|
Interfacing
Interfacing is a textile used on the unseen or "wrong" side of fabrics to make an area of a garment more rigid. Interfacings can be used to: *stiffen or add body to fabric, such as the interfacing used in shirt collars and cuffs *strengthen a certain area of the fabric, for instance where buttonholes will be sewn *keep fabrics from stretching out of shape, particularly knit fabrics Interfacings come in a variety of weights and stiffnesses to suit different purposes. They are also available in different colours, although typically interfacing is white. Generally, the heavier weight a fabric is, the heavier weight an interfacing it will use. Interfacing is sold at fabric stores by the yard or metre from bolts, similar to cutting fabric. Sewing patterns specify if interfacing is needed, the weight of interfacing that is required, and the amount. Some patterns use the same fabric as the garment to create an interfacing, as with sheer fabrics. Interfacing has three main 'type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interfacing At Hem
Interfacing is a textile used on the unseen or "wrong" side of fabrics to make an area of a garment more rigid. Interfacings can be used to: *stiffen or add body to fabric, such as the interfacing used in shirt collars and cuffs *strengthen a certain area of the fabric, for instance where buttonholes will be sewn *keep fabrics from stretching out of shape, particularly knit fabrics Interfacings come in a variety of weights and stiffnesses to suit different purposes. They are also available in different colours, although typically interfacing is white. Generally, the heavier weight a fabric is, the heavier weight an interfacing it will use. Interfacing is sold at fabric stores by the yard or metre from bolts, similar to cutting fabric. Pattern (sewing), Sewing patterns specify if interfacing is needed, the weight of interfacing that is required, and the amount. Some patterns use the same fabric as the garment to create an interfacing, as with sheer fabrics. Interfacing has thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and Nonwoven, non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to Bulletproof vest, bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and Medical gown, doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, Aesthetics (textile), aesthetics and Textile performance#Comfort, comfort are the most important factors, while in techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabrics
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, while in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. The durability of textiles is an important property, with common cotton or blend garments (such as t-shirts) able to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirt
A shirt is a cloth garment for the upper body (from the neck to the waist). Originally an undergarment worn exclusively by men, it has become, in American English, a catch-all term for a broad variety of upper-body garments and undergarments. In British English, a shirt is more specifically a garment with a collar, sleeves with cuffs, and a full vertical opening with buttons or snaps (North Americans would call that a " dress shirt", a specific type of collared shirt). A shirt can also be worn with a necktie under the shirt collar. History The world's oldest preserved garment, discovered by Flinders Petrie, is a "highly sophisticated" linen shirt from a First Dynasty Egyptian tomb at Tarkan, dated to : "the shoulders and sleeves have been finely pleated to give form-fitting trimness while allowing the wearer room to move. The small fringe formed during weaving along one edge of the cloth has been placed by the designer to decorate the neck opening and side seam." The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttonhole
A buttonhole is a reinforced hole in fabric that a Button (clothing), button can pass through, allowing one piece of fabric to be secured to another. The raw edges of a buttonhole are usually finished with stitching. This may be done either by hand or by a sewing machine. Some forms of button, such as a Frog (fastening), frog, use a loop of Textile, cloth or rope instead of a buttonhole. The term buttonhole can also refer to a flower worn in the lapel buttonhole of a coat or jacket, which is referred to simply as a "buttonhole" or "boutonnière". History Buttonholes for fastening or closing clothing with buttons appeared first in Germany during the 13th century. They soon became widespread with the rise of snug-fitting garments in 13th- and 14th-century Europe. Aspects of buttonholes Buttonholes often have a ''bar'' of stitches at either side of them. This is a row of perpendicular hand or machine stitching to reinforce the raw edges of the fabric, and to prevent it from frayi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knit
Knitting is a method for production of textile fabrics by interlacing yarn loops with loops of the same or other yarns. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine. Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row; they can be either on straight flat needles or in ''the round'' on needles with (often times plastic) tubes connected to both ends of the needles. There are usually many ''active stitches'' on the knitting needle at one time. Knitted fabric consists of a number of consecutive rows of connected loops that intermesh with the next and previous rows. As each row is formed, each newly created loop is pulled through one or more loops from the prior row and placed on the ''gaining needle so'' that the loops from the prior row can be pulled off the other needle without unraveling. Differences in yarn (varying in fibre type, ''weight'', uniformity and ''twist''), needle size, and stitch type allow for a variety of knitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
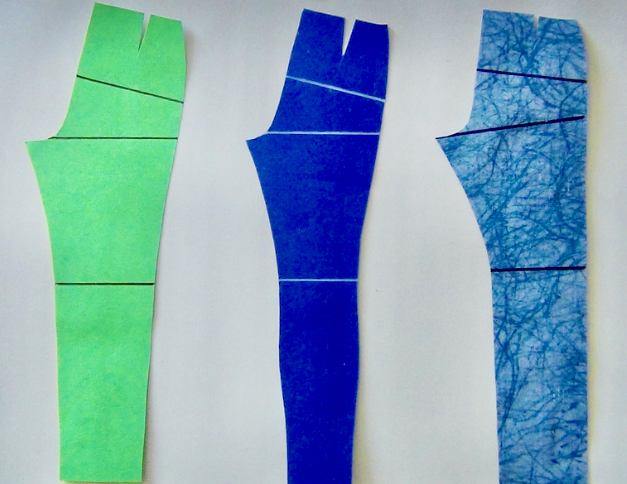
Pattern (sewing)
In sewing and fashion design, a pattern is the stencil, template from which the parts of a garment are traced onto woven fabric, woven or knitted fabrics before being cut out and assembled. Patterns are usually made of paper, and are sometimes made of sturdier materials like paperboard or cardboard if they need to be more robust to withstand repeated use. The process of making or cutting patterns is sometimes compounded to the one-word patternmaking, but it can also be written pattern making or pattern cutting. A sloper pattern, also called a ''block pattern'', is a custom-fitted, basic pattern from which patterns for many different styles can be developed. The process of changing the Clothing sizes, size of a finished pattern is called pattern grading. Several companies, like Butterick Publishing Company, Butterick and Simplicity Pattern, Simplicity, specialize in selling pre-graded patterns directly to consumers who will sew the patterns at home. These patterns are usually p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslin
Muslin () is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It is commonly believed that it gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq. Muslin was produced in different regions of the Indian subcontinent; Bengal Region was the main manufacturing area and the main centers were Sonargaon (near Dhaka), Shantipur and Murshidabad. Muslin was also produced in Malda and Hooghly. The muslin produced at Sonargaon and its surrounding areas was of excellent quality, which is popularly known as ''Dhaka Muslin''. The muslin produced in Shantipur came to be known as ''Shantipuri Muslin'', which was recognized by the East India Company. Muslin was made in Dhaka (Sonargaon) from very fine yarn, which is made from cotton called '' Phuti karpas''; while in Malda, Radhanagar and Burdwan, muslin was made from fine yarn made from ''nurma'' or ''kaur'' cotton. A minimum of 300-count yarn was used for the muslin, making the muslin as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haircloth
Haircloth is commonly understood as a stiff, unsupple fabric made from coarse fibre from camelids, bovines, horses, goats, rabbits, hares and reindeers. However, a softer variation is valued in the textile and fashion industries for their rarity, aesthetics and comfort. This is because there are two types of hair used in making haircloth; a rougher outer “guard coat”, and a softer undercoat. The outer coats are used in coarse fabrics, often applied to upholstery, carpets, underskirts and hairshirts, or cilices, while "luxury fabrics" use the softer undercoat. Description Haircloth is woven or knitted with fibres of uncommon animal varieties, including the following: # Mohair from the Angora goat, originating from Turkey. # Cashmere comes from the Himalayan cashmere goat of Central and Southwestern Asia. It is mostly produced in China, and is a popular Scottish knitting yarn. Cashmere from the Indian sub-continent is referred to as Pashmina. The fibres of Pashmina come f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigan (fabric)
Wigan is a stiff cotton material sometimes coated with latex rubber. It is typically sold in bias-cut strips and used as an interfacing or interlining in tailoring to stabilize seams and hemlines. Its name has been derived from Wigan, the name of a former mill town in Greater Manchester (historically Lancashire Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to ...), England. References {{Textile-stub Cotton Technical fabrics Woven fabrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckram
Buckram is a stiff cotton, or occasionally, linen or horse hair cloth with a plain, usually loose, weave, produced in various weights similar to muslin and other plain weave fabrics. The fabric is soaked in a sizing agent such as wheat-starch paste, glue (such as PVA glue), or pyroxylin (gelatinized nitrocellulose, developed around 1910), then dried. When rewetted or warmed, it can be shaped to create durable firm fabric for book covers, hats, and elements of clothing. Etymology In the Middle Ages, "bokeram" simply designated a fine cotton cloth. The etymology of the term remains uncertain; the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' considers the commonly mentioned derivation from the name of the city of Bokhara unlikely. Use in bookbinding Several of buckram's qualities make it attractive for bookbinding. Highly durable, buckram does not allow the bookbinder's paste to seep through and discolor or stain the book's front and back covers. Pyroxylin-impregnated buckram is often fav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |