|
Ice-shelf
An ice shelf is a large floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic. The boundary between the floating ice shelf and the anchor ice (resting on bedrock) that feeds it is the grounding line. The thickness of ice shelves can range from about to . In contrast, sea ice is formed on water, is much thinner (typically less than ), and forms throughout the Arctic Ocean. It is also found in the Southern Ocean around the continent of Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice. That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. In steady state, about half of Antarctica's ice shelf mass is lost to basal melt and half is lost to calving, but the relative importance of each process varies significantly between ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
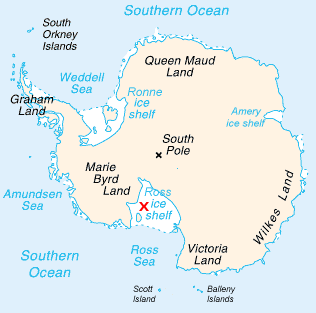
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Calving
Ice calving, also known as glacier calving or iceberg calving, is the breaking of ice chunks from the edge of a glacier.Essentials of Geology, 3rd edition, Stephen Marshak It is a form of ice ablation or ice disruption. It is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse. The ice that breaks away can be classified as an iceberg, but may also be a growler, bergy bit, or a crevasse wall breakaway.Glossary of Glacier Terms Ellin Beltz, 2006. Retrieved July 2009. Calving of glaciers is often accompanied by a loud cracking or booming sound before blocks of ice up to high break loose and crash into the water. The entry of the ice into the water causes large, and often hazardous waves. The waves formed in locations like |
Ward Hunt Ice Shelf
The Ward Hunt Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf in the Arctic, located near Ward Hunt Island, on the north coast of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada. During the 20th century the Ellesmere Ice Shelf broke up into six separate shelves, the largest being Ward Hunt. Ward Hunt Ice Shelf is currently about in size, and has been in place for approximately 4,000 years as part of a continuous ice shelf that encompassed the northern coast of Ellesmere Island until the beginning of the twentieth century. In 2005 one of the other shelves, the Ayles Ice Shelf, calved completely. The Ellesmere ice shelf was documented by the British Arctic Expedition of 1875–76, in which Lieutenant Pelham Aldrich's party went from Cape Sheridan (82.47°N, 61.50°W) west to Cape Alert (82.27°N, 85.55°W), including the Ward Hunt Ice Shelf. Reports from Robert Peary's expedition in 1906 described a “broad glacial fringe” covering much of the coast of northwestern Ellesmere Island. The Ward Hunt ice s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island ( iu, script=Latn, Umingmak Nuna, lit=land of muskoxen; french: île d'Ellesmere) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of , slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is . Lying within the Arctic Archipelago, Ellesmere Island is considered part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands. Cape Columbia at 83°06′ is the northernmost point of land in Canada and one of the northernmost points of land on the planet (the northernmost point of land on Earth is the nearby Kaffeklubben Island of Greenland). The Arctic Cordillera mountain system covers much of Ellesmere Island, making it the most mountainous in the Arctic Archipelago. More than one-fifth of the island is protected as Quttinirpaaq National Park. In 2021, the population of Ellesmere Island was recorded at 144. There are three settlements: Alert, Nunavut, Aler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Sound-2016-Joinville Island-Ice Shelf
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other island territories located on the Antarctic Plate or south of the Antarctic Convergence. The Antarctic region includes the ice shelves, waters, and all the island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence, a zone approximately wide varying in latitude seasonally. The region covers some 20 percent of the Southern Hemisphere, of which 5.5 percent (14 million km2) is the surface area of the Antarctica continent itself. All of the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude are administered under the Antarctic Treaty System. Biogeographically, the Antarctic realm is one of eight biogeographic realms of Earth's land surface. Geography As defined by the Antarctic Treaty System, the Antarctic regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M'Clintock Ice Shelf
The M'Clintock Ice Shelf was a Canadian ice shelf attached to northern Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island ( iu, script=Latn, Umingmak Nuna, lit=land of muskoxen; french: île d'Ellesmere) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. .... By 1961/62, its connection was tenuous. Most of the shelf broke away during the period of 1963 through 1965 with the remainder (10 km2 lodged at Borup Point) breaking off in 1966. Subsequently, multi year landfast sea ice, containing ice shelf fragments, has covered the M’Clintock Inlet mouth. References Ellesmere Island Ice shelves of Qikiqtaaluk Region {{QikiqtaalukNU-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Ice Shelf
Smith may refer to: People * Metalsmith, or simply smith, a craftsman fashioning tools or works of art out of various metals * Smith (given name) * Smith (surname), a family name originating in England, Scotland and Ireland ** List of people with surname Smith * Smith (artist) (born 1985), French visual artist Arts and entertainment * Smith (band), an American rock band 1969–1971 * ''Smith'' (EP), by Tokyo Police Club, 2007 * ''Smith'' (play), a 1909 play by W. Somerset Maugham * ''Smith'' (1917 film), a British silent film based on the play * ''Smith'' (1939 film), a short film * ''Smith!'', a 1969 Disney Western film * ''Smith'' (TV series), a 2006 American drama * ''Smith'', a 1932 novel by Warwick Deeping * ''Smith'', a 1967 novel by Leon Garfield and a 1970 TV adaptation Places North America * Smith, Indiana, U.S. * Smith, Kentucky, U.S. * Smith, Nevada, U.S. * Smith, South Carolina, U.S. * Smith Village, Oklahoma, U.S. * Smith Park (Middletown, Connecticut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milne Ice Shelf
The Milne Ice Shelf, a fragment of the former Ellesmere Ice Shelf, is located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is the second largest ice shelf in the Arctic Ocean. Situated on the north-west coast of Ellesmere Island, it is about west of Alert, Nunavut. In 1986, the ice shelf had an area of about , with a central thickness of . It had been the last ice shelf in the Canadian Arctic to be fully intact until July 2020, when over 40 percent of the sheet collapsed within two days, a consequence of global warming In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E .... An uninhabited research camp was lost when the shelf collapsed. It included instruments for measuring water flow through the ice shelf. References Ice shelves of Qikiqtaaluk Region {{QikiqtaalukNU-geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Ernest Ice Shelf
The Alfred Ernest Ice Shelf is an ice shelf on the north-west part of Ellesmere Island, Canada. This ice mass is one of four remaining Ice shelf, ice shelves on the island. This ice shelf lies between Alert Point and Cape Woods on the Wootton Peninsula. The Alfred Ernest Ice Shelf is regarded as a composite ice shelf that is composed of an inner unit of glacial origin and a trunk glacier originating from sea ice. Some time around 1955, a section of the ice shelf broke off. It is now called the ARLIS-II ice island. Further reading * Glaciers of North America - Canada, Satellite Image Atlas of Glaciers of the World, U.S.G.S. Professional Paper 1386 – J – 1, pg J111 – J143 * Carsten Braun, Douglas R. Hardy, and Raymond S. Bradley, Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol 109, (2004). Surface mass balance of the Ward Hunt Ice * Rise and Ward Hunt Ice Shelf, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada, Roy M. Koerner * Earth Observatory, by: Nasa Were a Part of the Earths Enterprise * Jianch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
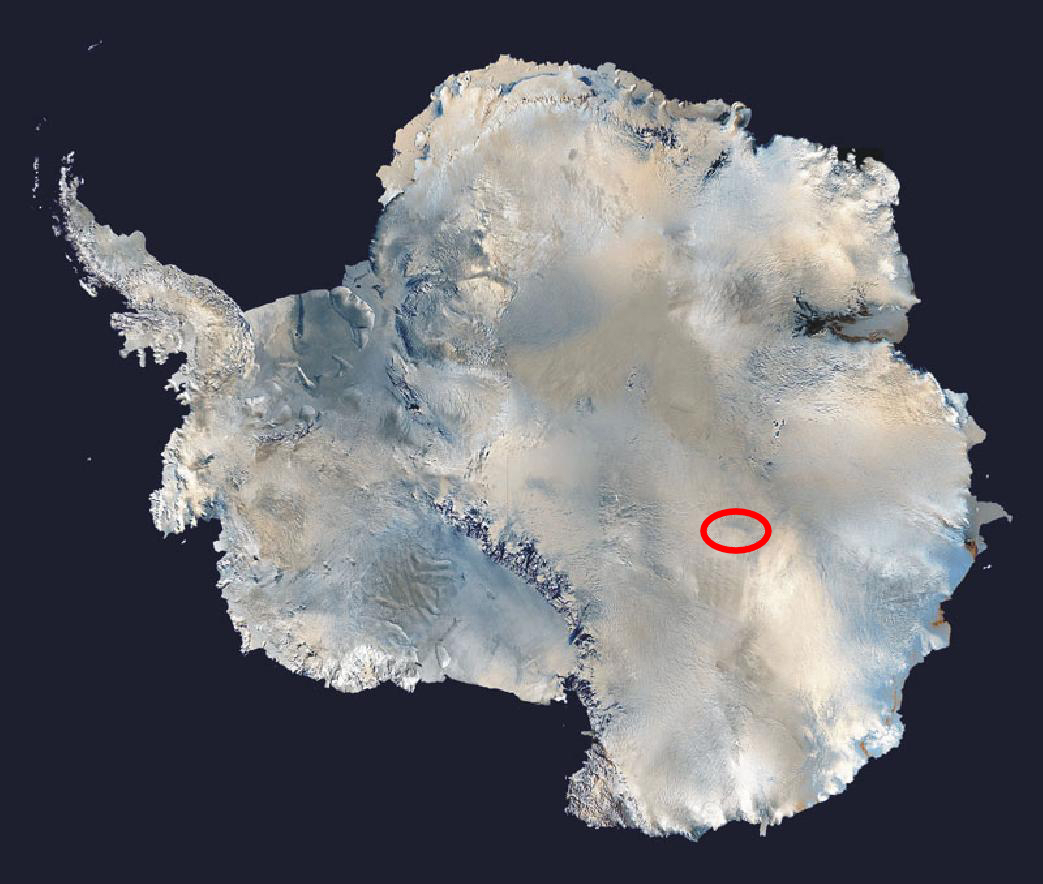
Lake Vostok
Lake Vostok (russian: озеро Восток, ''ozero Vostok'') is the largest of Antarctica's almost 400 known subglacial lakes. Lake Vostok is located at the southern Pole of Cold, beneath Russia's Vostok Station under the surface of the central East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is at above mean sea level. The surface of this fresh water lake is approximately under the surface of the ice, which places it at approximately below sea level. Measuring long by wide at its widest point, it covers an area of making it the 16th largest lake by surface area. With an average depth of , it has an estimated volume of , making it the 6th largest lake by volume. The lake is divided into two deep basins by a ridge. The liquid water depth over the ridge is about , compared to roughly deep in the northern basin and deep in the southern. The lake is named after Vostok Station, which in turn is named after the ''Vostok'' (Восток), a sloop-of-war, which means "East" in Russian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subglacial Lake
A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where gravitational pressure decreases the pressure melting point of ice. Over time, the overlying ice gradually melts at a rate of a few millimeters per year. Meltwater flows from regions of high to low hydraulic pressure under the ice and pools, creating a body of liquid water that can be isolated from the external environment for millions of years. Since the first discoveries of subglacial lakes under the Antarctic Ice Sheet, more than 400 subglacial lakes have been discovered in Antarctica, beneath the Greenland Ice Sheet, and under Iceland's Vatnajökull ice cap. Subglacial lakes contain a substantial proportion of Earth's liquid freshwater, with the volume of Antarctic subglacial lakes alone estimated to be about 10,000 km3, or about 15% of all liquid freshwater on Earth. As ecosystems is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |