|
Intratracheal Instillation
Intratracheal instillation is the introduction of a substance directly into the trachea. It is widely used to test the respiratory toxicity of a substance as an alternative to inhalation in animal testing. Intratracheal instillation was reported as early as 1923 in studies of the carcinogenicity of coal tar. Modern methodology was developed by several research groups in the 1970s. By contrast, tracheal administration of pharmaceutical drugs in humans is called endotracheal administration. Background As compared to inhalation, intratracheal instillation allows greater control over the dose and location of the substance, is cheaper and less technically demanding, allows lower amounts of scarce or expensive substances to be used, allows substances to be tested that can be inhaled by humans but not small mammals, and minimizes exposure to laboratory workers and to the skin of laboratory animals. Disadvantages include its nonphysiological and invasive nature, the confounding ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. It is epithelium lined with column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usually as a result of a viral illness affecting othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Rat
A laboratory rat or lab rat is a brown rat of the subspecies '' Rattus norvegicus domestica'' which is bred and kept for scientific research. While less commonly used for research than mice (see laboratory mouse), rats have served as an important animal model for research in psychology and biomedical science. Origins In 18th century Europe, wild brown rats ran rampant and this infestation fueled the industry of rat-catching. Rat-catchers would not only make money by trapping the rodents, but also by selling them for food or, more commonly, for rat-baiting. Rat-baiting was a popular sport, which involved filling a pit with rats and timing how long it took for a terrier to kill them all. Over time, breeding the rats for these contests may have produced variations in color, notably the albino and hooded varieties. The first time one of these albino mutants was brought into a laboratory for a study was in 1828 for an experiment on fasting. Over the next 30 years, rats were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an endotracheal tube is passed through the mouth and vocal apparatus into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Other methods of intubation involve surgery and include the cricothyrotomy (used almost exclusively in emergency circumstances) and the tracheotomy, used primarily in situations where a prolonged need for airway support is anticipated. Because it is an invasive and uncomfortable me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomaterials
* Nanomaterials describe, in principle, materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructured materials'', which have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saline (medicine)
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, acidosis, and high blood sodium. In those with long-standing low blood sodium, excessive use may result in osmotic demyelination syndrome. Saline is in the crystalloid family of medications. It is most commonly used as a sterile 9 g of salt per litre (0.9%) solution, known as normal saline. Higher and lower concentrations may also occasionally be used. Saline is acidic, with a pH of 5.5 (due mainly to dissolved carbon dioxide). The medical use of saline began around 1831. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, sodium was the 274th most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enflurane
Enflurane (2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a halogenated ether. Developed by Ross Terrell in 1963, it was first used clinically in 1966. It was increasingly used for inhalational anesthesia during the 1970s and 1980s but is no longer in common use. Enflurane is a structural isomer of isoflurane. It vaporizes readily, but is a liquid at room temperature. Physical properties Side effects Clinically, enflurane produces a dose-related depression of myocardial contractility with an associated decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption. Between 2% and 5% of the inhaled dose is oxidised in the liver, producing fluoride ions and difluoromethoxy-difluoroacetic acid. This is significantly higher than the metabolism of its structural isomer isoflurane. Enflurane also lowers the threshold for seizures, and should especially not be used on people with epilepsy. Like all potent inhalation anaesthetic agents it is a known trigger of malignant hyperthermia. Like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful in those who are difficult to intubate. It is given by inhalation. Side effects include an irregular heartbeat, respiratory depression, and hepatotoxicity. Like all volatile anesthetics, it should not be used in people with a personal or family history of malignant hyperthermia. It appears to be safe in porphyria. It is unclear whether use during pregnancy is harmful to the baby, and it is not generally recommended for use during a C-section. Halothane is a chiral molecule that is used as a racemic mixture. Halothane was discovered in 1955. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Its use in developed countries has been mostly replaced by newer ane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesiology, but others are used commonly in various fields of healthcare. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. Anesthetics are distinct from analgesics, which block only sensation of painful stimuli. Local anesthetics Local anesthetic agents prevent the transmission of nerve impulses without caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
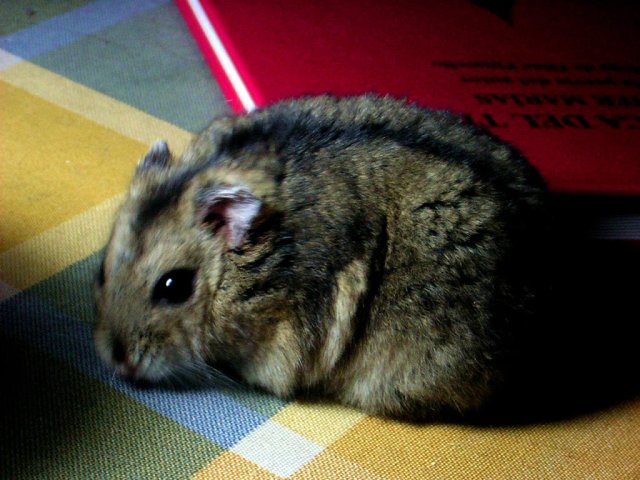
Laboratory Hamster
Hamsters are rodents (order Rodentia) belonging to the subfamily Cricetinae, which contains 19 species classified in seven genera.Fox, Sue. 2006. ''Hamsters''. T.F.H. Publications Inc. They have become established as popular small pets. The best-known species of hamster is the golden or Syrian hamster (''Mesocricetus auratus''), which is the type most commonly kept as pets. Other hamster species commonly kept as pets are the three species of dwarf hamster, Campbell's dwarf hamster (''Phodopus campbelli''), the winter white dwarf hamster (''Phodopus sungorus'') and the Roborovski hamster (''Phodopus roborovskii''). Hamsters are more crepuscular than nocturnal and, in the wild, remain underground during the day to avoid being caught by predators. They feed primarily on seeds, fruits, and vegetation, and will occasionally eat burrowing insects. Physically, they are stout-bodied with distinguishing features that include elongated cheek pouches extending to their shoulders, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Mouse
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species '' Mus musculus''. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues. Other mouse species sometimes used in laboratory research include two American species, the white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') and the North American deer mouse ('' Peromyscus maniculatus''). History as a biological model Mice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

