|
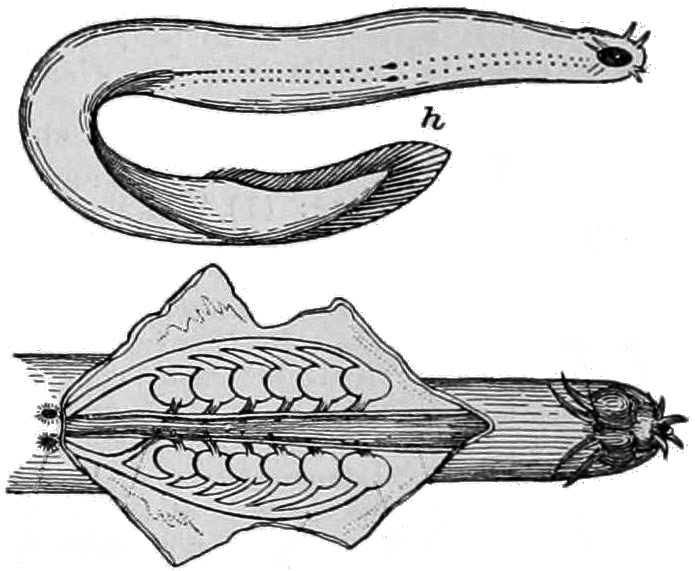
Lamprey
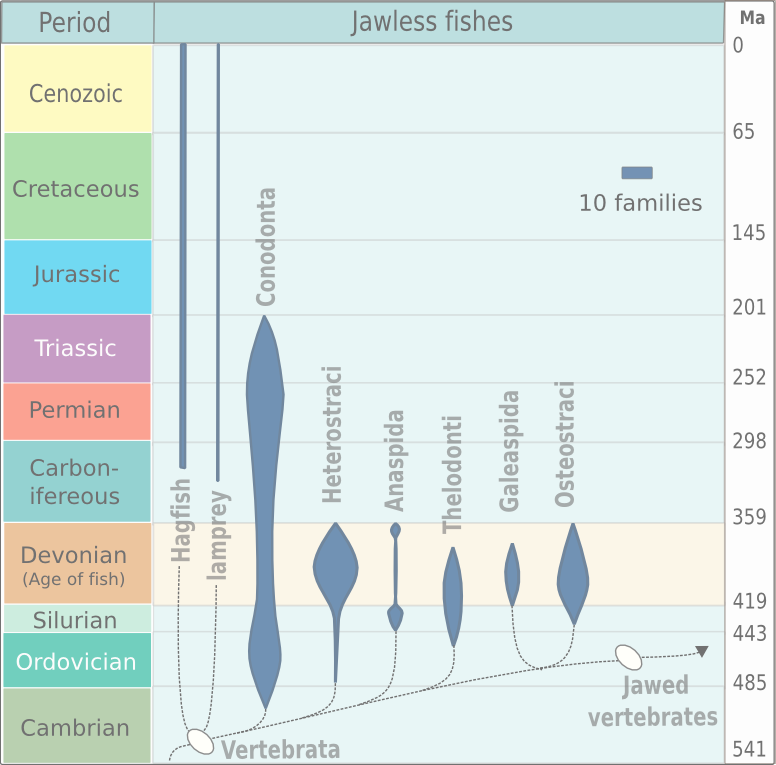
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. "Lamprey" is sometimes seen for the plural form. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families—two small families in the Southern Hemisphere (Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere (Petromyzontidae). Genetic evidence suggests that lampreys are more closely related to hagfish, the only other living group of jawless fish, than they are to jawed vertebrates, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossils of stem-group lampreys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lamprey Larva X Sect Pharynx Labelled
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of jawless fish comprising the order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. "Lamprey" is sometimes seen for the plural form. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families—two small families in the Southern Hemisphere ( Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere ( Petromyzontidae). Genetic evidence suggests that lampreys are more closely related to hagfish, the only other living group of jawless fish, than they are to jawed vertebrates, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossils of stem-group lampreys are from the latest Devonian, around 360 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Petromyzon Marinus
The sea lamprey (''Petromyzon marinus'') is a parasitic lamprey native to the Northern Hemisphere. It is sometimes referred to as the "vampire fish". It was likely introduced to the Great Lakes region through the Erie Canal in 1825 and the Welland Canal in 1919 where it has attacked native fish such as lake trout, lake whitefish, chub, and lake herring. Sea lampreys are considered a pest in the Great Lakes region as each individual has the potential of killing 40 pounds of fish through its 12–18 month feeding period. Description The sea lamprey has an eel-like body without paired fins. Its mouth is jawless, round and sucker-like, and as wide or wider than the head; sharp teeth are arranged in many concentric circular rows around a sharp, rasp-like tongue. There are seven branchial or gill-like openings behind the eye. Sea lampreys are olive or brown-yellow on the dorsal and lateral part of the body, with some black marblings, with lighter coloration on the belly. Within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European River Lamprey
The European river lamprey (''Lampetra fluviatilis''), also known as the river lamprey or lampern, is a species of freshwater lamprey. Description Adult river lampreys measure from in the marine forms and up to in the lake forms. The very elongated body is uniformly dark grey on top, paler to yellowish off-white on the sides and pure white underneath. Like all lampreys, they lack paired fins and have a circular sucking disc instead of jaws. They have a single nostril and seven small gill slits on each side behind the eye. The teeth are sharp and these fish can be distinguished from the somewhat smaller brook lamprey (''Lampetra planeri'') by the fact that the two dorsal fins are more widely separated. Distribution The European river lamprey is found in coastal waters around almost all of Europe from the northwestern Mediterranean Sea north to the lakes of Finland, Scotland, Norway (Mjøsa), Wales ( Cors Caron), and Russia, including rivers in the Alps; especially in Nakkila, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyclostomi
Cyclostomi, often referred to as Cyclostomata , from Ancient Greek κύκλος (kúklos), meaning "circle", and στόμα (stóma), meaning "mouth", is a superclass of vertebrates that comprises the living jawless fish classes: the lampreys and hagfishes. Both groups have jawless mouths with horny epidermal structures that function as teeth called ceratodontes, and branchial arches that are internally positioned instead of external as in the related jawed fishes. The superclass was named by Joan Crockford-Beattie. Possible external relationships This taxon is often included in the paraphyletic infraphylum Agnatha, which also includes several groups of extinct armored fishes called ostracoderms. Most fossil agnathans, such as galeaspids, thelodonts, and osteostracans, are more closely related to vertebrates with jaws (called gnathostomes) than to cyclostomes. Biologists historically disagreed on whether cyclostomes are a clade. The "vertebrate hypothesis" h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although they do have rudimentary vertebrae. Hagfish are marine animal, marine predators and scavengers that can defend themselves against other larger predators by releasing copious amounts of slime coat, slime from mucous glands in their skin. Although their exact relationship to the only other extant taxon, living group of Agnatha, jawless fish, the lampreys, was long the subject of controversy, genetic evidence suggests that hagfish and lampreys are more closely related to each other than to jawed vertebrates, thus forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest-known stem group hagfish are known from the Pennsylvanian (geology), Late Carboniferous, around Moscovian (Carboniferous), 310 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Priscomyzon
''Priscomyzon riniensis'' is an extinct lamprey that lived some 360 million years ago during the Famennian (Late Devonian) in a marine or estuarine environment in South Africa. This small agnathan is anatomically similar to the Mazon Creek lampreys, but is some 35 million years older. Its key developments included the first known large oral disc, circumoral teeth and a branchial basket. Context Though common and diverse during the Silurian and Devonian, jawless fish are today represented only by lampreys and hagfish, both groups being quite specialized. Lampreys have seven gill pouches (whereas jawed fish have only five), no paired fins, and a rudimentary skeleton of cartilage. They also have a sucker disc of cartilage surrounded by a soft lip and a central small mouth set about with simple hooked teeth. They attach to the bodies of other vertebrates by suction, securing their grip with the hooked teeth, after which a rasped tongue scrapes a hole providing access to the host' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caeruleum (lamprey)
''Caeruleum'' is an extinct genus of lamprey from the Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of China. The genus contains two species, ''C. miraculum'' and ''C. gracilis'', known from various specimens including complete and partial bodies. Discovery and naming The first described ''Caeruleum'' fossil material was discovered in sediments of the Jiufotang Formation near Naizi (or Naitou) Mountain in Weichang County of Chengde City, Hebei Province, China. Various lamprey specimens were found in this formation. In 2023, Weijia Huang described ''Caeruleum miraculum'' as a new genus and species of lamprey based on several fossil remains. The holotype specimen, BMM 3770, consists of a complete animal preserved on a slab and counterslab. Several additional specimens of various levels of completion were also assigned to ''Caeruleum'' as paratypes. These include BMM 3771 (an incomplete specimen with a complete tail), BMM 3772 (the posterior end of an animal with a mutilated tail), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yanliaomyzon
''Yanliaomyzon'' is an extinct genus of predatory lampreys that lived approximately 163 million years ago during the Middle Jurassic. It is found in the Yanliao Biota, including both the Daohugou Beds and the Tiaojishan Formation in Liaoning province, northern China. The genus has two species: ''Yanliaomyzon occisor'' and ''Yanliaomyzon ingensdentes''. These species are significant for being the earliest lampreys to closely resemble modern species. Description The species ''Y. occisor'' has a body length of , which would make it the largest extinct fossil lamprey discovered. Both members of this genus resemble the modern pouched lamprey (''Geotria australis''). ''Yanliaomyzon'' bears a toothed oral disc that is much more similar to those of modern lampreys than those of Paleozoic lampreys. The two species are distinguished by differences in the anatomy of the toothed oral disc, as well as that the tail occupies around 40% of the body length in ''Yanliaomyzon ingensdentes'' but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mesomyzon
''Mesomyzon mengae'' is an extinct lamprey from freshwater strata of the Early Cretaceous-aged Yixian Formation, in China. The animal's exquisitely preserved fossils show a creature very similar to modern-day lampreys, having a well-developed sucking oral disk, a branchial basket, at least seven pairs of gill pouches and corresponding gill arches, impressions of gill filaments, and at least 80 myomeres of its musculature. It had the same three phase life cycle found in modern lampreys. A phylogenetic analysis conducted in 2018 shows that ''Mesomyzon'' is the fossil lamprey most closely related to modern taxa, though it is not closely related to any modern group. On the other hand, Brownstein & Near (2022) found it to be a member of the lamprey crown group, most closely related to Petromyzontidae. However, a 2023 study found it again to be a derived stem Stem or STEM most commonly refers to: * Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant * Stem group * Science, technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mordaciidae
''Mordacia'' is a genus of lamprey, the sole genus of the family Mordaciidae, also known as the southern topeyed lampreys. The family Mordaciidae is most closely related to the lamprey family Geotriidae, which has a similar Gondwanan distribution, and both families diverged during the Early Cretaceous. Together, their common ancestor diverged from the Petromyzontidae during the Middle Jurassic. They are found in Chile and Australia; the Chilean and one Australian species (''M. lapicida'' and ''M. mordax'') are anadromous fish that spawn in Pacific-draining river basins and mature in the ocean, while the other Australian species (''M. praecox'') spends its whole life in freshwater. Phylogenetic evidence indicates ancient divergences within this genus, with the Chilean and Australian lineages diverging from one another during the Late Cretaceous (100 mya), although both Australian species only diverged from each other during the Pleistocene. Species There are currently three rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |