|
Inferior Phrenic Vein
The inferior phrenic veins drain the diaphragm and follow the course of the inferior phrenic arteries; * the right ends in the inferior vena cava; * the left is often represented by two branches, ** one of which ends in the left renal or suprarenal vein, ** while the other passes in front of the esophageal hiatus in the diaphragm and opens into the inferior vena cava The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of th .... References Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
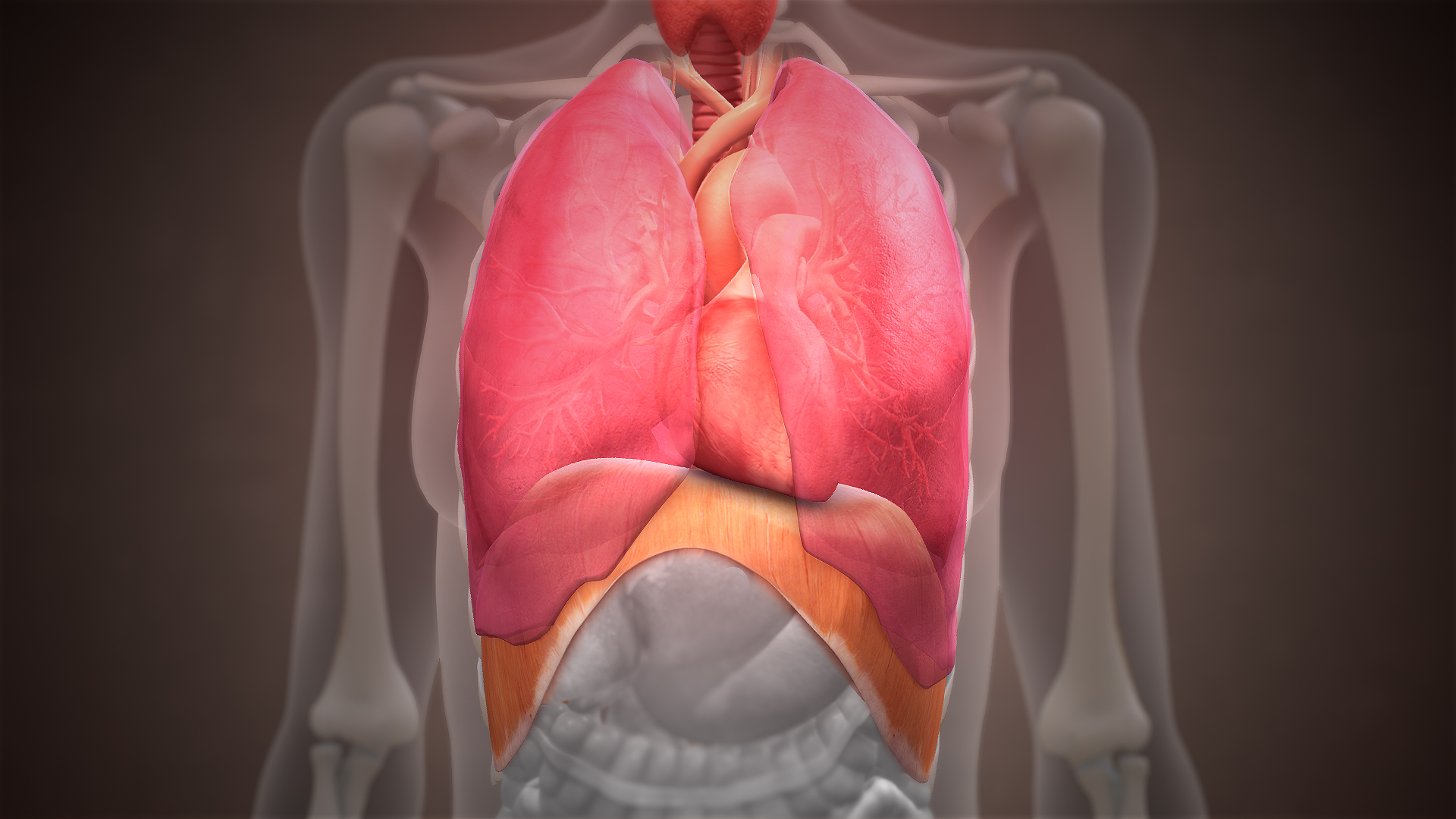
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower (" inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart. The name derives from la, ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Phrenic Arteries
The inferior phrenic arteries are two small vessels which supply the diaphragm. They present much variety in their origin. Structure Origin The inferior phrenic arteries usually arise between T12 and L2 vertebrae. They may arise separately from the front of the aorta, immediately above the celiac artery, or by a common trunk, which may spring either from the aorta or from the celiac artery. Sometimes one is derived from the aorta, and the other from one of the renal arteries; they rarely arise as separate vessels from the aorta. Branches They diverge from one another across the crura of the diaphragm, and then run obliquely upward and lateralward upon its under surface. * The ''left phrenic'' passes behind the esophagus, and runs forward on the left side of the esophageal hiatus. * The ''right phrenic'' passes behind the inferior vena cava, and along the right side of the foramen which transmits that vein. Near the back part of the central tendon each vessel divides i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Vein
The renal veins are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Because the inferior vena cava is on the right half of the body, the left renal vein is longer than the right one. Structure One renal vein drains each kidney. A renal vein is situated anterior to its corresponding accompanying renal artery. The renal veins empty into the inferior vena cava, entering it at nearly a 90° angle. Due to the right-ward displacement of the inferior vena cava from the midline, the left renal vein is some 3 times longer than the right one (~7.5 cm and ~2.5 cm, respectively). The renal vein divides into 4 divisions upon entering the kidney: * the anterior branch which receives blood from the anterior portion of the kidney and, * the posterior branch which receives blood from the posterior portion. Tributaries Because the tributaries of the inferior vena cava are not bilaterally symmetrical, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprarenal Vein
The suprarenal veins are two in number: * the ''right'' ends in the inferior vena cava. * the ''left'' ends in the left renal or left inferior phrenic vein. They receive blood from the adrenal glands The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex whic ... and will sometimes form anastomoses with the inferior phrenic veins. Additional images File:Gray480.png, Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins File:Gray1183.png, Suprarenal glands viewed from the front File:Gray1184.png, Suprarenal glands viewed from behind References External links Veins of the torso Adrenal gland {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass. Structure It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine. Fibers of the right crus cross one another below the hiatus. It is located approximately at level of the tenth thoracic vertebra ( T10) and the 8th or 9th intercostal spaces. The esophageal hiatus is situated in the muscular part of the diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra, and is elliptical in shape. It is placed superior, anterior, and slightly left of the aortic hiatus, and transmits the esophagus, the vagus nerve, the left inferior phrenic vessels, and some small esophageal arteries from left gastric vessels. The right crus of the diaphragm loops around forming a sling around the esophagus. Upon inspiration, this sling would constrict the esophagus, forming a functional (not anatomical) sphincter that prevents sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |