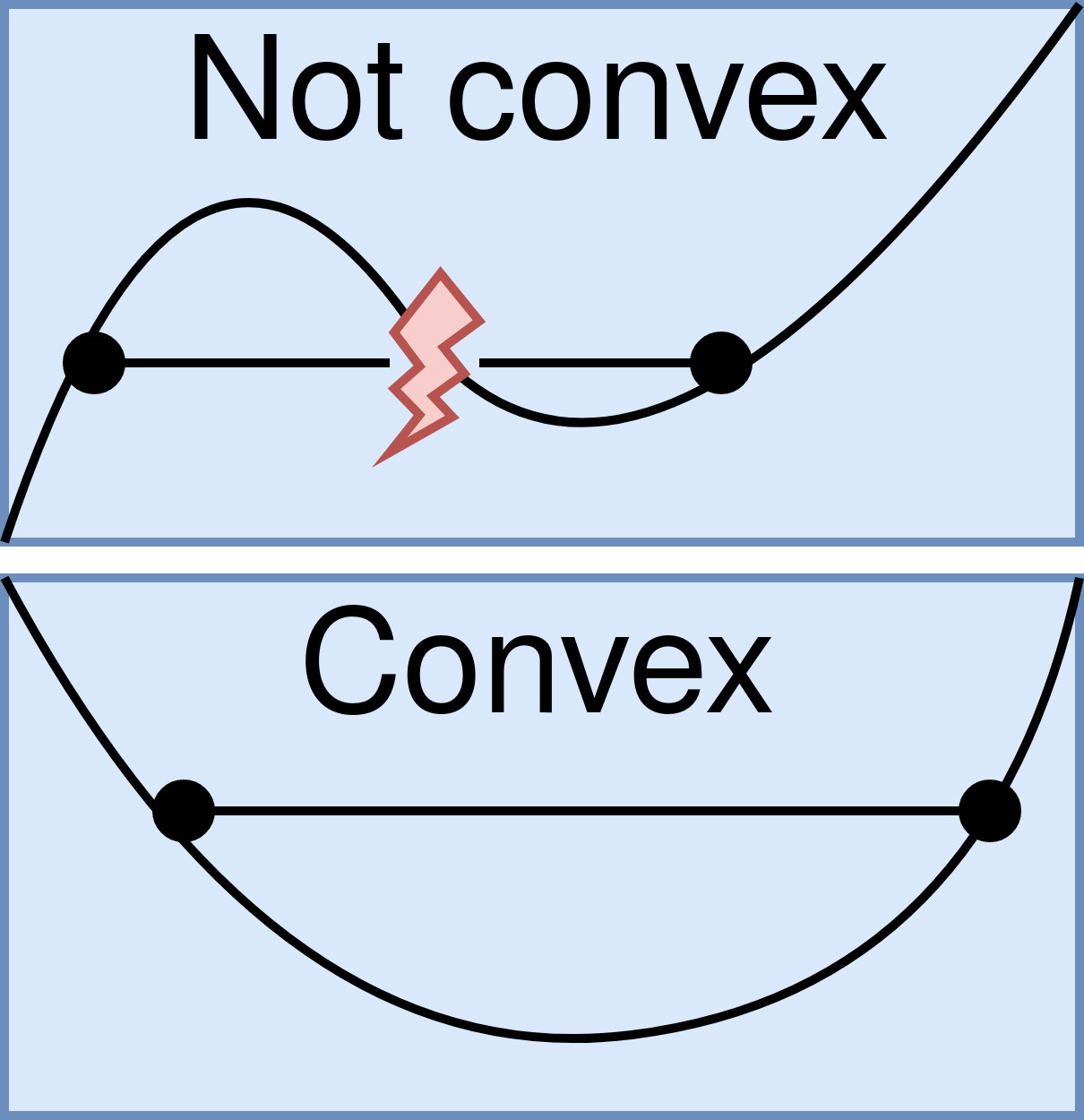
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two distinct points on the graph of a function, graph of the function lies above or on the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (mathematics), ''epigraph'' (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. In simple terms, a convex function graph is shaped like a cup \cup (or a straight line like a linear function), while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. A twice-differentiable function, differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain of a function, domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include a linear function f(x) = cx (where c is a real number), a quadratic function cx^2 (c as a nonnegative real number) and an exponential function ce^x (c as a nonnegative real number). Convex functions pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Convex Set
In geometry, a set of points is convex if it contains every line segment between two points in the set. For example, a solid cube (geometry), cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary (topology), boundary of a convex set in the plane is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval (mathematics), interval with the property that its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of a function, graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization, optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets. The branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex sets and convex f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Real Numbers
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measurement, measure a continuous variable, continuous one-dimensional quantity such as a time, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limit (mathematics), limits, continuous function, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally mathematical notation, denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction (mathematics), fraction . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative And Positive Numbers
In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or 0. Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as having its own unique sign, having no sign, or having both positive and negative sign. In some contexts, it makes sense to distinguish between a positive and a negative zero. In mathematics and physics, the phrase "change of sign" is associated with exchanging an object for its additive inverse (multiplication with −1, negation), an operation which is not restricted to real numbers. It applies among other objects to vectors, matrices, and complex numbers, which are not prescribed to be only either positive, negative, or zero. The word "sign" is also often used to indicate binary aspects of mathematical or scientific objects, such as odd and even ( sign of a permutation), sense of orientation or rotation ( cw/ccw), one sided limits, and other concepts described in below. Sign of a number Numbers from various number s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |