|
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ; Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
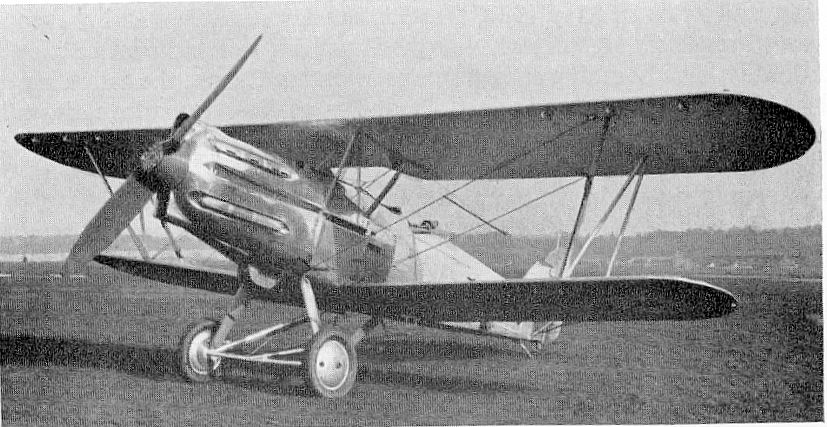
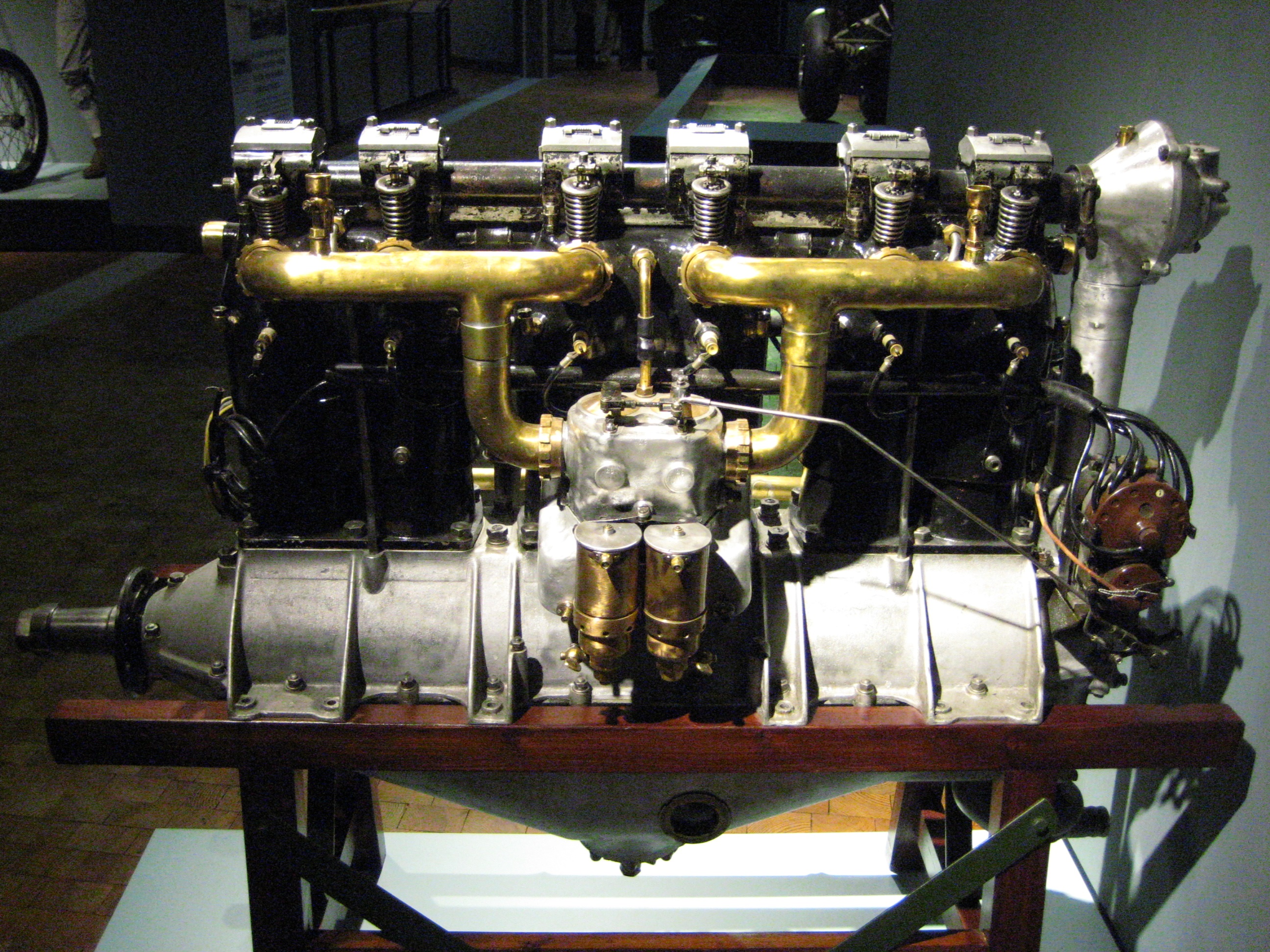
Daimler D II
Daimler is a German surname. It may refer to: People * Gottlieb Daimler (1834–1900), German inventor, industrialist and namesake of a series of automobile companies * Adolf Daimler (1871–1913), engineer and son of Gottlieb Daimler * Paul Daimler (1869–1945), engineer and son of Gottlieb Daimler Places * Mount Daimler, a peak in Antarctica named after Gottlieb Daimler Companies Germany * Daimler AG, the past name of the Mercedes-Benz Group from 2007 to 2022, known to the public as Mercedes-Benz, formerly known as Daimler-Benz AG (1926–1998) and DaimlerChrysler AG (1998–2007) ** Daimler Mobility, banking and credit/debit card services subsidiary renamed as Mercedes-Benz Mobility in 2022. * Daimler Truck, demerged in 2021 ** Daimler Truck North America, formerly Freightliner Corporation, Portland, Oregon ** Daimler India Commercial Vehicles, a subsidiary based in Chennai, India ** Daimler Buses North America, subsidiary in Greensboro, North Carolina, US * Daimler Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine 12Eb
The Lorraine 12E Courlis was a W-12 (broad arrow) aero engine produced by the French company Lorraine-Dietrich during the 1920s and 1930s. Variants ;12E: ;12Eb: ;12Ebr: ;12Ed: ;12Edr: ;12Ee: ;12Ew:The standard Eb fitted with a supplementary supercharger. ;Elizalde A: The 12E built under licence in Spain by Elizalde S.A. Applications Aircraft * Aichi AB-1 * Bernard SIMB V.1 * Blériot-SPAD S.86 * Breguet 19 * Canete Pirata * Caudron C.17 * Dewoitine D.12 * Dewoitine D.25 * FMA AeT.1 * Grigorovich MR-2 * Grigorovich ROM-1 * Hiro H1H * Levasseur PL.4 * Levasseur PL.5 * Levasseur PL.8 * Lioré et Olivier LeO H-134 * Potez 24 * Potez 25 * Potez 26 * PWS-10 * Rohrbach Ro IIIa Rodra * SET 2 * Villiers II * Villiers XXIV * Wibault 73 * Yokosuka E1Y Other applications * Argentine Nahuel tank The Nahuel DL-43 tank was a medium tank developed in Argentina during World War II. It was the Argentine equivalent of the M4 Sherman and the M3 Grant American medium tanks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposed-piston Engine
An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and factories. Current manufacturers of opposed-piston engines include Fairbanks-Morse, Cummins and Achates Power. Design Compared to contemporary two-stroke engines, which used a conventional design of one piston per cylinder, the advantages of the opposed-piston engine have been recognized as: * Eliminating the cylinder head and valvetrain, which reduces weight, complexity, cost, heat loss, and friction loss of the engine. * Creating a uniflow-scavenged movement of gas through the combustion chamber, which avoided the drawbacks associated with the contemporary crossflow-scavenged designs (however later advancements have provided methods for achieving uniflow scavenging in conventional piston engine designs). * A reduced height of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Dagger
The Napier Dagger was a 24-cylinder H-pattern ''(or H-Block)'' air-cooled engine designed by Frank Halford and built by Napier before World War II. It was a development of the earlier Napier Rapier. Design and development The H-Block has a compact layout, as it essentially consists of two vertically opposed, flat-twelve inline engines lying side-by-side and driving side-by-side crankshafts. Another advantage is that since the cylinders are opposed, the motion in one is balanced by the opposite motion in the one on the opposite side, leading to very smooth running. The Dagger was remarkable for its fast rotation, running at up to 4,000 rpm but unlike the later Napier Sabre, it had conventional poppet valves. Although considered a masterpiece of engine design by Frank Halford, there were problems with cooling, maintenance, manufacturing and weight, which were not solved during the Dagger's lifetime and went unresolved well into the lifetime of the Napier Sabre, its successo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Sabre
The Napier Sabre is a British H-24-cylinder, liquid-cooled, sleeve valve, piston aero engine, designed by Major Frank Halford and built by D. Napier & Son during World War II. The engine evolved to become one of the most powerful inline piston aircraft engines in the world, developing from in its earlier versions to in late-model prototypes. The first operational aircraft to be powered by the Sabre were the Hawker Typhoon and Hawker Tempest; the first aircraft powered by the Sabre was the Napier-Heston Racer, which was designed to capture the world speed record. Other aircraft using the Sabre were early prototype and production variants of the Blackburn Firebrand, the Martin-Baker MB 3 prototype and a Hawker Fury prototype. The rapid introduction of jet engines after the war led to the quick demise of the Sabre, as there was less need for high power military piston aero engines and because Napier turned its attention to developing turboprop engines such as the Naiad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
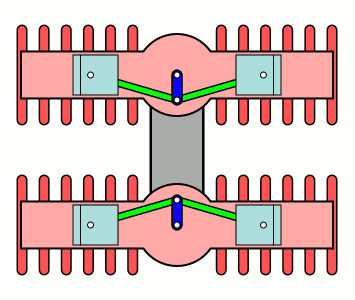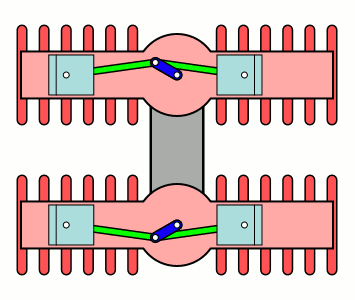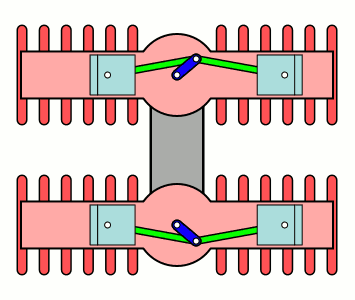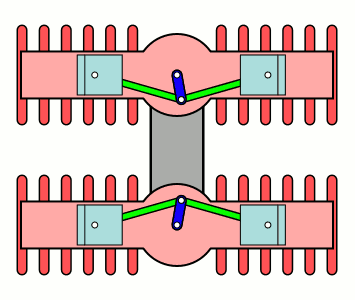
H Engine
An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate flat engines (complete with separate crankshafts), most often geared to a common output shaft. The name "H engine" is due to the engine blocks resembling a letter "H" when viewed from the front. The most successful "H" engine in this form was the Napier Dagger and its derivatives. The name was also applied to engines of the same basic layout, but rotated through 90 degrees—most famously the Napier Sabre series. A variation on the "H" theme were the Fairey Prince (H-16) & Fairey P.24 Monarch, where the two engines retained separate drives, driving Contra-rotating propellers through separate concentric shafts. Although successful, they only existed in prototype form. The H engine is a relatively rare layout, with its main use being in aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s. The 1966 Lotus 43 Formula One car used a BRM 16-cylinder H engine, and an 8-cylinder H engine was used for powerboat racing in the 1970s. Desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
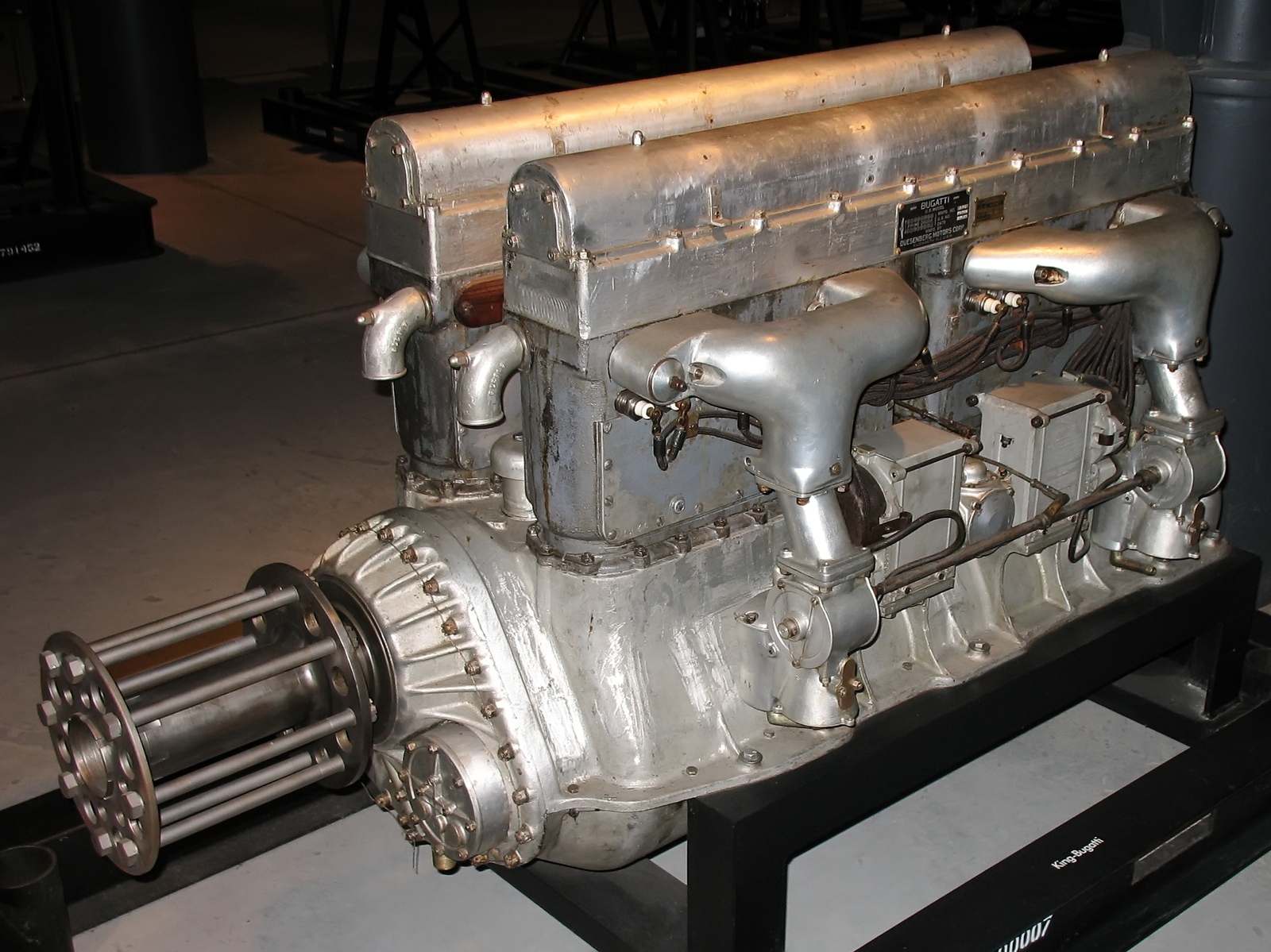
Bugatti U-16
The Bugatti U-16 was a 16-cylinder water-cooled double-8 vertical in-line "U engine", designed by Ettore Bugatti in 1915-1916 and built in France in small numbers. The US Bolling Commission bought a license to build the engine in the US, and small numbers of a slightly revised version were built by the Duesenberg Motor Corporation as the King-Bugatti. Probably about 40 King-Bugattis were made before the end of World War I caused building contracts to be canceled. Design and development The U-16 engine was designed to use as many features of a previous Bugatti 8-cylinder in-line "straight-eight" engine as possible. Two eight-cylinder banks were mounted vertically side by side on a common cast aluminium crankcase, each bank driving its own crankshaft. The two crankshafts were geared to and drove a single common airscrew shaft. The shaft was bored to accept a 37-mm gun barrel, and a clear passage was provided through the crankcase in line with the shaft boring for the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U Engine
A U engine is a piston engine made up of two separate straight engines (complete with separate crankshafts) placed side-by-side and coupled to a shared output shaft. When viewed from the front, the engine block resembles the letter "U". Although much less common than the similar V engine design, several U engines were produced from 1915-1987 for use in airplanes, racing cars, racing and road motorcycles, locomotives, and tanks. Design The main benefit of a U engine layout is the ability to share common parts with straight engine upon which is it based. Additionally, if the two crankshafts rotate in opposite directions, the gyroscopic effect of the rotating components in each cylinder bank cancel each other out. However, a V engine is typically more compact and lighter than a U engine (in part due to the lack of a second crankshaft), therefore V engines are far more common than U engines. The H engine layout uses a similar concept to U engines, whereby two flat engines are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings around the edge of the master rod. Extra "rows" of radial cylinders can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumo205 Cutview
Jumo was a social network service and website launched on November 30, 2010, to index charities so that people can find and evaluate them. Jumo was founded by Facebook co-founder Chris Hughes. On August 17, 2011 he announced Jumo was merging with the GOOD organization, providing a social engagement platform to complement their magazine content. Jumo reported raising $3.5 million in donations and sponsorships prior to its launch, including up to $750,000 from Omidyar Network. Acquisition On August 17, 2011, Jumo announced that it had been acquired by the GOOD, a collaborative magazine and event media company headquartered in Los Angeles, USA. The company blog states the purpose to be "to create a powerful online content and social engagement platform". One of the reasons behind that acquisition is believed to be that Jumo's platform was not receiving the level of user traffic it has anticipated to grow itself. Open source Two months after being acquired by GOOD In most cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Cub
The Napier Cub was an unusual and very large experimental 16-cylinder 'X' pattern liquid-cooled aero engine built by the British engine company D. Napier & Son. The Cub was the only Napier 'X' engine design. First flown on 15 December 1922 in an Avro Aldershot biplane bomber aircraft, the only other application was in the Blackburn Cubaroo. Only six engines of this type were ordered and produced.Lumsden 2003, p.171. Design The four banks of four cylinders were arranged in a flattened 'X' when viewed from the front. The angle between the upper cylinders was 52.5 degrees, the lower cylinders 127.5 degrees, which gave an angle of 90 degrees between the outer cylinder banks. The cylinders consisted of separate individual steel forgings with welded steel water cooling jackets. The carburettor was situated below the propeller reduction gear at the front of the engine and fed the inlet valves through four inlet manifolds. The valve drive gear, magnetos and pumps were fitted to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |