|
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris-Rex Ovirs Gsfc 20150619 2015-12655 019-023
OSIRIS-REx was a NASA asteroid-study and sample-return mission that visited and collected samples from 101955 Bennu, a C-type asteroid, carbonaceous near-Earth object, near-Earth asteroid. The material, returned in September 2023, is expected to enable scientists to learn more about the formation and evolution of the Solar System, its initial stages of planet formation, and the source of organic compounds that led to the Abiogenesis, formation of life on Earth. Following the completion of the primary OSIRIS-REx (Regolith Explorer) mission, the spacecraft is planned to conduct a flyby of asteroid 99942 Apophis, renamed as OSIRIS-APEX (Apophis Explorer). OSIRIS-REx was launched on 8 September 2016, flew past Earth on 22 September 2017, and rendezvoused with 101955 Bennu, Bennu on 3 December 2018. It spent the next two years analyzing the surface to find a suitable site from which to extract a sample. On 20 October 2020, OSIRIS-REx touched down on Bennu and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
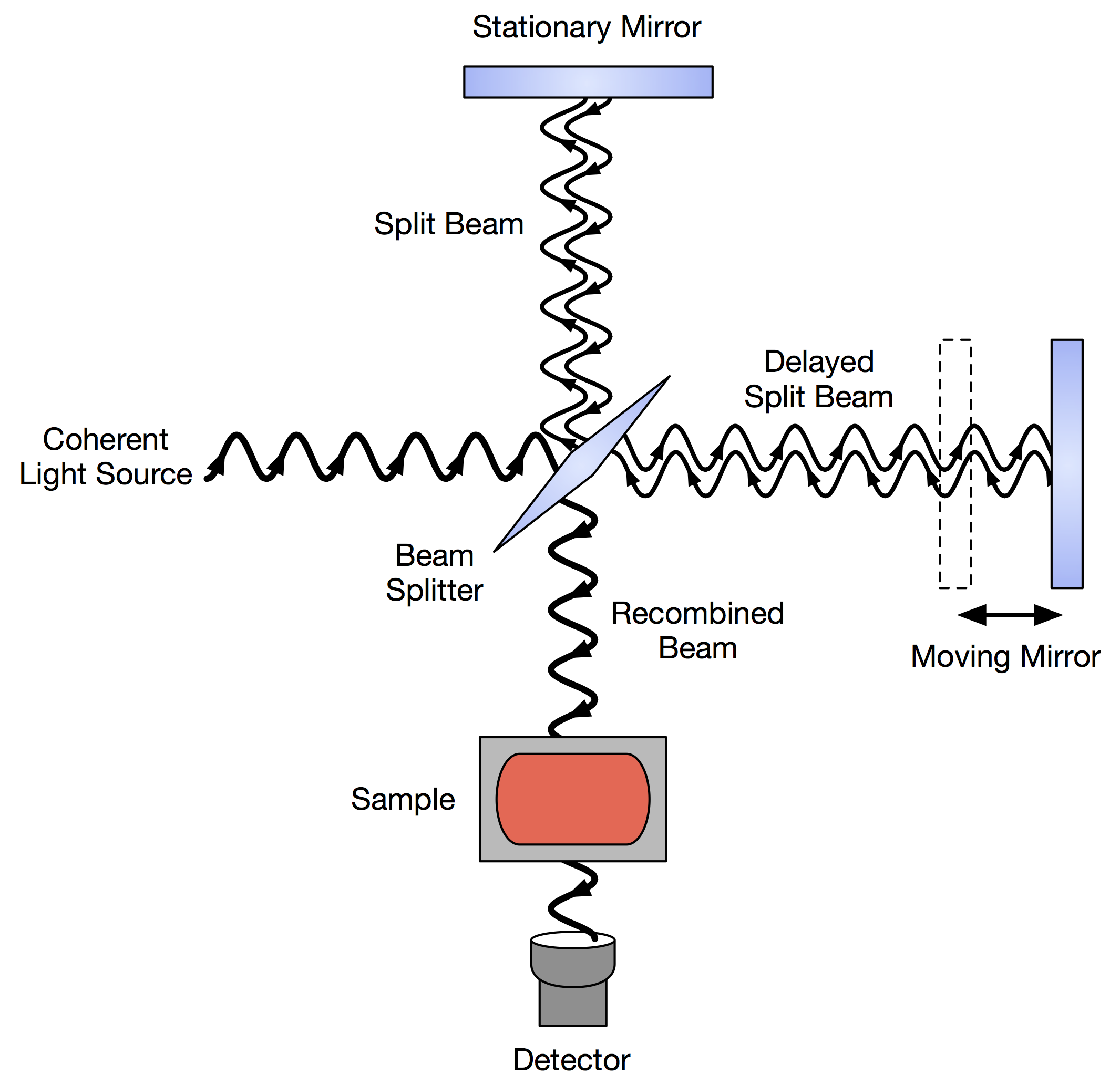
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared Electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum of Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission of a solid, liquid, or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a Dispersion (optics), dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time. The term ''Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy'' originates from the fact that a Fourier transform (a mathematical process) is required to convert the raw data into the actual spectrum. Conceptual introduction The goal of absorption spectroscopy techniques (FTIR, Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible ("UV-vis") spectroscopy, etc.) is to measure how much light a sample absorbs at each wavelength. The most straightforward way to do this, the "dispe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Screening Devices (1435) (8225044148)
Portable may refer to: General * Portable building, a manufactured structure that is built off site and moved in upon completion of site and utility work * Portable classroom, a temporary building installed on the grounds of a school to provide additional classroom space where there is a shortage of capacity * Portable toilet, a modern, portable, self-contained outhouse manufactured of molded plastic Computing * Portable object (computing), a distributed computing term for an object which can be accessed through a normal method call while possibly residing in memory on another computer * Software portability, software that can easily be ported to multiple platforms * Portable applications, applications that do not require any kind of installation onto a computer, and can store data in the program's directory Electronics * Portable electronics * Portable device, a wearable or handheld device * Portable audio player, a personal electronic device that allows the user to listen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Moffit Using Infrared Spectrophotometer 2012 017 B1f6 79407z11s
Mary may refer to: People * Mary (name), a female given name (includes a list of people with the name) Religion * New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below * Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blessed Virgin Mary * Mary Magdalene, devoted follower of Jesus * Mary of Bethany, follower of Jesus, considered by Western medieval tradition to be the same person as Mary Magdalene * Mary, mother of James * Mary of Clopas, follower of Jesus * Mary, mother of John Mark * Mary of Egypt, patron saint of penitents * Mary of Rome, a New Testament woman * Mary the Jewess, one of the reputed founders of alchemy, referred to by Zosimus. Royalty * Mary, Countess of Blois (1200–1241), daughter of Walter of Avesnes and Margaret of Blois * Mary of Burgundy (1457–1482), daughter of Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy * Queen Mary of Denmark (born 1972), wife of Frederik X of Denmark * Mary I of England (1516–1558), aka "Bloody Mary", Queen of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terahertz Radiation
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency (THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the International Telecommunication Union-designated band of Frequency, frequencies from 0.1 to 10 Hertz#SI prefixed forms of hertz, terahertz (THz), (from 0.3 to 3 Hertz#SI prefixed forms of hertz, terahertz (THz) in older texts, which is now called "decimillimetric waves" ), although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and has been considered by some sources to be 30 THz. One terahertz is 1012 Hertz, Hz or 1,000 GHz. Wavelengths of radiation in the decimillimeter band correspondingly range 1 mm to 0.1 mm = 100 μm and those in the terahertz band 3 mm = 3000 μm to 30 μm. Because terahertz radiation begins at a wavelength of around 1 millimeter and proceeds into shorter wavelengths, it is sometimes kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 30 cm and 3 mm), or between 1 and 3000 GHz (30 cm and 0.1 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire super high frequency, super high frequency (SHF) band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. The boundaries between far infrared, terahertz radiation, microwaves, and ultra-high-frequency (UHF) are fairly arbitrary and differ between different fields of study. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' indicates that microwaves are small (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology. Frequencies in the micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational Spectroscopy
Rotational spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of the energies of transitions between quantized rotational states of molecules in the gas phase. The rotational spectrum (power spectral density vs. rotational frequency) of chemical polarity, polar molecules can be measured in Absorption (optics), absorption or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission by microwave spectroscopy or by far infrared spectroscopy. The rotational spectra of non-polar molecules cannot be observed by those methods, but can be observed and measured by Raman spectroscopy. Rotational spectroscopy is sometimes referred to as ''pure'' rotational spectroscopy to distinguish it from rotational-vibrational spectroscopy where changes in rotational energy occur together with changes in vibrational energy, and also from ro-vibronic spectroscopy (or just vibronic spectroscopy) where rotational, vibrational and electronic energy changes occur simultaneously. For rotational spectroscopy, molecules are cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational–vibrational Spectroscopy
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy that is concerned with Infrared spectroscopy, infrared and Raman spectroscopy, Raman spectra of molecules in the Gas, gas phase. Transitions involving changes in both Molecular vibration, vibrational and Rotational transition, rotational Quantum state, states can be abbreviated as rovibrational (or ro-vibrational) transitions. When such transitions emit or absorb photons (electromagnetic radiation), the frequency is proportional to the difference in energy levels and can be detected by certain kinds of spectroscopy. Since changes in rotational energy levels are typically much smaller than changes in vibrational energy levels, changes in rotational state are said to give fine structure to the vibrational spectrum. For a given vibrational transition, the same theoretical treatment as for pure rotational spectroscopy gives the rotational quantum numbers, energy levels, and selection rules. In linear and spheric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
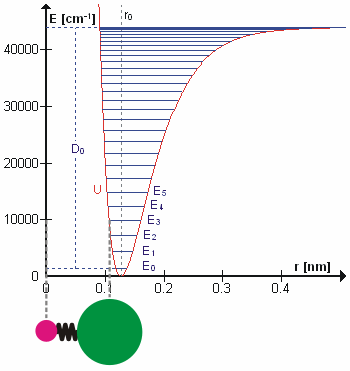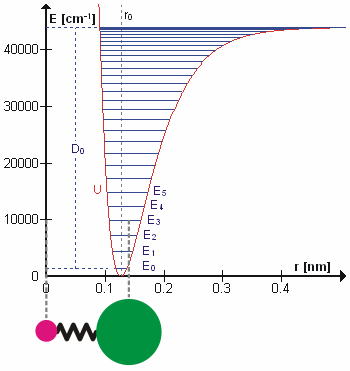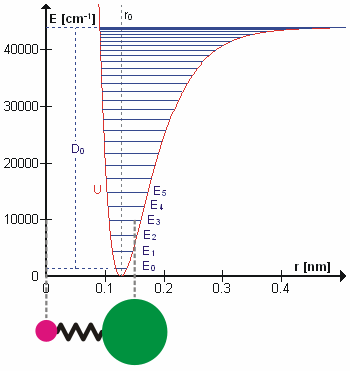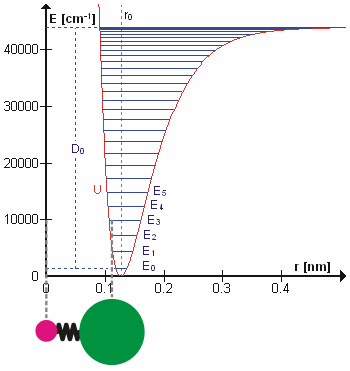
Molecular Vibration
A molecular vibration is a Periodic function, periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The infrared spectroscopy correlation table, typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 hertz, Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 μm. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has vibrational mode, normal modes of vibration, but a ''linear'' molecule has modes, because rotation about the molecular axis cannot be observed. A diatomic molecule has one normal mode of vibration, since it can only stretch or compress the single bond. A molecular vibration is excited when the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overtone Band
In vibrational spectroscopy, an overtone band is the spectral band that occurs in a vibrational spectrum of a molecule when the molecule makes a transition from the ground state (v=0) to the second excited state (v=2), where v is the vibrational quantum number (a non-negative integer) obtained from solving the Schrödinger equation for the molecule. Generally, in order to study the vibrational spectra of molecules, chemical bond vibrations are assumed to be approximable as simple harmonic oscillators. Thus a quadratic potential is used in the Schrödinger equation to solve for the vibrational energy eigenstates and their eigenvalues. These energy states are quantized, meaning they can assume only some "discrete" values of energy. When electromagnetic radiation is shined on a sample, the molecules can absorb energy from the radiation and change their vibrational energy state. However, the molecules can absorb energy from radiation only under certain condition, namely- there should ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far Infrared
Far infrared (FIR) or long wave refers to a specific range within the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. It encompasses radiation with wavelengths ranging from 15 μm ( micrometers) to 1 mm, which corresponds to a frequency range of approximately 20 THz to 300 GHz. This places far infrared radiation within the CIE IR-B and IR-C bands. The longer wavelengths of the FIR spectrum overlap with a range known as terahertz radiation. Different sources may use different boundaries to define the far infrared range. For instance, astronomers often define it as wavelengths between 25 μm and 350 μm. Infrared photons possess significantly lower energy than photons in the visible light spectrum, with tens to hundreds of times less energy. Applications Astronomy Objects within a temperature range of approximately 5 K to 340 K emit radiation in the far infrared range as a result of black-body radiation, in accordance with Wien's displac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar, pulse oximetry, functional neuroimaging, sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics, rehabilitation, neonatal research, brain computer interface, urology (bladder contraction), and neurology (neurovascular coupling). There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical, food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry, combustion propagation. Theory Near-infrared spectroscopy is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. Overtones and combinations exhibit lower intensity compared to the fundamental, as a result, the molar absorptivity in the near-IR region is typically quite small. (NIR absorption bands are typically 10–100 times weaker than the corresponding fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |